PL/SQL Unit Tests¶
Unit Tests framework provides the ability to test PL/SQL functions and procedures, and monitoring the results of such tests over time. Developers create unit tests by providing information about what is to be tested and what result is expected.
Create Unit Test File¶
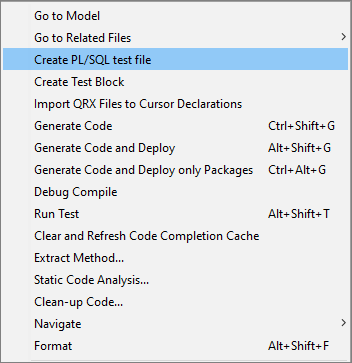
Open the plsql/plsvc file in Developer Studio and choose 'Create PL/SQL test file' RMB menu option in the editor. This creates a connected pltst file and opens it for editing. A pltst file can contain multiple unit tests.
Write Unit Test¶
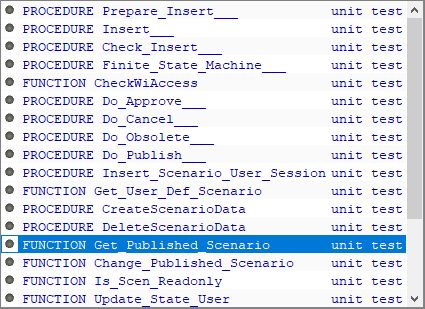
IntelliSense (Ctrl+Space in the editor) can be used to insert unit test skeleton for a given function/procedure.

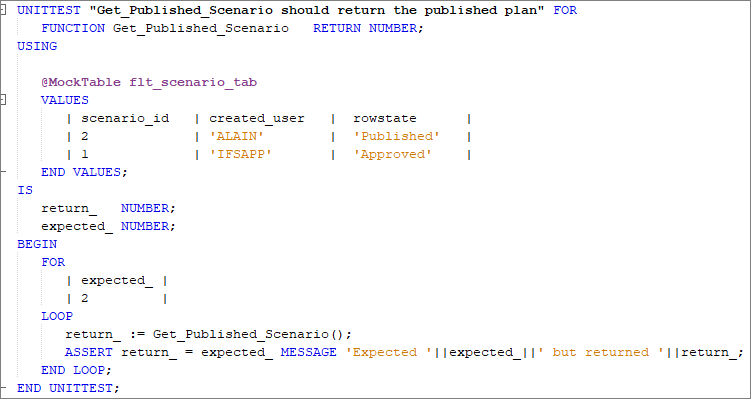
The text 'should... when...' within the header of the generated skeleton should be replaced with a short description of the unit test. The signature of the function/procedure for which the unit test is being written should be left unchanged.
The behavior of function/procedure, for which the unit test is being written, alone should be tested. Any external objects (e.g. tables, methods) the function/procedure uses should be mocked within the USING section of the unit test.
Each unit test is run by passing a set of test data and ASSERTing the test outcome against the expected result. This is done in the BEGIN section of the unit test. The test data can be passed to the function/procedure using an optional FOR LOOP.
Mock Annotations¶
Listed below are the supported annotations which are used to mock external objects (e.g. tables, methods).
-
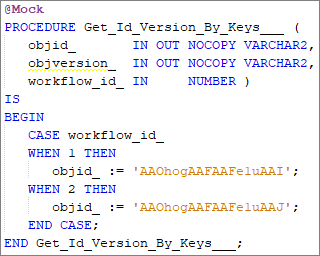
@Mock: Used to mock a function/procedure definition from connected plsql/plsvc
-
@MockPackage: Used to mock a function/procedure definition of a specific package

-
@MockPassThrough: Used to make direct API calls without having to mock them

-
@MockTable: Used to mock a database table/view

-
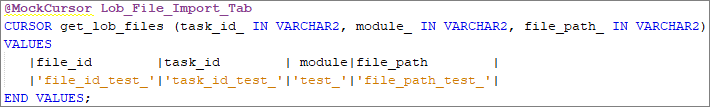
@MockCursor: Used to mock an external cursor declaration
-
@OptionalMocks: Used to make internal method mocks (@Mock) optional
Usage: Specify @OptionalMocks annotation above all the unit tests.
Some of the unit test might need original logic of internal methods to be executed. Using @OptionalMocks annotation,
the framework is generating original logic from the PL/SQL code and use that during the unit test execution.
Its important to note that even @OptionalMock is specified at the file level, developers can define mock methods in
Unit test. If @Mock method present in the unit test it will be execute, otherwise original method logic will get invoked.
Global Mock¶
Mocking external objects are essential part of unit test framework. In some implementations same sub method are invoked by multiple procedures or functions. Global Mock section can be used to reduce duplication of mocks. Mocks which are define under Global Mock section apply on all unit test on pltst file. Even mock method implemented as global mock, it is possible to implement internal mock in each unit test, and internal mock will take precedence over the global mock. By centralizing mock logic, global mock feature simplifies the testing process and enhances maintainability throughout the framework.
Example
PL/SQL Code
FUNCTION Get_Text___ (
text_ VARCHAR2)RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
txt_ VARCHAR2(200);
BEGIN
txt_ := Get_Subcall_Text___(text_);
RETURN text_ || ' Main Call AND ' || txt_;
END Get_Text___;
FUNCTION Get_Subcall_Text___ (
text_ VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
BEGIN
RETURN text_ || ' Sub Call ';
END Get_Subcall_Text___;
-------------------- GLOBAL MOCKINGS -------------------------------------------
@Mock
FUNCTION Get_Subcall_Text___ (
text_ VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
BEGIN
RETURN text_ || ' Global Mock';
END Get_Subcall_Text___;
-------------------- LU SPECIFIC PUBLIC METHODS -----------------------------
UNITTEST "Get_Text___ should retrun global mock when internal mock not define" FOR
FUNCTION Get_Text___ (
text_ VARCHAR2)RETURN VARCHAR2;
USING
--Insert your mock directives and mock return variables here
IS
--Insert your test variables here
return_ VARCHAR2(2000);
expected_ VARCHAR2(2000);
BEGIN
FOR
| expected_ | text_ |
| 'Expected Global Mock' | 'Expected'|
LOOP
--Insert your test code here
return_ := Get_Text___(text_);
--Insert your assertions here
ASSERT return_ = expected_ MESSAGE 'Expected '||expected_||' but returned '||return_;
END LOOP;
END UNITTEST;
UNITTEST "Get_Text___ should retrun internal mock when internal mock is define" FOR
FUNCTION Get_Text___ (
text_ VARCHAR2)RETURN VARCHAR2;
USING
--Insert your mock directives and mock return variables here
@Mock
FUNCTION Get_Subcall_Text___ (
text_ VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
BEGIN
RETURN text_ || ' Internal Mock';
END Get_Subcall_Text___;
IS
--Insert your test variables here
return_ VARCHAR2(2000);
expected_ VARCHAR2(2000);
BEGIN
FOR
| expected_ | text_ |
| 'Expected Internal Mock' | 'Expected'|
LOOP
--Insert your test code here
return_ := Get_Text___(text_);
--Insert your assertions here
ASSERT return_ = expected_ MESSAGE 'Expected '||expected_||' but returned '||return_;
END LOOP;
END UNITTEST;
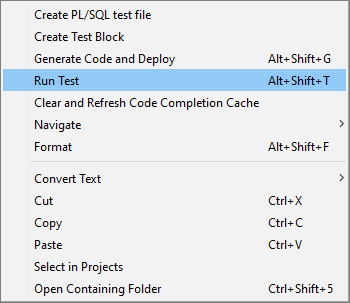
Run Unit Tests¶
The unit tests written in a pltst file can be run using 'Run Test' RMB menu option in the editor. Unit test passes if the boolean expression in the ASSERT statement of the BEGIN section evaluates to TRUE, else the test fails.