This page gives information on how to set up basic data in IFS Applications in order to make the OLAP cubes in the IFS Analysis Models work properly. It is also important to point out that the basic data configuration is closely related to configuration of lookup data.
To in general make sure that IFS OLAP cubes are correctly created it is mandatory to define the following basic data in IFS Applications
Other mentioned basic data is also important but only affects specific cubes.
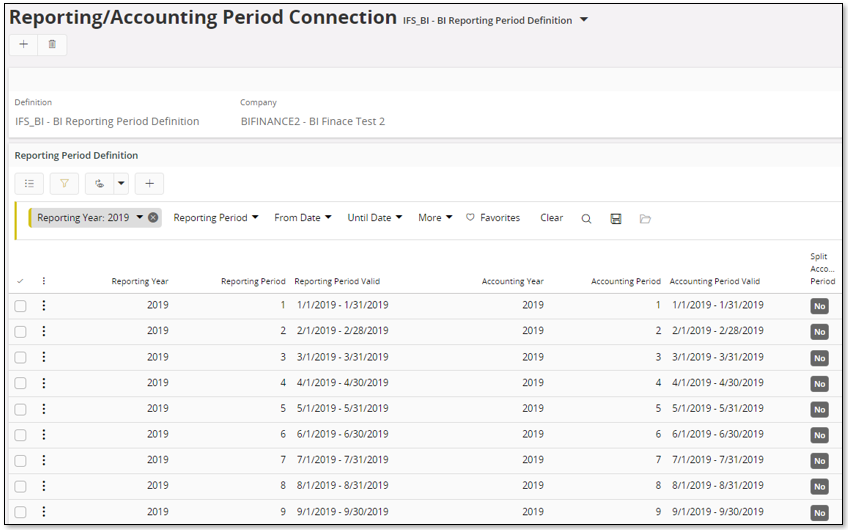
Most of the cubes in the IFS Analysis Models use a dimension named Company Reporting Period, related to the Reporting Period framework is defined in Accounting Rules. The purpose is to supply a common period definition that can be used as a replacement for accounting periods especially for cross product reporting. It is also possible to use Reporting Periods on a non-company level, grouping a cross product related date into a set of periods.
It is in the ETL process necessary to define the Reporting Period Definition ID to be used by each product area. In IFS Applications this means setting up the Company Reporting Period information that should apply for each and every company to be analyzed.
OLAP cubes (delivered by IFS) in the following areas are affected:
Note: If Reporting Periods are not supplied, the OLAP cubes will not be correctly created.
Note: The dimension Company Reporting Period will in most OLAP cubes be represented by the cube dimension named Reporting Period. The date used as a key attribute when defining the Company Reporting Period identify in each Information Source, will also be used to define the time dimension named Reporting Date.
The OLAP cube dimension Reporting Period makes it possible to combine Information Sources from different product areas into one single cube, thus enhancing cross product analysis possibilities.
For more details please refer to Lookup Configuration.
For the Financials cube the following is important:
Normally this is handled automatically (see functionality described below).
This normally leads to that fiscal period 0 (Incoming Balances) and period 1 are part of Reporting Period 1. For a year with 12 fiscal period, Reporting Period 12 will include fiscal period 12 and year end periods.
All companies to be analyzed should thus have the same accounting period calendar definition and they must also share the same reporting period definition.
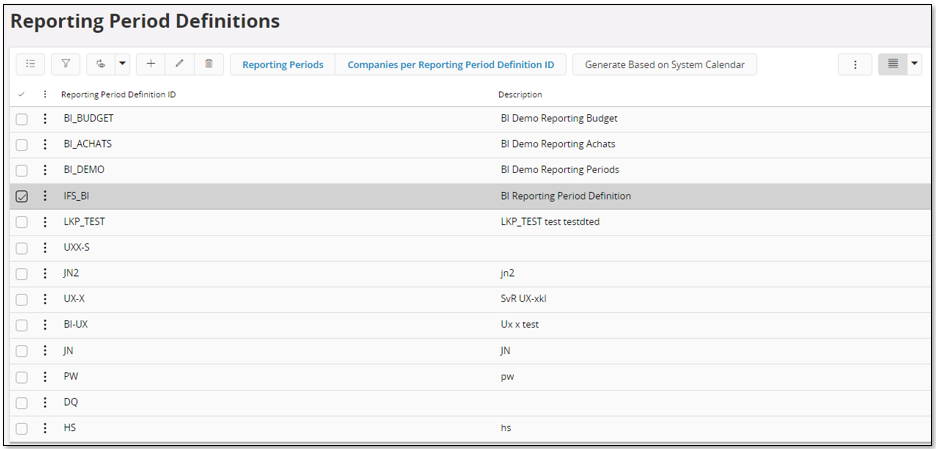
Start by defining the Reporting Period Definition IDs to be used in the Reporting Period Definitions page.

There are two ways to proceed:
Starting with the manual approach.
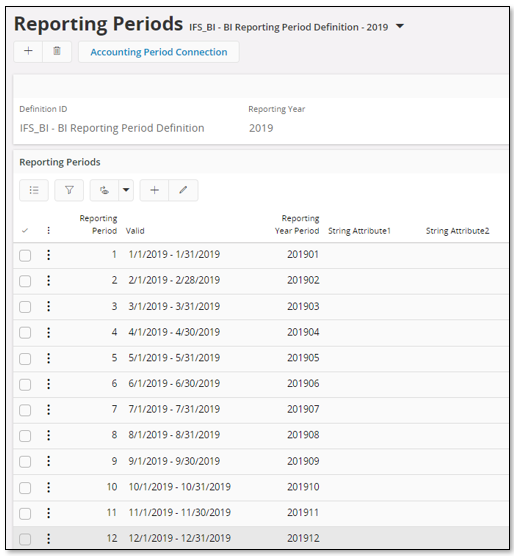
Define the reporting period details, dates per year and period, for each Report Period Definition ID. This is done in the Reporting Periods page.
Next step will be to define all companies that should be connected to the same Reporting Period Definition ID and to map accounting periods with reporting periods.
This is handled in the Companies per Reporting Period Definition page.
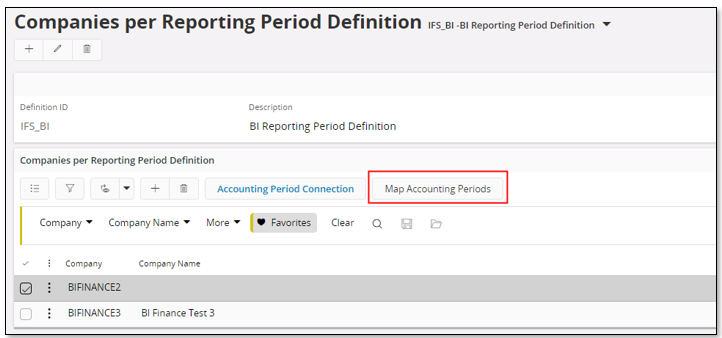
It is of course also possible to modify automated mappings or to define mappings between accounting period and reporting period manually via the Accounting Period Connection page.
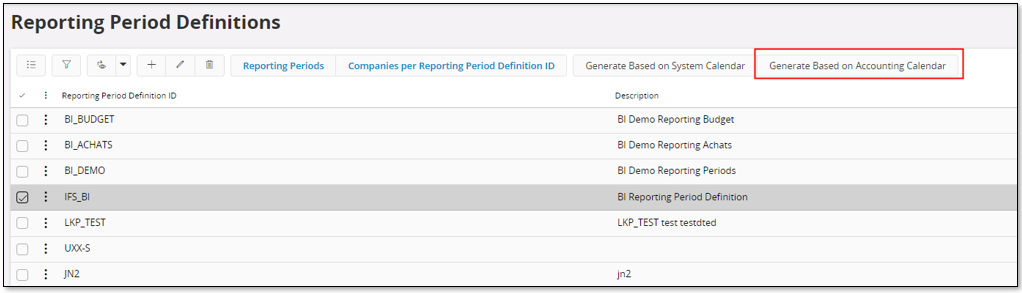
The second approach is to handle the creation of reporting periods automatically.
After having created the reporting period definition, select the definition and use command Generate Based on Accounting Calendar.
Select a company. This is typically the master company that will be defined in ETL Lookup Configuration. Then specify from and until accounting year and make sure to also include Year End (and Incoming Balances) periods.
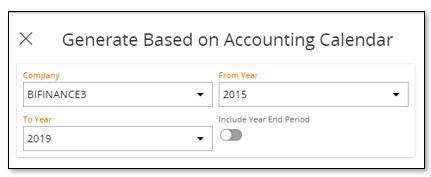
The selected company will be connected to the reporting period definition and the accounting periods within the given year interval will be used to create reporting periods as well as the mapping between reporting periods and accounting periods.
Most of the cubes in the Analysis Models support calculation of amounts in base currency into a reporting currency. To make this possible it is required to define the rates to be used for the calculations. It is only possible to define one definition of rates, i.e. one single combination of company and rate type must be defined as the reporting currency rate source.
Note: It is mandatory to define the Reporting Currency Rate Type to make sure that affected cubes are correctly generated.
Please also refer to Lookup Configuration.
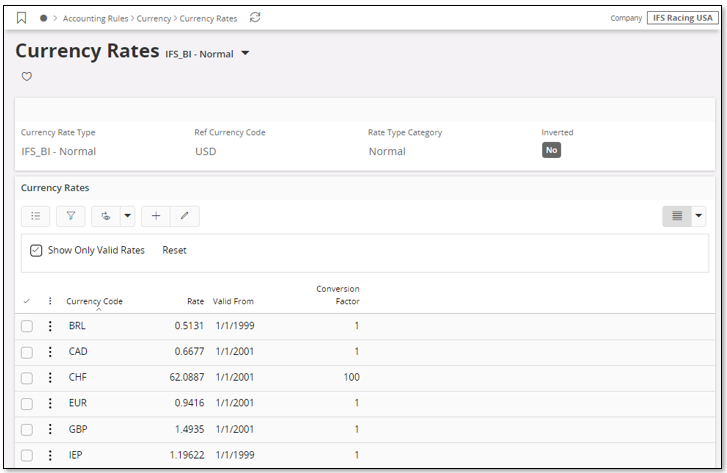
The rate type is defined for the selected source company in the Currency Rate Types page.
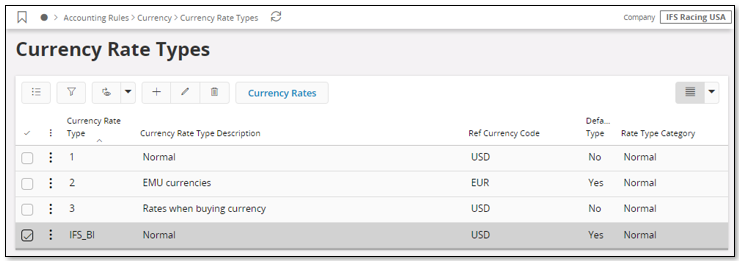
In the above case, the Currency Rate Type with identity IFS_BI in company 10 (IFS Racing USA) has been selected as the rate source for reporting currencies.
Details, i.e. rates per currency, are defined in the Currency Rates page.
The cubes in the Financials area (General Ledger and Group Consolidation) are using information from different balance set specific Information Sources; GL Balance Set Analysis and Consolidation Period Balance Set Analysis respectively. For General Ledger the Information Source retrieves information from:
This Information Source has a connected dimension named GL Balance Set. Balance Sets are defined on company level. The idea is to define which one of the four mentioned sources that applies to a given accounting period, opening up for rather flexible analysis possibilities.
For Group Consolidation the Information Source retrieves information from:
This Information Source has a connected dimension named Consolidation Balance Set. It works similar to GL Balance Set.
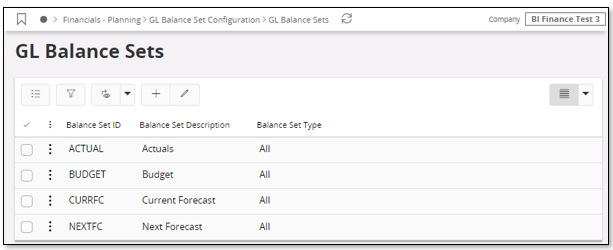
In the following section the setups for the different areas are described using GL Balance Set as an example. GL Balance Sets are defined for the current company in the GL Balance Sets page. Setup for Consolidation Balance Set works in exactly the same way for Group Consolidation cube. In the latter case you use the page Consolidation Balance Sets.
Note: In the case of Group Consolidation the cube only contains data for one master company.
Any number of balance sets can be created. However it is important to notice that the GL cube by default supports analysis information based on four specific GL Balance Sets, in the cube recognized by the following:
| Cube Balance Set Identifier | Description |
|---|---|
| ACT | Actual Values |
| BUD | Budget Values |
| CFC | Current Forecast |
| NFC | Next Forecast |
In addition to the specified GL Balance Sets above, another three measures, X1, X2, X3. exist for the Consolidation Balance Sets. Those can be used freely, for example to analyze consolidated balances using the currency rates of the previous year.
It is recommended to define GL Balance Sets for one or more of the above four alternatives to prepare for flexible GL analysis. In the above example the balance sets with identities ACTUAL, BUDGET, CURRFC and NEXTFC have been defined to represent the specific analysis sets.
Balance sets to be configured by using the Balance Set Configuration command to open the GL Balance Set Period Configuration page.
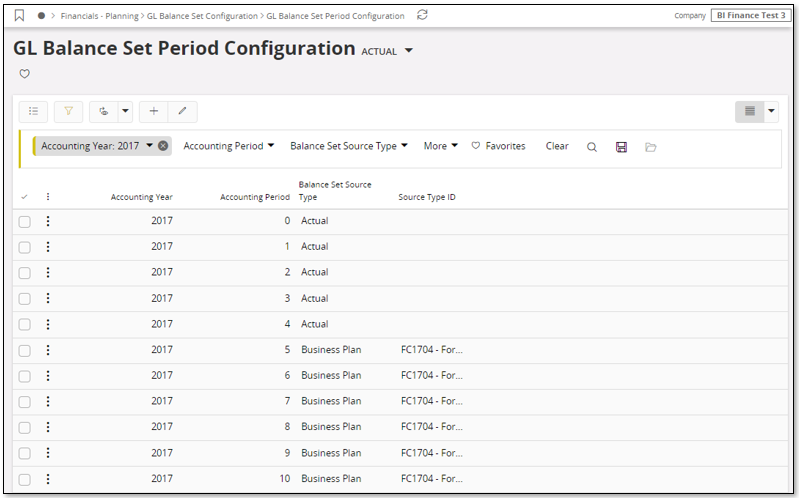
The period configuration is done per balance set. For each period in the accounting years to be analyzed the source type is defined. The source types are:
| Source Type | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Actual | GL Balances |
| Budget Version | GL Period Budget |
| Budget Process | Budget Template Transaction |
| Business Plan | Business Planning Transaction - Valid Version |
For the source types Budget Version, Budget Process and Business Plan it is necessary to supply the source type identity, i.e. the budget version or the budget process identity or the business plan identity. One example can be seen in the above image where for the Balance Set Source Type = Business Plan a business plans is supplied as the Source Type ID.
The described functionality provides the possibility for a Financial administrator/manager to set up different analysis scenarios that can be configured rather easily and that will affect the information transferred to the ETL process and at the end affect the OLAP cube content. E.g. at the beginning of the year the actual analysis set may contain only information from GL Period Budget. When the second period is entered, the first period can be modified to represent the actual values. At the same time a budget and a current forecast analysis set can be defined, enabling analysis of actual values versus budget and current forecast over a whole year.
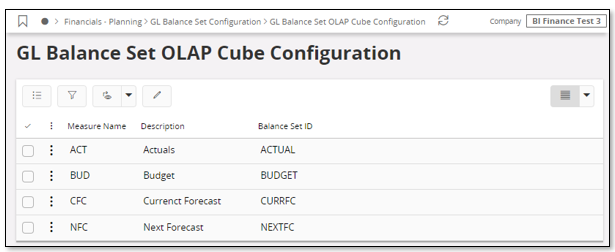
To define the GL Balance Set identities that should be used in the GL Balance OLAP cube to represent the fixed cube measures ACT (Actual), BUD (Budget), CFC (Current Forecast) and NFC (Next Forecast) the GL Balance Set OLAP Cube Configuration page is used. Similarly for Group Consolidation, the Consolidation Balance Set OLAP Cube Configuration window is used. Here you can also define the extra measures X1-X3, unique to Group Consolidation model.
Cubes in the Financials area use Accounting Structures to in a rather flexible way be able to visualize accumulated values on structure node level.
The following is supported:
To analyze more than one company in the cube it is required that all these companies have the same structures defined.
Accounting Structures are defined for the selected source company in the Accounting Structure page.
For more information please also refer to Lookup Configuration.
The Income Statement (IS), typically defines a structure suitable for analysis of profit and loss in a company. The structure is based on Account.
Remember the following:
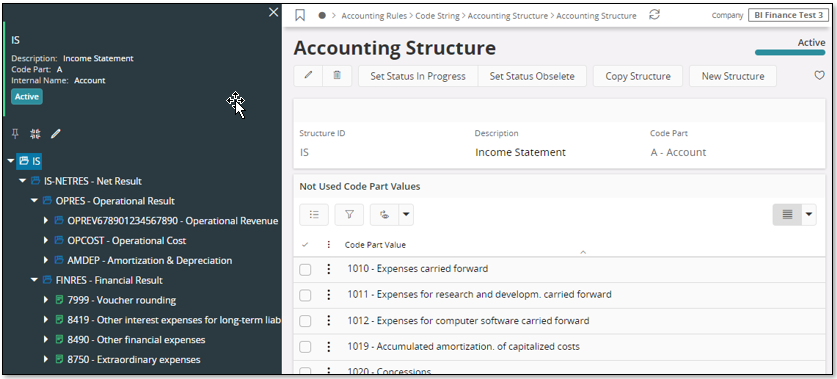
The balance sheet structure is based on Account.
Remember the following:
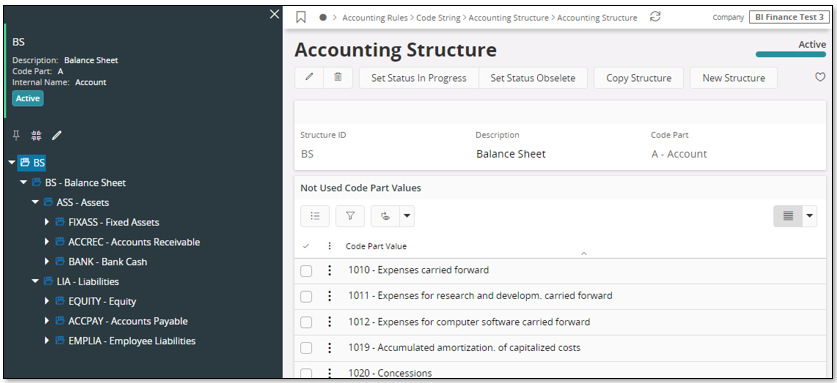
The Financial cube also supports structures based on code parts other than Account.
The Financials cube also supports Code Part Attributes (previously named Accounting Attributes).
One Code Part Attribute per code part is supported and to analyze more than one company it is necessary to define the same attributes in all these companies.
Code Part Attributes are defined for the selected source company in the pages Code Part Attributes, Attribute Value and Connect Attribute.
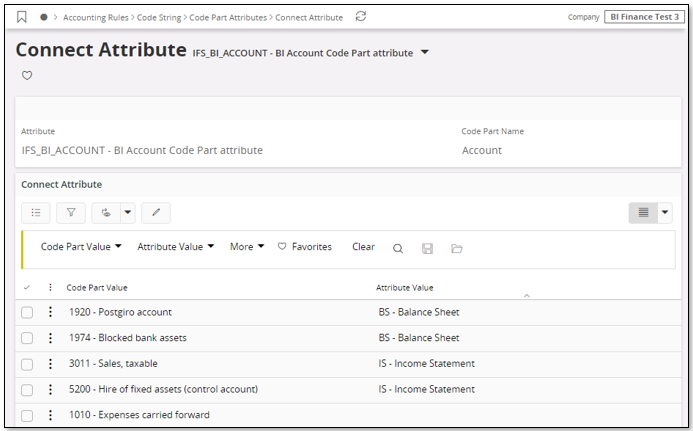
In the above example an attribute with identity IFS_BI_ACCOUNT has been defined for Account. The attribute has two attribute values, BS and IS, representing Balance Sheet and Income Statement accounts. For each attribute value the appropriate accounts are connected.
This Accounting Attribute definition can now be used in the Financial cube.
For more information please also refer to Lookup Configuration.
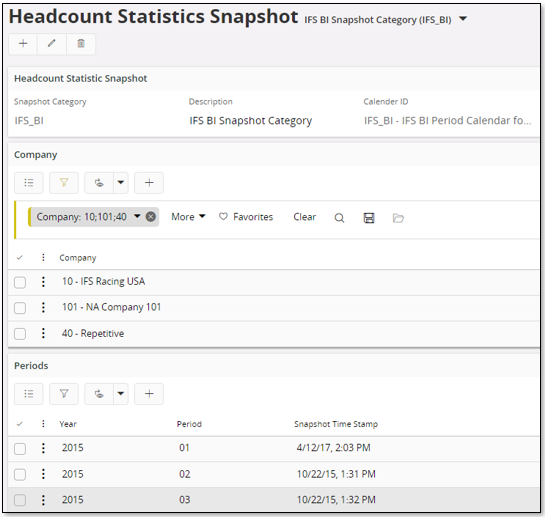
In order to use the Headcount Cube in the HR area, some basic data as well as Headcount Statistics Snapshots must be created.
Define an age group class, an employment duration class, the period calendar to be referenced when creating Headcount Snapshots and of course create necessary snapshots.
In order to use the Headcount Cube in the HR area, it is necessary to define one Age Group Class to be used by the cube. It is possible to configure which one to be used. Please refer to Lookup Configuration.
Use the page Age Group Class to define the necessary data.
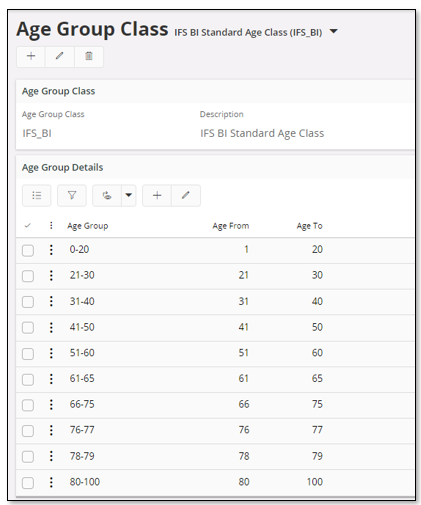
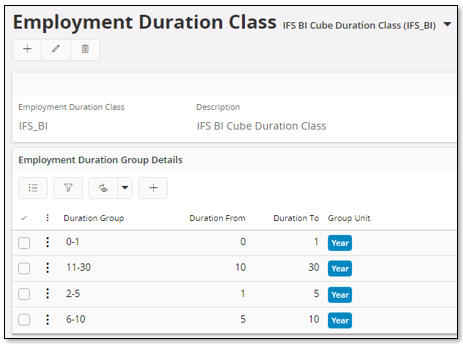
In order to use the Headcount Cube in the HR area, it is necessary to define one Employment Duration Class to be used by the cube. It is possible to configure which one to be used. Please refer to Lookup Configuration.
Use the page Employment Duration Class to define the necessary data.
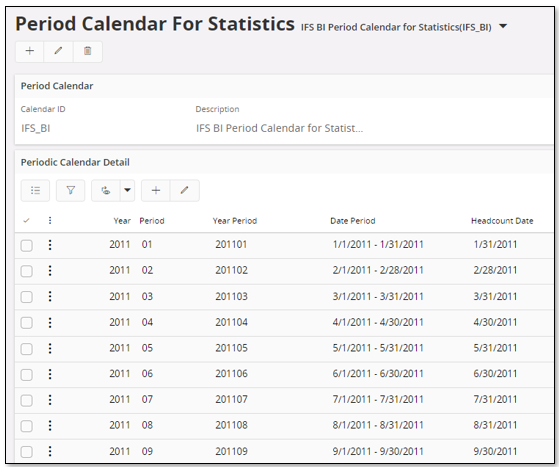
Use the page Period Calendar For Statistics to define the calendars to use.
A Headcount Snapshot is created by using the page Headcount Statistics Snapshot. Each category references one period calendar. Make sure to connect the companies to be part of the snapshot before creating. Next the snapshots are created in the Periods section.