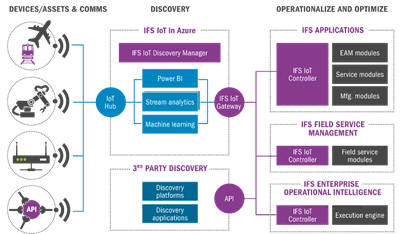
About IoT Controller
The IoT Controller is the name of the component in IFS Cloud. In the picture down below the purple parts are part of the IoT Controller. The Business connector includes all the steps in the picture below. It includes the sensors on the devices and the Discovery Manager. The Discovery Manager connects to the IoT Controller by the IoT Gateway. It is also possible to have a third party Discovery instead of the IFS Discovery and connect it to the IoT Controller. The IoT Controller consists of the basic data requirements defining the connection between devices and objects in IFS Cloud, observations we expect to receive and what operations we want to execute on these observations. Once the basic data is defined, daily operations are followed by the other part which shows the observations that comes in as well as the possibility to handle and analyze observations that are or suspected to be faulty.
IoT Gateway
The IoT Gateway connects the Discovery environment to the IFS controller. The gateway is implemented as a Service on a Windows Server and provided to the customers by IFS. The only purpose of the gateway is to listen to the Service Bus Queue and forward the data to the IFS back-end systems. It calls the IFS Middleware web service to save the observations coming via the cloud into the IoT Observations table in IFS Cloud. The IoT Gateway if so configured can also send messages to Field Service Management (FSM). It sends an XML insert message into the FSM server which then the server uses to create an IoT observation record. As seen in the picture below the IoT Gateway also connects and can send messages to the Enterprise Operational Intelligence (EOI). This is done by using a SOAP service which receives values and then processes them into a EOI model and then it creates an IoT observation record. This process can be adjusted by the user in order to get the best result.