Shop Order Operation
A shop order operation represents a work step required to manufacture, repair, disposition or disassembly parts on a shop order.
An operation can contain both machine and/or labor actions and is normally inherited from the routing revision/alternate of the ordered part selected on the shop order. The operations can also be inherited from order structures such as DOP and interim order. Operations may be manually entered or modified on a shop order if an order-specific list of operations are required.
Operation Lead Time Components
An operation is scheduled considering the below lead time factors:
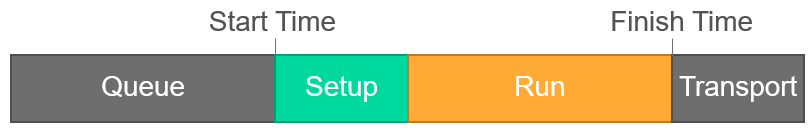
- Queue Time: The time the operation waits at the work center before the work starts. WIP from previous operation and operation material is ordered to be available at the start of the queue time. This gives a flexibility to sequence the operations waiting at the work center in an optimal order to minimize setup times. The queue time is inherited from the work center to the shop order operation.
- Setup Time: The time required to convert the resource from the previously produced parts to produce the parts of this operation. The setup time is fixed per shop order and does not multiply by the lot size. Can be defined for machine and setup irrespectively, but only machine is used for the scheduling of the operation. The start of the setup indicates the operation start date/time.
-
Run Time: The time required to perform the value adding work on the operation. Can be defined for
machine and setup irrespectively, but only machine is used for the scheduling of the operation. The end of the
run time indicates the operation finish date/time. Depending on the value in the Factor Unit field this
value can be expressed in different ways:
- Hours/Unit: How many hours it takes to manufacture a unit.
- Units/Hour: How many units can be manufactured in an hour.
- Hours: How many hours the manufacturing process takes, regardless of the number of units.
- Transport Time: The time required to move the WIP from the operation to the next (or to stock for the last operation).
Operation Quantities
The following types of quantities are relevant for a shop order operation:
- Operation Qty: The quantity expected to pass through the operation. This value is originally set equal to the lot size of the shop order, or if the corresponding routing operation has a defined Operation Qty Factor it is set to that percentage of the lot size. The value can be updated manually when Manual Operation Qty is enabled. That is typically done for a rework or repair operation when the full quantity is not expected to pass through the operation. The value can be automatically adjusted if the lot size of the shop order is changed, if the operation is split, if scrap is reported on a preceding operation with Increase Lot Size on Scrap disabled or if a preceding operation has been over/under reported and the shop order has Adjust for Op Deviation Qty enabled.
- Bypass Qty: The quantity that will bypass the operation without being reported. This value is automatically updated when manually setting Operation Qty. If Operation Qty is decreased, Bypass Qty is increased with the same quantity and if Operation Qty is increased Bypass Qty is decreased with the same quantity. Bypass Qty can also be automatically adjusted if the lot size of the shop order is changed, if scrap is reported on a preceding operation with Increase Lot Size on Scrap disabled or if a preceding operation has been over/under reported and the shop order has Adjust for Op Deviation Qty enabled. This quantity is only applicable when the operation has Manual Operation Qty enabled.
- Completed Qty: The quantity that has been reported as complete on the operation.
- Scrapped Qty: The quantity that has been reported as scrapped on the operation.
- Deviation Qty: Deviation between the actual completed and scrapped quantities relative to the planned Operation Qty. A positive operation deviation is created when an operation is over reported. A negative operation deviation is created when an operation is closed with a reported quantity (Completed Qty plus Scrapped Qty) which is less than the planned Operation Qty. This value affects the Operation Qty of the succeeding operations and the remaining net supply of the shop order.
-
Executable Qty: The quantity that is possible to execute on the operation. The value is
calculated as the quantity that has become available on the operation (based on preceding operations) minus
Completed Qty minus Scrapped Qty. It will never be negative or greater than
the Operation Qty. The quantity that has become available on the operation is set depending on
several factors:
- If the operation is the first operation or parallel with the first operation, it is set to the Operation Qty.
- If the operation has a preceding operation that is a split operation, it is set to the sum of the Completed Qty for the preceding set of split operations.
- If the operation has a preceding operation that is parallel to other operation(s), it is set to the lowest Completed Qty for the preceding set of parallel operations.
- If the operation has a preceding operation without Manual Operation Qty enabled, it is set to the Completed Qty on the preceding operation.
- If the operation has a preceding operation with Manual Operation Qty enabled, it is set to the Completed Qty on the preceding operation plus the quantity that currently can bypass that preceding operation without being reported as complete.
When the lot size of the shop order is decreased, when scrap is reported on an operation with Increase Lot Size on Scrap disabled or when an operation has been under reported and the shop order has Adjust for Op Deviation Qty enabled, quantities are decreased on succeeding operations with the same amount. For a succeeding operation with Manual Operation Qty disabled, Operation Qty is decreased. For a succeeding operation with Manual Operation Qty enabled, Bypass Qty is decreased first and if it goes down to zero also Operation Qty is decreased.
When the lot size of a shop order is increased or when an operation has been over reported and the shop order has Adjust for Op Deviation Qty enabled, quantities are increased on succeeding operations with the same amount. For a succeeding operation with Manual Operation Qty disabled, Operation Qty is increased. For a succeeding operation with Manual Operation Qty enabled, Bypass Qty is increased.
Operation Status Codes
Operation status varies during the manufacturing process. The status tells you which step of the process the operation has reached.
| Status | Description |
| Planned | The operation is planned and no actions can be taken. |
| Released | The operation is released and manufacturing can begin. |
| Setup Started | The setup phase has started. |
| Setup Complete | The setup phase is complete. |
| In Process | The manufacturing phase is in process. |
| Partially Reported | The manufacturing phase is partially performed. |
| Interruption | The operation has been interrupted for some reason. |
| Closed | The operation is closed; the work in the operation is finished. |