This page deals with how to create custom attributes for a Dimension.
Custom attributes are added in IFS Enterprise Explorer and can be done by any end user having necessary privileges. All functionality related to Dimension specific custom attributes can be found in Solution Manager as a part of the Information Source framework.
The following prerequisites must be met to be able to create custom attributes for a Dimension:
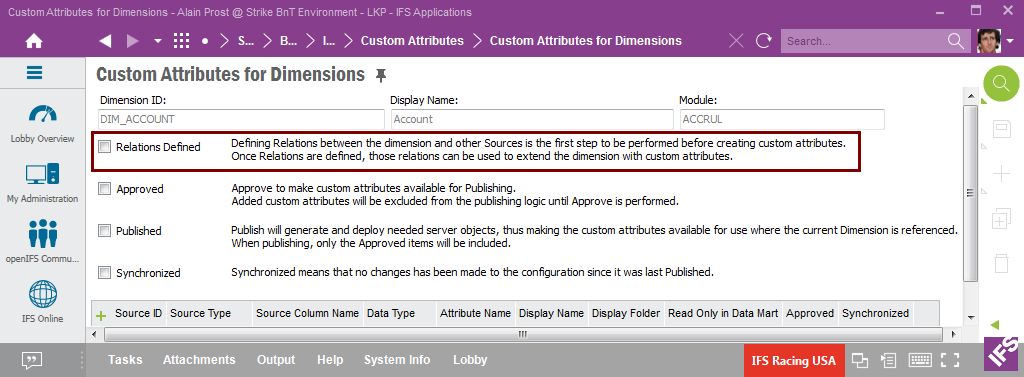
Custom attributes are defined in the Custom Attributes for Dimensions window. Query for the requested Dimension, e.g. DIM_ACCOUNT. If the check box Relations Defined is not selected, it is not possible to define any custom attributes. The remedy is to open the Relations for Dimensions window and create the needed relations and approve them for the Dimension before defining custom attributes.

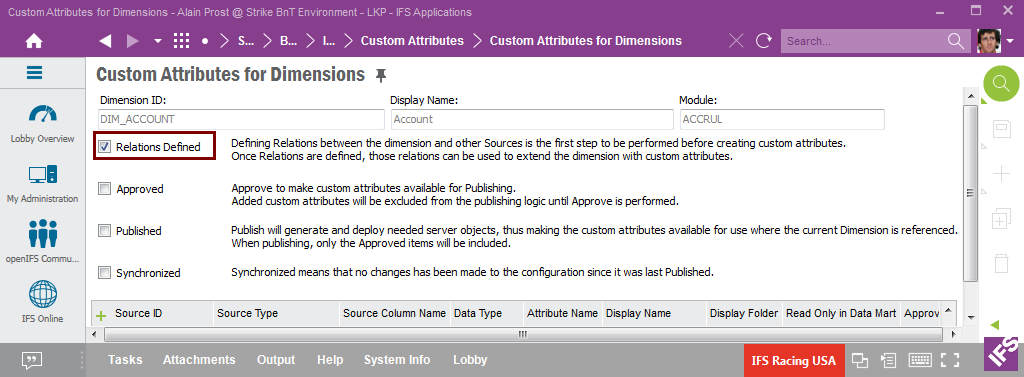
Once there are approved relations the window should look like below.
Next step is to define the custom attributes. This is done in the detail section.
The following custom attributes will be added in this example:
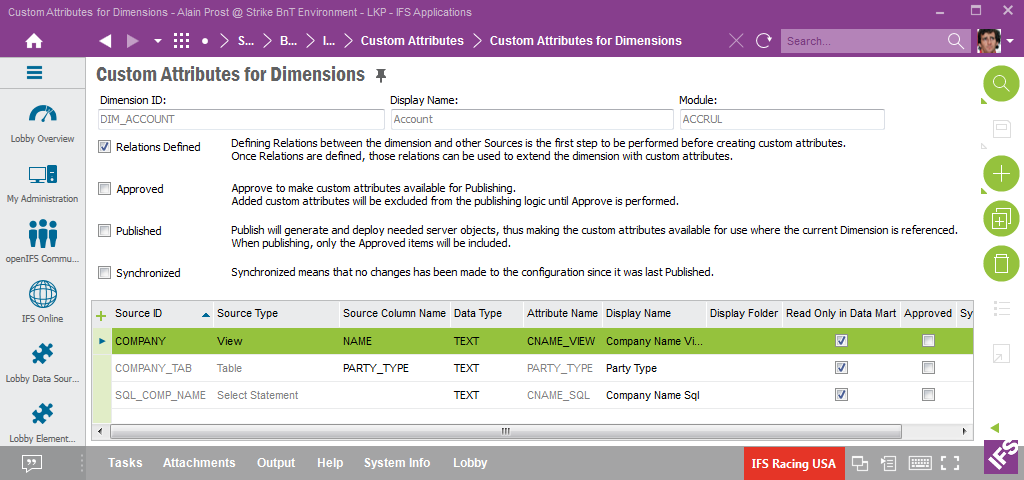
Some detailed information about the detail section:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Source ID | The identity of the custom attribute source as defined in the Relations for Dimensions window |
| Source Type | The source type as defined for the relation to be used |
| Source Column Name | The name of a column in the source
if the source type is
View, IAL View or Table An attribute reference if the source type is Dimension or Fact For source types Select Statement, Function Call and Expression, a column name should not be specified. |
| Date Type | Data type of the custom attribute |
| Attribute Name | The name of the custom attribute when added
to the Dimension. Only uppercase characters are allowed. No spaces can be
used. Possible characters are also limited. The resulting Dimension Item Id will be <Dimension ID>.<Attribute Name> e.g. DIM_ACCOUNT.COMP_NAME |
| Display Name | The display name of the custom attribute in the Information Source navigator in e.g. IFS Business Reporter and IFS Lobby. |
| Display Folder | The name if the folder in the Information Source navigator where the custom attribute should appear. The Display Folder always defines a sub level to the dimension attribute folder. |
| Read Only in Data Mart | If the Dimension supports
incremental load, it is important to specify if the custom attribute
should be stored in the database or not. By default this check box
is not selected, meaning that the custom attribute will be stored in
a special incremental table dedicated for custom attributes for the
current entity. If the check box is selected, the attribute will not
be stored in the database, only added as read-only attribute in the
access view. A typical case is when the value of the attribute is dependent of the context, e.g. current user, current language. For this case the attribute should be defined as a read-only attribute. |
| Approved | Selected when the definition has been approved. |
| Synchronized | Selected as long as the referenced relations or the published custom attributes are unchanged. |
Once the custom attributes have been defined, the next step is approval. Two levels have to be considered:
If we decide to add the defined attributes, use RMB Approve for each row and then perform Approve on the entity level.
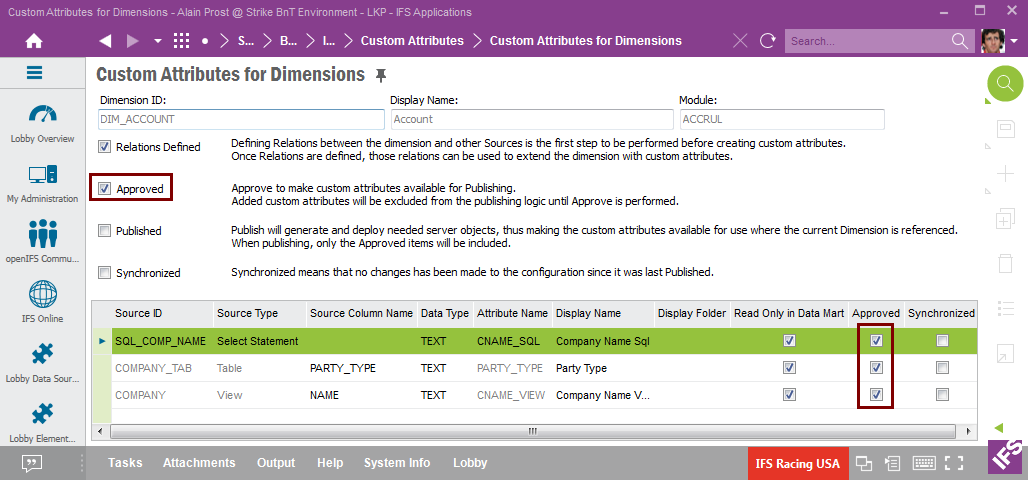
The last step is to publish the approved custom attribute definitions and this requires approval on both attribute and entity level.
Publishing is simply done via the RMB Publish on the entity level.
Publishing leads to:
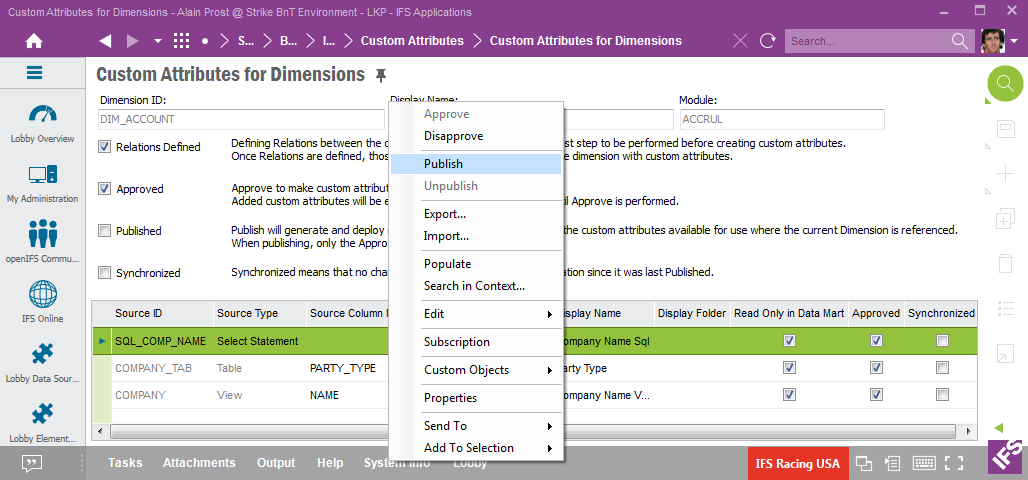
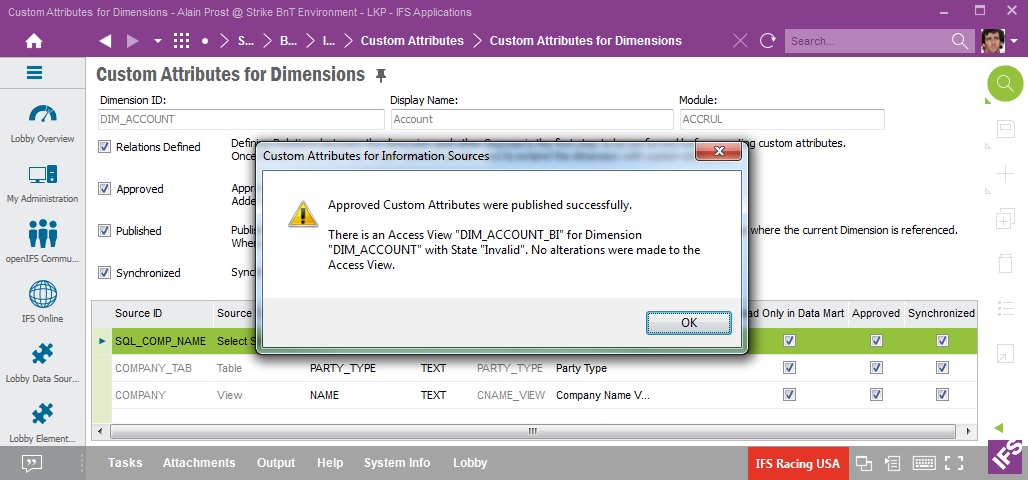
Some observations:
If there is a need to find out what happened during the publishing step, please check the Information Sources - Installation Log window.
The following error might appears during publishing:
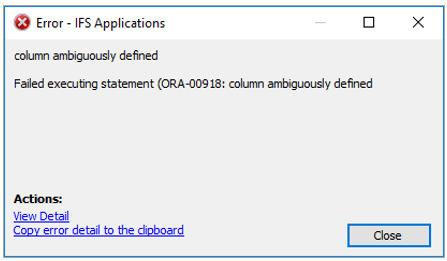
The reason is most likely that a relation based on type SQL Expression has
been defined using column references in the expression without an alias
definition. E.g. the expression SITE || ' - ' || DESCRIPTION instead
of d.SITE || ' - ' || d.DESCRIPTION
Please refer to dimension relations
for more info.
The framework keeps track of changes related to the source relations for all approved custom attributes.
Say e.g. that the relation based on the view COMPANY has changed. This leads to the following:
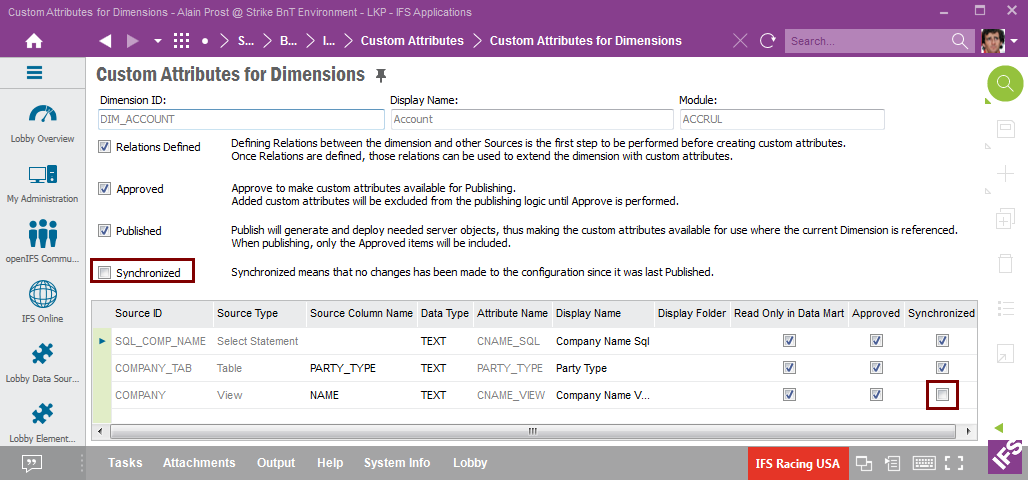
If custom attribute definitions for a Dimension entity have to be modified, the first steps will be to:
When the above actions are done the custom attribute definitions can be modified.
When the changes have been made, the actions are as before:
When custom attributes have been added to a Dimension, it is possible to find out in the Information Sources feature if a Dimension has custom attributes and also which attributes that have been added.
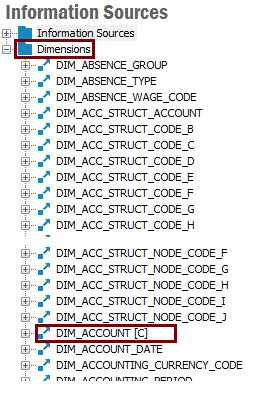
Dimensions to which custom attributes have been added are in the Information Sources feature, Dimensions node, marked with [C] after the name in the navigator.
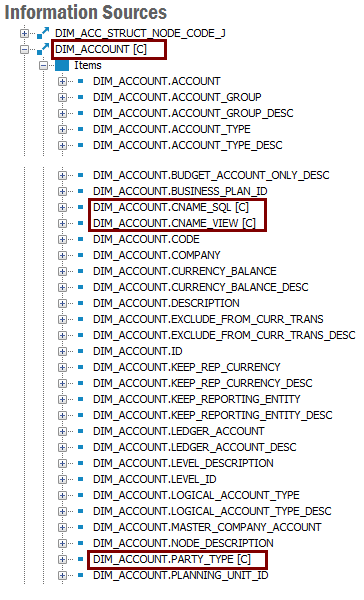
Added custom attributes also have the suffix [C] added to the attribute identity in the navigator.
The window Custom Attributes for Dimensions provides the possibility to export and import relations and custom attributes.
The options Export... and Import... are available as RMB options in the header.
The export will consider:
The content is exported as a XML file.
The import option takes a previously exported XML file and imports the custom attributes and relations. Import will not succeed if a relation or attribute to be imported already exists.
This functionality can be used when moving custom attribute definitions from
one environment to another.
When the metadata of a Dimension is deployed, e.g. through a bug correction or an update, the custom attributes will still be available after the deployment process has ended. This is not the case if a new attribute or any other changes are made e.g. through the Information Sources feature.
Through the Information Sources feature it is possible to modify custom attributes of a Dimension and also to reference added custom attributes as part of the entities metadata, e.g. adding parameter functions for a custom attribute, using a custom attribute as part of a LoV definition. Generally, all it will be made sure that these definitions are kept after having deployed the metadata of the entity.
Custom attributes that are based on the source type Select Statement or Function Call or based on other source types but using the join type Sub Select, will generally have a bigger impact on performance than attributes where an outer join is performed between the original source and the referenced source. Read performance can be affected but might also be good enough. The big problem is when a custom attribute is used as a conditional attribute, easily leading to bad performance.