Product Structures
A product structure or bill of material identifies the material that makes up a parent part and that is required to manufacture, purchase, repair, disassemble, remanufacture, or disposition that parent part. It also identifies the by-products and disassembly components produced from the respective process. Product structure is a generic definition. Shop orders might involve order-specific changes to this list of needed components, but the list of components for the order is initially created in accordance with the product structure definition of the ordered part.
Product structures are used by IFS/Master Scheduling (MS) to determine which components are in demand. Discrete and repetitive manufacturing uses these structures to determine the components required to manufacture/remanufacture a part, or the additional material needed to repair one. Product structures are also used in calculating costs and production lead times. Much of planning and manufacturing depends on product structure definitions.
Product structures are divided into three elements: a structure header, a structure alternate, and structure line items.
Structure Header
A structure header is where the part, site, inventory part revision, and type of product structure are identified. The structure type represents the process in which the structure is used:
| Type | Description |
| Manufacturing | Used when the part is planned or manufactured. It contains the components required to manufacture the part and possible by-products and disassembly components produced in addition to the main product during the manufacturing process. A product structure header of this type is automatically created for inventory parts with Part Type set to Manufactured. |
| Purchasing | The typical makeup of a part purchased from a supplier. It contains the components that should be shipped to the supplier. A product structure header of this type is automatically created for inventory parts with Part Type set to Purchased. |
| Repair | Used when repairing the part. It contains the components required for the repair process, and possible by-products and disassembly components to be received in addition to the main product during the repair process. If the components required are not known in advance, the structure can be left empty and still set to buildable. Note that the repair part is not included in the structure but automatically added as a component on the repair shop order. |
| Prototype | Used when prototyping a part. It contains the components required to manufacture the prototype part and possible by-products and disassembly components produced in addition to the main product. Note that a prototype creates a unique part revision with the Prototype Part Revision Prefix defined on Site/Manufacturing, and always remains in status Tentative. |
| Disassembly | Used when the part is disassembled. It contains the disassembly components and possible by-products expected to be received from the disassembly process and optionally components consumed during the disassembly. Note that the part to disassemble is not included in structure but automatically added as a component on the disassembly shop order. |
| Remanufacturing | Used to remanufacture a part. I.e., restoring it to a like-new condition. It contains the components required to remanufacture the part and possible by-products and disassembly components produced in addition to the main product during the remanufacturing process. A remanufactured product can consist of both new and used components. It is recommended to add the new components in the structure and the corresponding used components as the primary alternate components. A product structure header of this type is automatically created for inventory parts with Part Type set to Remanufactured. |
| MRO Assembly | Used when the part is assembled within the MRO process. Structure headers are automatically created as the result of template structure transfer functionality. |
| MRO Disassembly | Used when the part is disassembled within the MRO process. Structure headers are automatically created as the result of template structure transfer functionality. |
| Disposition | Used when dispositioning the part within the MRO/CRO processes. |
A part revision may have several structure headers associated with it, one for each of the structure types. A structure header of corresponding type is automatically created when a new part revision is created for an inventory part of part types Manufactured, Remanufactured or Purchased.
Note: A structure with the type Prototype creates a unique part revision with the Prototype Part Revision Prefix defined on Site/Manufacturing.
Structure Alternate
A structure alternate defines the status of a product structure and represents a slightly different way of making the same part. The differences might be based on the quantity of parent parts being built, the use of acceptable alternate materials, or some other non-standard condition that indicates a different structure. All structure headers have at least one defined structure alternate, known as the default alternate, which is indicated with an asterisk (*) in the Alternate field.
The status of the structure alternate indicates how the structure information can be used. The ability to change the component records depends upon the status of the alternate structure, defined in Product Structure, and the site's Structure/Routing Update setting, defined on Site/Manufacturing. Possible statuses are:
| Status | Description |
| Tentative | A structure alternate is created in Tentative status and, normally, this is the default value. This status indicates that the structure alternate is not yet usable, and the structure data will not be used by Planning or Manufacturing. Components may be changed to this status. |
| Plannable | A structure alternate promoted to Plannable status can be used to calculate cost and planning information, but is still not used for Manufacturing. Components may be changed to this status. |
| Buildable | Structure alternates promoted
to Buildable status are completely visible in the system, and
can now be seen and used by Manufacturing, as well as for planning and
costing purposes and for generating order components. The Structure/Routing Update setting, defined on Site/Manufacturing, determines your ability to modify a component's attributes in this status. If Simplified, most changes are allowed. If Enhanced, only some changes are allowed. If Restricted, most changes are not allowed. |
| Canceled | The structure alternate has been canceled and will not be available for use in Manufacturing or Planning nor used to generate costing information. You can change to this status at any time; however, once in this status, only the status may be changed. |
| Obsolete | The structure alternate has been obsolete and will not be available for use in Manufacturing or Planning nor used to generate costing information. You can change to this status at any time; however, once in this status, only the status may be changed. |
Note: If the structure type is prototype the structure alternate can only have Tentative and Obsolete statuses. The structure alternate is created in Tentative status and can be used by Manufacturing. Structure alternates in the Obsolete status will not be available for use in Manufacturing and cannot be changed to a different status.
Structure Line Items
Component
Components are parts required to manufacture, repair, prototype, disassemble, remanufacture, disposition, assemble, or purchase the parent part. Each line item identifies a component and quantity per assembly, which is quantity required to manufacture, repair, prototype, disassemble, remanufacture, disposition, assemble or purchase one unit of the parent part.
- A component can be identified as a Non-Consumed item, which means that although the part appears in the product structure, the demand for that component will not be generated when an order is created for the parent part.
- A structure line item may also be associated with an operation number from the routing for the parent part, indicating that the component will be issued or used during the indicated operation. Functions within Shop Order Operation Reporting will automatically issue material linked to specific operations, and a pick list report can be generated for an operation, showing only material linked to that operation.
- A component can be defined as a Lot/Batch Origin component. The parent part will then inherit the Lot/Batch number from the Lot/Batch Origin component, with a suffix attached. An item can only be named Lot/Batch Origin for shop orders.
- A component can also be defined as an Expiration Date Origin component. The parent part will then inherit the expiration date from the selected component, or calculate it based on the manufacturing date of the selected component, depending on whether the parent part has a shelf life or not. Several components in a product structure or recipe structure can be selected as Expiration Date Origin components. If this happens, several expiration dates will be calculated and the date closest in the future will be set as the expiration date of the parent part.
By-Product
By-products are secondary products produced in addition to the main product during manufacturing, repair, prototyping, disassembly, or remanufacturing. Each line item identifies a by-product part and quantity per unit, which is the quantity produced relative unit of the parent part.
- A by-product may be associated with an operation number from the routing for the parent part indicating that the by-product will be received when this operation is reported.
Disassembly Component
Disassembly component are parts disassembled from a product during disassembly, repair, manufacturing, prototyping, or remanufacturing. Each line item identifies a disassembly component part and quantity per unit, which is the quantity disassembled from one unit of the parent part.
- If it is not expected to recover all disassembled components, an expected scrap percentage can be set.
- A disassembly component may be associated with an operation number from the routing for the parent part indicating that the component will be received when this operation is reported.
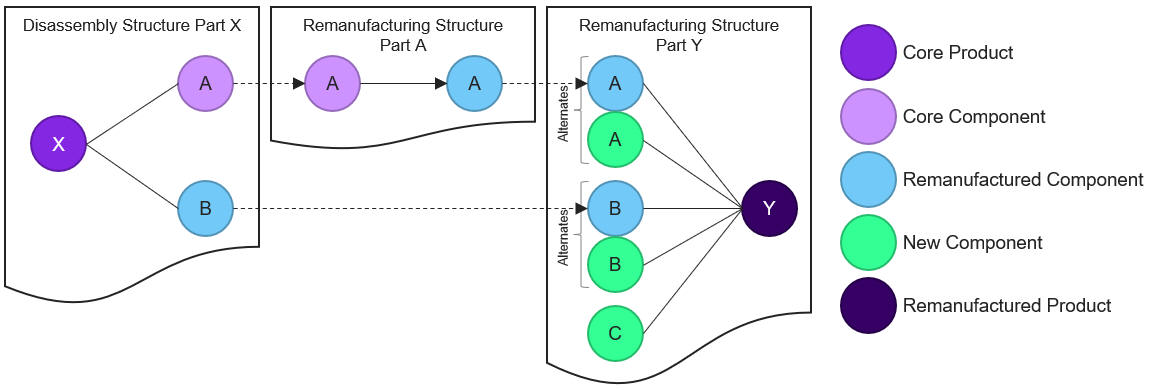
Direct Supply
For remanufacturing structure alternates, parts that could be disassembled or remanufactured to directly supply the remanufacturing of the main product can be defined. It is possible to rank the priority for each part that is defined as direct supply according to how optimal supply the parts are expected to provide.
Example:
- Product X should be disassembled and Component A should be remanufactured to supply the remanufacturing of Product Y. I.e., the parts received from the disassembly of Product Y and the remanufacturing of Component A should supply the remanufacturing of Product Y.
- Product X with Supply Type set to Disassembly and Component A with Supply Type set to Remanufacturing are added as direct supply to the remanufacturing structure of Product Y.
- When a remanufacturing shop order for Product Y is created, a pegged disassembly shop order for Product X and a pegged remanufacturing shop order for Component A can be created. The part received from the pegged orders will automatically be reserved to the demand order when required. For additional information about pegged supply on remanufacturing shop order, see Remanufacturing Shop Order.