Calculate Purchase Lead Time
Explanation
Use this assistant to calculate the total purchase lead time for inventory-registered purchase parts. You can
either use the standard options to calculate the purchase lead times, based on the lead times set up for
Supply Chain Matrix and Supplier for Purchase Part, or utilize
historical data for selected Receipts and calculate an average purchase lead time.
Standard Update Options
The total purchase lead time is the amount of time that elapses between the time when the part is ordered and the
time it is available in inventory. The total purchase lead time consists of these elements:
- Supplier Manufacturing Lead Time: The time that normally elapses between the time an order is received by a supplier and the time the order is shipped. This information is entered on the Supplier for Purchase Part/General/Order Information.
- External Transport Lead Time: The time that normally elapses from the time when the supplier makes the product available for shipment to when it is registered as Arrived at the receiver (or Delivered at the delivery point if using Transport Lead Time). This information is entered in the Supply Chain Matrix for Supplier page.
- Transport Lead Time: The transportation time from the delivery point to a receiving point, as required, where the demanding party holds responsibility. This information is entered in the Supply Chain Matrix for Supplier page.
- Internal Transport Lead Time: The time that normally elapses from the time the product is registered as Arrived until the time it is available for inspection. This information is entered in the Supply Chain Matrix for Supplier page.
- Internal Inspection Lead Time: The time that normally elapses from the time the product is available for inspection until it is available in inventory. This information is entered on the Supplier for Purchase Part/Inspection Info tab.
To calculate the total purchase lead time, specify the site and choose whether you want to update the lead time of the part or if you only want to create a report.
Example:
| Supplier for Purchase Part | |
| Internal Inspection Lead Time | 1 |
| Supplier Manufacturing Lead Time | 10 |
| Supply Chain Matrix for Supplier | |
| External Transport Lead Time | 2 |
| Transport Lead Time | 0 |
| Internal Transport Lead Time | 1 |
When the calculation is run, the total purchase lead time is 14 days.
Update using Average Historical Lead Time
When this update option is used, the standard setup lead times on Supply Chain Matrix and Supplier for Purchase Part are not applied.
Instead, the Purchase Lead Time is calculated based on the actual received and approved dates of the historical receipts. The average lead time for the selected data serves as both Purchase Lead Time and Expected Lead Time. The Expected Lead Time, together with its associated Standard Deviation is recorded for IPR (Inventory Part Planning and Replenishment) purposes.
The assistant provides several selection parameters that limit the receipts included in average lead time calculations:
- Primary Supplier
- Part Number
- Forwarder
- Ship Via Code
- Date Interval
Purchase Lead Time calculations are based on historical receipt dates, i.e. the Approved Date of the Receipt. This date is compared with the order start date. Alternative start dates may apply in the calculation to accomodate different business practices.
- PO Line Created Date: Compares the Purchase Order line Created Date with the Approved Date of the Receipt to determine the Purchase Lead Time.
- PO Release Date: Compares the Purchase Order header Release Date with the Approved Date of the Receipt to determine the Purchase Lead Time.
- PO Line Confirmation Date: Compares the Purchase Order line Confirmation Date with the Approved Date of the Receipt to determine the Purchase Lead Time.
- Estimate PO Line Start Date: Compares an estimated order start date with the Approved Date of the Receipt to deteremine the Purchase Lead Time. The order start date is estimated by using the Actual Delivery Date and relate it with the External Transport Lead Time (from Supply Chain Matrix) and Supplier Manufacturing Lead Time (from Supplier for Purchase Part), to assume the order start date (working day in Distribution Calendar).
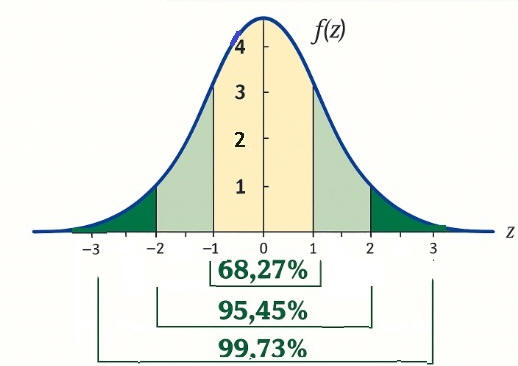
Once the average lead time has been calculated for the selected receipts, the standard deviation will be calculated and used to determine the Z-scores. This statistical measure indicates whether the dataset contains outlier values that may require consideration, i.e. if they should be excluded or not based on the circumstances. Values with a Z-score higher than 2.5 are excluded by default, but this threshold can be adjusted to 2 or 3 if better suited. If all values in the selection should be considered, no matter which z-score, the indicator for Exclude outlier values based on Z-score should be disabled.
Example:
The average Purchase Lead Lead Time in table below is 4,166... and rounded up to nearest full day
is 5 days (same for Expected Lead Time). The Std Dev Expected Lead Time is
calculated based on the mean 4,166..., which gives a result of 2,136 => 2,14 rounded in this field. With no
extreme outlier values to consider (z-scores are below 2), the final Purchase Lead Time is 5 and
Std Dev Expected Lead Time is 2,14.
If outlier values with high z-scores would have been there for any receipt, and the indicator was set to exclude
those, another recalculation would give a result without the outlier values included.
|
Selection of Receipts |
Purchase Lead Time |
Lead time difference compared to mean |
Standard Deviation |
Z-score |
|
Receipt 1 |
2 |
2-4,17=-2,17 => ^2=4,69 |
SQRT(22,83/(6-1)=2,14 |
-2,17/2,14=-0,095 =><2 |
|
Receipt 2 |
3 |
3-4,17=-1,17 => ^2=1,36 |
2,14 |
-1,17/2,14=-0,051 =><2 |
|
Receipt 3 |
4 |
4-4,17=-0,17 => ^2=0,03 |
2,14 |
-0,17/2,14=-0,007 =><2 |
|
Receipt 4 |
3 |
3-4,17=-1,17 => ^2=1,36 |
2,14 |
-1,17/2,14=-0,857 =><2 |
|
Receipt 5 |
8 |
8-4,17=3,83 => ^2=14,69 |
2,14 |
3,83/2,14=0,261 =><2 |
|
Receipt 6 |
5 |
5-4,17=0,83 => ^2=0,69 |
2,14 |
0,83/2,14=0,036 =><2 |
|
Average Lead Time: |
4,166… => 5 days |
Sum of squared: 22,83 |
|
|
Standad Deviation Formula for a sample:

Formula for Z-score:
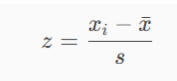
A standard normal distribution curve and z-scores can be visulized as below:
Prerequisites
Lead time information must be entered on the Supplier for Purchase Part and/or Supply Chain Matrix for Supplier pages before calculating with standard lead times in order to get a value.
If using calculations based on average historical purchase lead times, existing historical receipts for the selected data are necessary with an Approved Date. Additionally, values for Supplier Manufacturing Lead Time and External Transport Lead Time are required, if they are to be considered in the estimation of order start date, when using the Estimate PO Line Start Date calculation option.
System Effects
When you use option Update, the result of the calculation of Purchase Lead Time is stored in Inventory Part/Main/Lead Times and Supply Dates in the Inventory Part page. If using option Update Also Expected, both Purchase Lead Time and Expected Lead Time is updated with same value, where Expected Lead Time also is shown in page Warehouse Management/Part/Inventory Part Planning Data/IPR Parameters. (No standard deviation value should be shown when using these options.)
If you select the Do Not Update option, there is no update in the system and only a report is created.
If using option Update Using Average Historical Lead Time, both Purchase Lead Time and Expected Lead Time on the Inventory Part page will be updated. When using IPR (Inventory Part Planning and Replenishment setup for Warehouse Management at Site), the Expected Lead Time and Std Dev Expected Lead Time fields will also be updated on Warehouse Management/Part/Inventory Part Planning Data/IPR Parameters.