Manage Event Actions is about setting up which actions to perform when Events are triggered in IFS Applications. The Events are predefined in the system. The action can be for example to send a mail when an order is released.
Read more about concept Events.
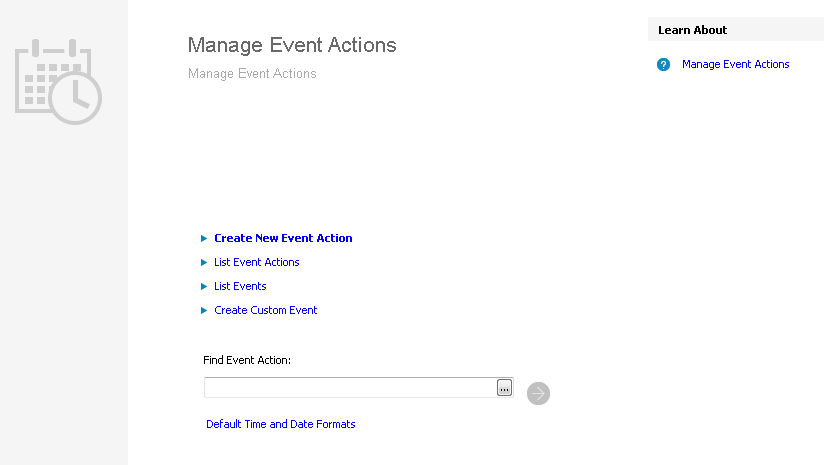
The Manage Event Actions form is the starting point when managing event actions. The most common tasks are available on this page for example Create Event Action and List Event Actions.

From this start page you can easily find and navigate to existing Event Actions. Type the initial letters of the Event in Find Event Action followed by <Ctrl>-K. Once the Event Action is shown in the field press the navigate button to the right and the Event Action including detail information is shown in the Event Action form. To edit the default date and time formats for event actions click on the Default Time and Date Formats link and modify the format values in the dialog box.
New event Actions are created in the New Event Action form. You can do that by clicking on Create New Event Action in the start page or in the start menu navigator in folder Solution Manager/Integration/Events or you can list the Events or Event Actions and right-click on one selected Event and select Create New Action for Event.
Action Type, Perform upon Event and Action Description are mandatory. The Event Action must be enabled in order to be performed. When the Event Action is enabled the Event will also get enabled. If the Event is disabled manually no Evenrt Actions are performed for that Event.
Next to the Action Description there is a text informing whether the Event Action is System Defined or Custom Defined. System defined Event Actions are delivered by IFS. The settings of the System Defined Event Actions are Read-Only, except the settings concerning subscriptions. It is possible to duplicate a system defined Event Action and make changes to the copy, if there is a need to modify the predefined action.
There are different types of actions that can be performed when an event is triggered. The same event can also have several actions. The action can be E-Mail, Execute Online SQL, Application Message, Task, Start Workflow or Streams Message. These action types are described in the table below.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Sends a mail to receiver using Mail Server setup in IFS Connect. This event action is possible to subscribe to. .Parameters:
|
|
Execute Online SQL |
Executes the SQL-statement. The statement will be executed in the
current database. Parameters:
|
|
Application Message |
Creates an Application Message to be handled by IFS Connect.
All the information available in the Event is included in the message. No
formatting of a specific text is available here; it is all handled by Connect.
It is though possible to set Connector, Address Data, Envelope
and Transformer. If Connector is specified Address Data is
mandatory. If Connector is not specified the message will be routed by
Connect.
Parameters:
|
| Task |
Creates a Task to one or many users. Tasks are shown to users in IFS Enterprise Explorer
in the Task panel.
Parameters:
|
| Start Workflow |
Calls an external web service. The intention is to be able to call a workflow engine that expose web services to start a new instance of a defined workflow. Parameters:
|
| Streams Message |
Creates a new stream message Parameters:
|
| REST Call |
Sends a REST Call using REST Sender setup in IFS Connect Parameters:
|
This option is only available for action type E-Mail. By checking the "Make this action subscribable"-checkbox below Subscription the Event Action gets available for subscription by end users. You can limit the possibility to subscribe to the action by entering a required permission set. Only users that are granted this permission set can then subscribe to the event action.
If an end user subscribes to this action, the user will also get the email as well as the receivers specified in the action.
To be able to control the execution of the action you can enter conditions that must be fulfilled. The action is thus only performed if all conditions are met. Click on Conditions for performing this action to edit the condition for the event action. When using the condition type 'LIKE' if the condition value contains '%' or '_' characters an escape character '\' should be used to avoid confusion with wildcard characters that can also be used. When using the condition type 'IS NULL' a condition value is not needed as it will not be considered for that condition type.
To create an action that contains useful information about the event it is possible to enter substitution fields into the message or subject. There are two types of substitution fields, Event and General.
Each event supplies a number of substitution fields with valuable information about the specific event. Select the substitution field and drag it into the message and place it where appropriate. The substitution field will automatically get prefixed "&" to mark it as a substitution field that will be replaced by real data.
The application provides a list of general Context Substitution Variables. These are not related to the actual event but can be useful to include in the message. A context substitution field can for example be the current users email address. Select the substitution field and drag it into the message and place it where appropriate. The substitution field will automatically get a pre- and postfix "#" marker to mark it as a context substitution variable substitution field that will be replaced by real data.
For email event actions you can add one or more files as attachments. Click on 0 Attachments to open a dialog where you can add, edit and remove attachments. If you click on Add in the Attachment-dialog, another dialog will open with options to add three different attachment types: From File, From Event and Create New.
For REST event actions you can add one or more files as attachments. Click on 0 Attachments to open a dialog where you can add, edit and remove attachments. If you click on Add in the Attachment-dialog, another dialog will open. There, you can give the shared path of the particular file.
All event actions are shown in Event Actions in folder Solution Manager/Integration/Events.
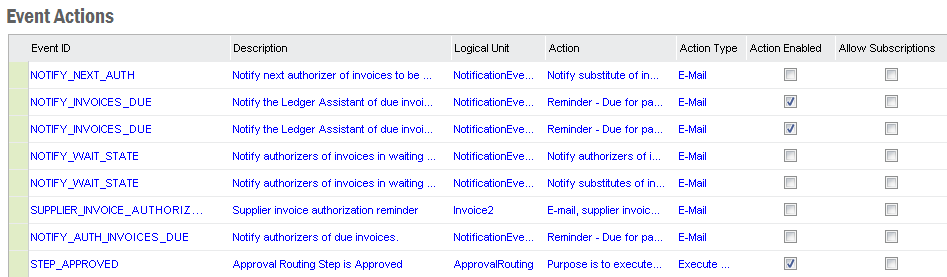
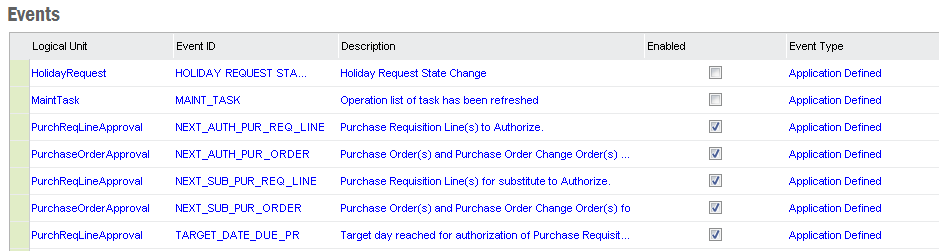
All Events are shown in Events in folder Solution Manager/Integration/Events.
The see the actions for an event right-click and select Show Actions. For
Custom Defined Events you can also select
Show Details in the same menu to view/edit the event.
Custom Defined Events are events that are defined in a specific installation. The difference between Custom Defined Events and Application Defined Events is that Application Defined Events is defined in the business logic delivered by IFS while Custom Defined Events is configured in Solution Manager and is technically executed by database triggers. The triggers is only created when the event is enabled, in order to recreate the triggers you need to disable the event and then enable it again.
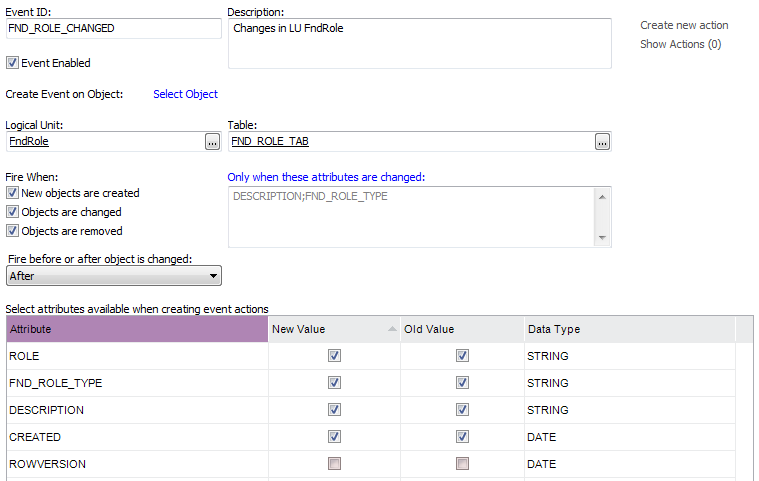
When you create a Custom Defined Event you select a Table on a Logical Unit that should handle the event. The event can be fired on three different occasions; New, Update and Remove.
There is also a choice of when the trigger should be executed; Before or After the object is changed. Before results in that the trigger will be executed before the business logic is executed. After means that the business logic will be executed first and the trigger will be fired afterwards.
Almost all attributes in the table are available to use in the Event Action
message. The only exceptions are LOB's and other special data types. In the attribute
list select which attributes that should be available when creating event actions
by checking the New Value and
Old Value. This creates variables called
NEW:<AttibuteName> for New Value
and OLD:<AttributeName> for Old Value,
for example "DESCRIPTION" and "NEW:DESCRIPTION" or "OLD:DESCRIPTION".
When the event is fired due to an object has changed the NEW:<AttibuteName>
is the variable for the new value after the transaction has occurred and OLD:<AttributeName>
is the variable for the old value before the transaction did take place. This is
how the variables get their value when event is firing:
NEW:<AttibuteName> and OLD:<AttributeName>
is the same value since no old values exists.NEW:<AttibuteName> is the new value after the transaction
and OLD:<AttributeName> is the old value before the transaction.NEW:<AttibuteName> and OLD:<AttributeName>
is the same value since no new value exists.Note: CLOB type columns are not supported in Events due to a limitation.
A Custom Defined Event can have Custom Defined Attributes. To enter a new attribute
right-click in the list of Custom Attributes and select
Insert. Enter a name for the parameter and
a PL/SQL function <Package name>.<Method>. The PL/SQL function can
use Attributes described above as arguments.
Note: It is not possible to use Context Substitution Variables
as arguments to Custom Attributes.
Fnd_User_API.Get_Description(#USER_ID#) is not allowed.
Example:
Fnd_Role_API.Get_Description(&NEW:ROLE)orFnd_Role_API.Get_Description(&OLD:ROLE)
Note: If a Custom Defined Parameter selects from the Custom
Defined Events table you will run into Oracle error 4091.
ORA-04091: table SCOTT.Emp_tab is mutating, trigger/function may not see it
A Custom Defined Event can be exported to the file system as a (*.ins) file.
Right-Click in the Custom Defined Event detail form
to open the context menu and select Export Custom Event.
Set a filename for the export file and click on save to save the file. The Event
can then be imported into another environment by executing the export file in the
database.
Custom Events can also be exported using
Application Configuration Packages.