Inter-Site Message Handling
An inter-site order set basically consists of the following:
- An internal purchase order at demand site
- An internal customer order at supply site
The starting point can be a customer order, a purchase order, or a distribution order. These orders in turn can be created for instance by a planning tool. When the starting point is a customer order or a purchase order and IFS Connectivity is used, different messages are sent between the two sites. This document describes the messages that can be used in an inter-site trading situation when the starting point is a:
- Customer Order
- Purchase Order
This document does not describe the setup procedure. For further information about how to setup the system, please, study the setup guides in the training material.
Please note that the system uses the conversion factors entered in the Supplier for Purchase Part page, and, when appropriate, in the Sales Part Cross Reference page, when recalculating quantities between the two sites. In other words, the system will neither warn nor make any conversion if the conversion factors are 1 even if the unit of measures actually differ between the two sites.
Customer Order
It is recommended that you read the following documents for further information on this subject: About Reservation Management, About Sourcing and About EDI Messages.
When sourcing an external customer order internally, there are two different scenarios depending on the material flow:
- Transit delivery: When the supply site sends goods to the demand site, and this site, in turn, sends them further to the end customer.
- Direct delivery: When the supply site sends goods directly to the end customer.
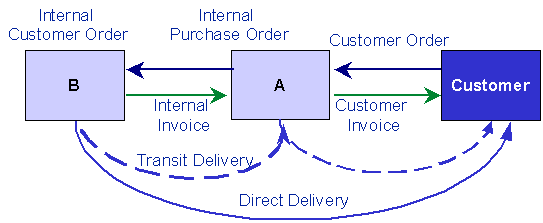
Transit Delivery
For internal orders with Transit Delivery, the following messages are used:
- ORDERS Customer Order Transfer: Sent from the demand site to the supply site as an order.
- ORDCHG Customer Order Change: Sent from the demand site to the supply site when changes are made to the order.
- ORDRSP Customer Order Confirmation: Sent from the supply site to the demand site as an acceptance of order and order terms.
- DESADV Dispatch Advice: Sent from the supply site to the demand site as a delivery note. Can only be used together with package verification.
- INVOIC Invoice Transfer: Sent from the supply site to the demand site as an internal customer invoice if the demand site is to be charged.
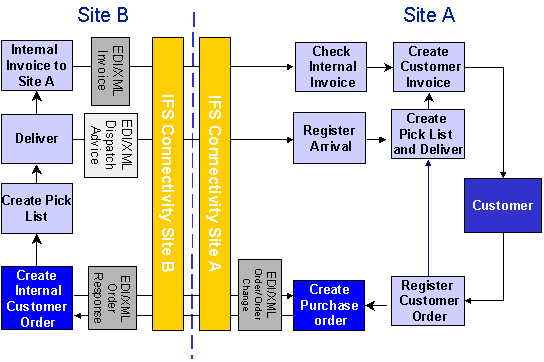
When releasing the external customer order, the internal purchase order is automatically created. The ORDERS message is automatically created and sent. This message is received by the supply site. You can decide whether the approval should occur automatically or be handled manually. Once approved, an internal customer order is created in the supply site.
In the supply site, the internal customer order is processed as any other normal customer order.
If the demand site needs to make changes to the purchase order, it will send an ORDCHG message to the supply site, which in turn will accept or reject the changes.
The supply site can use the ORDRSP message to confirm the order.
If desired, the DESADV message can be used (in combination with package verification) to send a detailed delivery note electronically to the demand site.
The demand site will register the arrival of the parts and process its external customer order as usual by picking, delivering, and invoicing it. Reservations are not necessary since the system will automatically peg the materials to the original customer order.
If the sites that are interacting belong to the same financial company, no internal invoice will be created. If the sites belong to different companies, the supply site creates an invoice, which can then be sent electronically to the demand site with the INVOIC message.
Direct Delivery
For internal orders with Direct Delivery, there are other messages involved:
- ORDERS Customer Order Transfer: Sent from the demand site to the supply site as an order.
- ORDCHG Customer Order Change: Sent from the demand site to the supply site when changes are made to the order.
- ORDRSP Customer Order Confirmation: Sent from the supply site to the demand site as an acceptance of order and order terms.
- DIRDEL Direct Delivery: Sent from supply site to demand site as notification that the ordered goods have been sent to the end customer.
- INVOIC Invoice Transfer: Sent from supply site to demand site as an internal customer invoice if the demand site is to be charged.
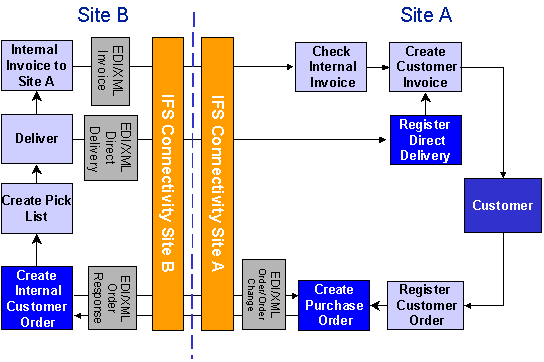
When the demand site releases the external customer order, an internal purchase order is automatically created. The ORDERS message is automatically created and sent. This message is received by the supply site. Its approval also can be set to occur automatically or be handled manually, as decided by the user. By approving the message, an internal customer order is created.
In the supply site, the internal customer order is processed as any other normal customer order but the delivery address is the end customer's address, instead of the demand site's address.
If the demand site needs to make changes to the purchase order, it will send an ORDCHG message to the supply site, which in turn will accept or reject the changes.
The supply site can use the ORDRSP message to confirm the order.
If desired, the DIRDEL message can be used by the supply site to send a direct delivery notification to the demand site.
On the demand site, when approving this message, the internal purchase order is changed to a Closed status and this, is turn, notifies the external customer order that the goods have been delivered, and the external customer order status is automatically changed to Delivered. At that point, the demand site can invoice the external customer.
If the sites that are interacting belong to the same financial company, no internal invoice will be created. If the sites belong to different companies, the supply site will create an invoice, which can be sent electronically to the demand site with the INVOIC message.
Purchase Order
When a distribution center replenishes from a central inventory, there are two different scenarios:
- Normal/Discrete
- Repetitive
Discrete

The following messages are used in this flow:
- ORDERS: Sent from the demand site to the supply site as an order.
- ORDCHG: Sent from the demand site to the supply site when changes are made to the order.
- ORDRSP: Sent from the supply site to the demand site as acceptance of order and order terms.
- DESADV: Sent from the supply site to the demand site as a delivery note. Can only be used together with package verification.
- INVOIC Invoice Transfer: Sent from the supply site to the demand site as an internal customer invoice if the demand site is to be charged.

When a distribution center notices a demand of goods, through the use of a planning tool like order point or manually, a purchase requisition is created towards the central inventory. This requisition is transformed into a purchase order towards the central inventory, which acts as an internal supplier. The purchase order is manually sent to the other site with the ORDERS message.
The ORDERS message is received by the supply site. Its approval can be set to occur automatically or be handled manually, as decided by the user. By approving it, an internal customer order is created in the supply site.
If the demand site needs to make changes to the purchase order, it will send a ORDCHG message to the supply site, which in turn will accept or reject the changes.
The supply site can use the ORDRSP message to confirm the order.
On the supply site, the internal customer order is processed as any other normal customer order.
If desired, the DESADV message can be used (in combination with package verification) to send a detailed delivery note electronically to the demand site. The demand site will register the arrival of the parts as usual, and fill its inventory.
If the sites that are interacting belong to the same financial company, no internal invoice will be created. If the sites belong to different companies, the supply site will create an invoice, which can be sent electronically to the demand site with the INVOIC message.
Repetitive
In a repetitive scenario, delivery plans are sent and received by sites. This scenario is quite similar to the one mentioned above.
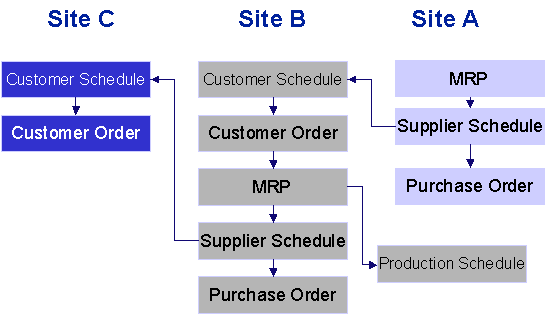
The following messages are used:
- DELSCH: Sent from the demand site to the supply site as a delivery plan.
- DESADV: Sent from the supply site to the demand site as a delivery note. Can only be used together with package verification.
- INVOIC Invoice Transfer: Sent from the supply site to the demand site as an internal customer invoice if the demand site is to be charged.
This is a picture of the flow:
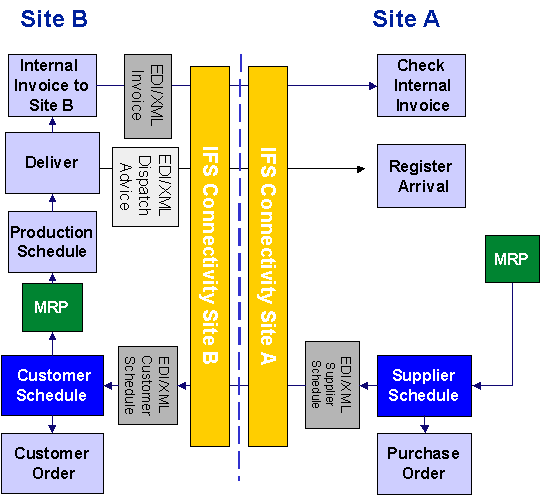
When a distribution center notices a demand of goods, through the use of a planning tool like MRP or manually, a delivery plan or supplier schedule is created towards the central inventory. The schedule order is manually or automatically sent to the other site with the DELSCH message.
The DELSCH message is received by the supply site. Its approval can be set to occur automatically or be handled manually, as decided by the user. Upon approving it, a customer schedule is created in the supply site.
In the supply site, the customer schedule is processed as usual.
If desired, the DESADV message can be used (in combination with package verification) to send a detailed delivery note electronically to the demand site. The demand site will register the arrival of the parts as usual, and fill its inventory.
If the sites that are interacting belong to the same financial company, no internal invoice will be created. If the sites belong to different companies, the supply site will create an invoice, which can be sent electronically to the demand site with the INVOIC message.