Field Service Management and IFS Cloud Integration
Integration between IFS Field Service Management (FSM) and IFS Cloud allows inventory stock maintenance using FSM while procurement and financial transactions are handled using IFS Cloud.
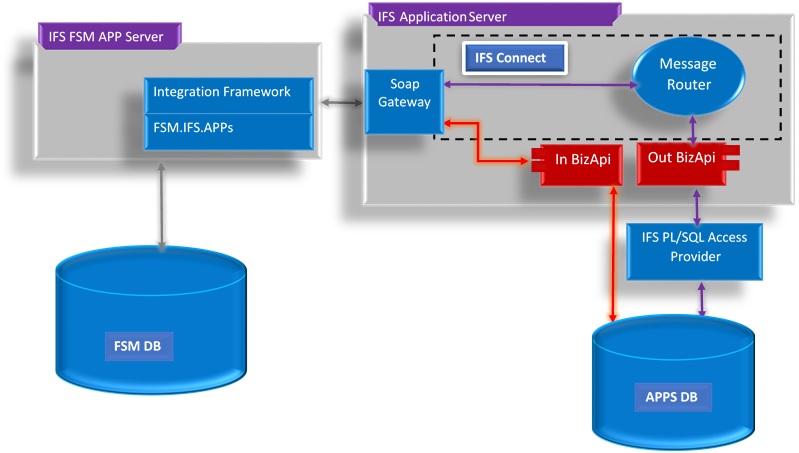
A diagram of the integration architecture is shown below. The Integration Framework, which is a server module that generically supports inbound/outbound integrations between FSM and other systems, is included in IFS FSM APP Server. It uses import/export maps defined in the metadata of the FSM database to map XML messages and API calls between IFS Cloud and FSM in a flexible way that is easily adaptable to customer needs and extensible via metadata edits in the FSM client. The standard IFS PL\SQL Access Provider is used to communicate with IFS Cloud.
The SOAP Gateway of IFS Cloud Server gives a client or another software the possibility to integrate with the IFS business logic in a controlled and performance efficient manner. With the use of the IFS SOAP access provider format, BizAPI is invoked without any involvement of IFS Connect framework. This allows fast and efficient calling of the business logic interface and is suitable for clients where a tighter integration is preferable, resulting high performance and less administration.
Note: To be able to use integration between FSM and IFS Cloud, the IFS Cloud end user needs to be granted with the IFS/FND Role: FND_CONNECT.
The routing address Connect to FSM server is used to make the connection between FSM and IFS Cloud.
Three new outbound routing rules which are FSM- No Part Receiving, FSM- Part Receiving and IFS Cloud PO Data to FSM PO are introduced to integrate IFS Clouds procurement to FSM.
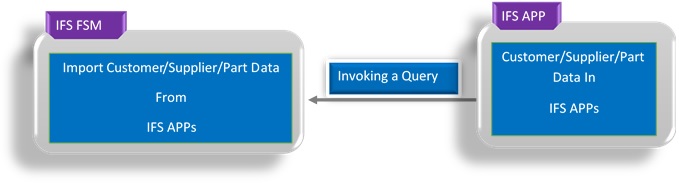
The following diagrams represent the process of how FSM import metadata from
IFS Cloud.
Data sync process for Customer/Supplier/Part
IFS Cloud FSM Transactions page
Once the FSM transactions are generated in the part tran. Log, it will trigger the TRNASFER_FSM_TRANSACTION inbound BizApi to pass that information to IFS Cloud. With the use of commands, user can view additional details in the FSM Transaction History page. The FSM transaction postings can be viewed in the Supply Chain and Manufacturing Postings Analysis page.
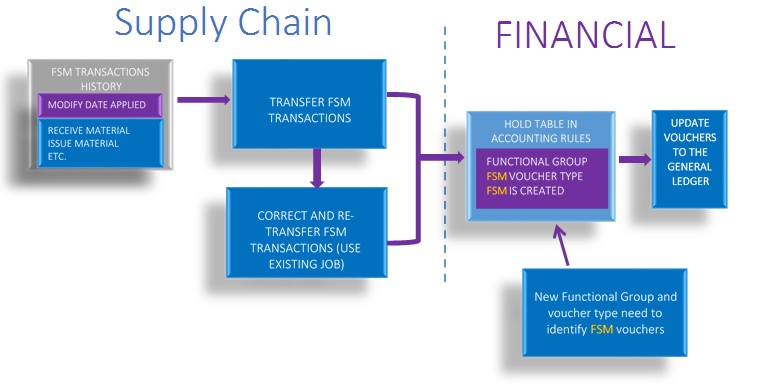
The process diagram below illustrates this process.
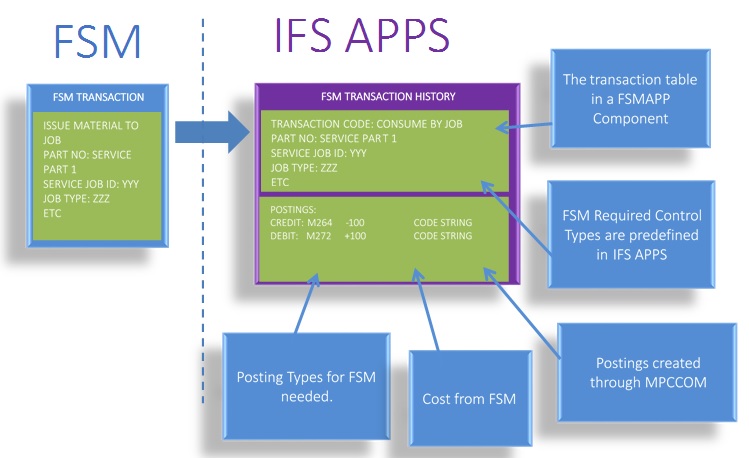
User can change the transaction date in this page by using the Modify Date Applied command.
IFS Cloud inventory transactions created corresponding to FSM inventory part transactions are as follows.
| System Event ID | System Event Description | Mapped FSM transactions |
| INTERN-IN | FSM Internal In | CC Cost Change
- 4995 BOMD De-kitting 4091 BOMK Kitting -4091 PC Physical Count in 4091 SC On Line Screen (ID) - 1400 |
| INTERN-OUT | FSM Internal Out | PC Physical Count Out-4091 PU - part that has been used-5460 BOMD De-kitting 4091 BOMK Kitting -4091 SC On Line Screen (ID) 1405 CC Cost Change - 4996 |
| EXTERN-IN | FSM External In | PD - Part Disposition-5613 RP - RC Part Change (Increased new part)-4022 RR - RC Receipt-4022 |
| EXTERN-OUT | FSM External Out | RP - RC Part Change(Decreased
old part)-5500 RQ Request-5500 SH Shipper-4021 |
| FSMPRDIFF+ | FSM Price Difference - Higher Price | |
| FSMPRDIFF- | FSM Price Difference - Lower Price | |
| FSMARRIVAL | FSM PO receipt for inventory Part |
When RQ Issue Transaction is generated in FSM, and the transaction is passed to IFS Cloud by triggering the TRNASFER_FSM_TRANSACTION inbound BizApi, mapping that occurs would be as follows.
| FSM Transaction Table | ||||||||
| Transaction Code | Part No | Quantity | Unit Cost | FSM Transaction Type | FSM Info | |||
| External-Out | SEAL-123 | 10 | 50 | RQ Request Issue | Other FSM info. E.g., order references | |||
| Postings | ||||||||
| Debit/Credit | Posting Type | Value | Account | |||||
| Debit | M272 FSM External-Out | 500 | 5501 Repair Costs | |||||
| Credit | M264 FSM Inventory | 500 | 1400 - Inventory | |||||
IFS Cloud Transfer FSM Transactions
In IFS Cloud, once the FSM transactions are generated, the user can transfer them to the GL. This would create vouchers for FSM transactions in IFS Financials.
- The voucher will be created in the hold table in Accounting Rules and later updated to the General Ledger.
- Voucher type (FSM) to be used is defined in voucher types. A voucher from function group FSM will be created.
Posting control data for each financial transaction can be viewed in FSM Transaction History. This page is also used to view transaction status to ensure that there are no erroneous FSM transactions.
If the FSM transactions did not get transferred, view the details of the transaction.
- When viewing the transaction, you will see 99 or Incorrect Accounting in the Status Code field if it is an error.
- An error message will be visible on the accounting tab explaining the posting error. This is often due to incorrect/incomplete setup in Accounting Rules, but can occur due to missing data in distribution.
Make all required corrections and then correct the transaction postings using Rerun Erroneous Distribution and Manufacturing Postings.
- This process screens all the erroneous transactions for a site against accounting rules and supply chain basic data, to correct the transaction so that it can be transferred.
- Repeat the transfer transaction and verify that all transactions are transferred correctly.
The Transfer FSM Transactions diagram shown below illustrates the processes