Manufacturing Scheduling and Optimization (MSO) solution optimize the Use of manufacturing resource constraints and in turn creates finite schedule for the shop floor to execute production activities. The primary users of MSO are manufacturing planners, supervisors and machine operators. Production schedule decides the Overall time sequence of manufacturing execution. Therefore, the Most optimized schedule will be given to achieve the business objectives of a manufacturing organization
MSO solution uses Planning Scheduling and Optimization (PSO) solution as the scheduling and optimization engine. MSO create optimized schedule by scheduling activities in the Most appropriate time interval in the timeline while giving due consideration to the scheduling cost of the resource and other scheduling parameters, namely, characteristic constraints, resource share capabilities of machine and labor resources, shop order scheduling information and priorities and calendars.
The planners can decide the level of scheduling and optimization acceptance quality they expect from the schedule and the maximum time the MSO solution should spend searching for a scheduling result. These settings are defined per Site basis and upon the MSO dataset enablement. MSO is natively designed to reduce the Number of Late Orders in either of Scheduling Directions. This helps MSO to achieve timely demand fullfillments as much as possible.
In Manual Scheduling mode in MSO solution it starts working on finding a optimized scheduling solution no sooner it gets a scheduling request from the planner. In Automatic Scheduling mode it is continuously doing the scheduling adapting each and every change in demands and supplies in production environment. The scheduling algorithms in MSO will work on optimized solution and no sooner it reaches a solution, which may not be the most optimized will check if the waiting time target or accepetance quality target is exceeded. If yes , then MSO will immediately return the schduling result to the end user. Based on the scheduling mode the planner is using for the site the optimization process may continue or stop. In the case of “Manual” scheduling mode in MSO it will stop looking for more optimized solution while in MSO “Automatic” scheduling mode, it will continue to look for more optimized solution until it finds the best solution for the Scheduling problem. After the Scheduling completion achieved plan quality will be shown in 'Shop Order Scheduling Analysis' window and 'Smart Manufacturing Planning Board' together with the Schduling result.
MSO creates finite schedule as per the manufacturing and shop order scheduling data. Therefore, it is essential to set the data that affect the shop order schedule before using MSO.
System Administrator has to refer detailed Technical Documentation for Scheduling Optimization and Machine Learning Configuration to set-up PSO Configuration and also the MSO profile should be set in PSO workbench.
In Techdocs; Solution Manager User Guide->Automation & Optimization->Scheduling Optimization->Scheduling Optimization Business components->Manufacturing Scheduling Optimization (MSO)
For all other parameters default values will be used; OpenIdAutority and OpenIdClientId are set based on the PSO client tenant IDs
If User is expecting a less than 5 minutes optimization time accuracy in the Schdule it is adviced to set below parameter as well. This may affect the Performance of Scheduling Service.
DelayActivityIncrement - 1 minute
- Refer Activity Descriptions for
TIme Horizon (Days) : Shop Orders which has the Need date inbetween the current time and count end date counting this number of Time Horizon days will be considered for the Scheduling.
Shop Orders with Need dates in the Past will also be considered using this number of days times 10 and this 10 number factor in MSO can be changed by a customization.
These are the Hard contraints which are following by MSO Scheduling Service while generating the Scheduling Result.
Scheduling Rules in MSO are strictly following constraints when scheduling while achiving other business goals like;
MSO is natively designed to reduce the Number of Late Orders in either of Scheduling Directions. This helps MSO to achieve timely demand fullfillments as much as possible.
User can enable the Automatic schedule adjustment based on the Remaining time of shop order operation. The remaining time is calculated based on the Quantity remaining to report. This setting can be used to re-adjust started or partially reported shop orders.
User can advice the Scheduling service to consider the Project Activity Early Start and Project Activity Late Finish time range as period to schedule for project activity connected shop order's operations.
Operation blocks consideration in MSO is treated as a hard constrant in the Schedule.
In Operation blocks page this site setting can be overrided with Schedule Operation blocks with MSO assistant. This assistant also supports to define proceeding and succeeding blocks, prefferred resource, Start/finish horizons for block scheduling,etc..
Note:- This is released as a limited feature. i.e. this will work only with 24 hours single shift working workcenter resources.
These are the Soft contraints which are following by Scheduling Service while generating the Scheduling Result. Optimization Goals in MSO are not strictly following rules when scheduling. They are targets that scheduling engine is trying to achieve while strictly following standard scheduling aspects and Scheduling Rules. As well as the Finite Scheduling Baic Data Page, In MSO Manual scheduling mode Users can overide these goals via Optimization assistant given in Resource Cards of Visual Planning pages as well as the 'Smart Manufacturing Planning Board'.
By enabling this option Scheduling Service will give a higher opportunity to schedule passed due shop orders. This opportunity to schedule will be based on the Number of late days from particular Shop Order Need dates.
By enabling this option Scheduling Service will consider the Setup Matrices in the Finite schedule relevant to Shop Orders which are within the defined Selection Window time period.
- Refer Activity Descriptions for Specify Scheduling Optimization Constraints and Modify Scheduling Optimization Constraints
MSO is natively designed to reduce the Number of Late Orders in either of Scheduling Directions. This helps MSO to achieve timely demand fullfillments as much as possible.
However for passed due shop orders user can give some higher opportunity in the Schedule by enabling Prioratize Passed Due Shop Orders option in Optimization Goals in Finite Scheduling Basic Data. This feature gives a higher opportunity to schedule based on the Lateness of pass-due shop orders.
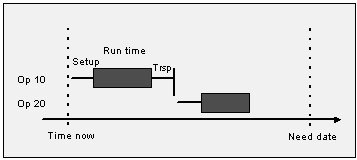
In Forward Scheduling User expects to start production and execute the Demand fullfillment as soon as possible. Forward scheduling means that you schedule the first operation as soon as possible, then the second operation as soon as possible after the first one, etc., until finally, the last operation is scheduled in the same way. With Capacity Constraint scheduling, forward scheduling means as soon as possible when there are materials and resources available. Forward scheduling ensures that the schedule is realistic with respect to all constraints. Forward scheduling means that the scheduled order might not be completed in time. It can also get started unnecessarily early.
In this direction MSO schedule gives the Highest opportunity to EPST(Earliest Possible Start Time) of Shop Order Operations. If EPST is pased at the time of schedule generation then the highest opportunity will be given to current time to start those orders as early as possible.

Figure 1 - Forward scheduling starts from the current date or EPST with the first operation
In Backward Scheduling User expects to start production and execute the Demand fullfillment as late as possible. This is also called Just in time (JIT) manufactuing.Backward scheduling is based on the need date. The work has to be completed before a certain date and time. To ensure that the work is scheduled before that date and time, the last task that ends on the need date is scheduled first, then you can proceed with the second to last, etc., until finally, you reach the first operation. Backward scheduling ensures that the order is completed on time and that the order is not started too early. This approach is most commonly used in food, dairy manufacturing or similar wheas the finish product has an expiration date.
In this direction MSO schedule gives the Highest opportunity to LPST (Latest Possible Start Time) of Shop Order Operations. If the LPST already passed at the time of scheduling execution that means the Shop order that particular operation belongs must become tardy so those shop orders may get secondary opportunity over the others to reduce number of late shop orders.
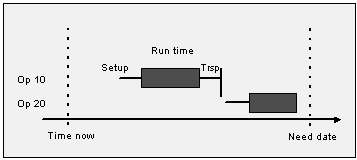
Figure 2 - Backward scheduling starts from the need date of the last operation
Priority Category in Shop Order is the key input to define the Priority of Shop Orders when scheduling in MSO. In Shop Order Priorities Overview user can define a MSO priority score for each priority category. This Priority Score value can be defined as a number from 0 to 10 based on business requirement. Higher scores will get higher opportunity to schedule and they will be pushed towards the EPST or the Need Date based on their scheduling direction. Lower Scores get lower opportunity when scheduling.
Standard or medium priority score is 5. If a priority category is not defined then they also will be considered as MSO priority score 5 and will get similar opportunities to schedule.
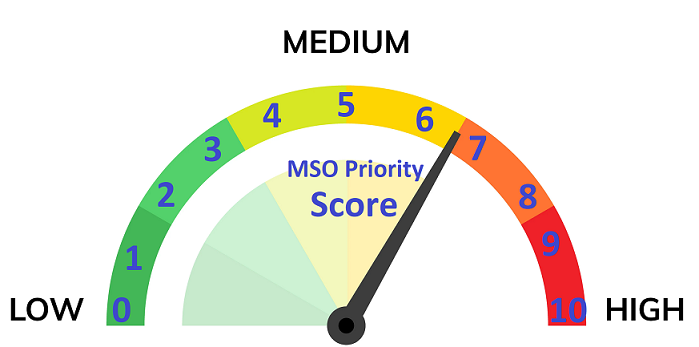
Figure 3 - MSO Priority Scores
Machine Operations and Labor Operations are equaly treated respectively when allocating to resources in MSO.
Natively in MSO architecture it is considering both Machine and Labor operations in similar opportunity when allocating shop order operations. If certain shop order operation has both machine and labor hours defined scheduling service consider that as a single booking that is required to schedule together consuming the same time.
If machine hours and labor hours are not equal in a shop order operation then MSO always will consider the Largest hours load required operation (i.e. machine or labor) to set a base duration and allocate it in full capacity (i.e. 100% capacity). Then the lower hours load will be allocated for the same duration with a partial capacity booking based on the Load difference. This is considered similarly for both Setup & Run operations seperately.
Example:-
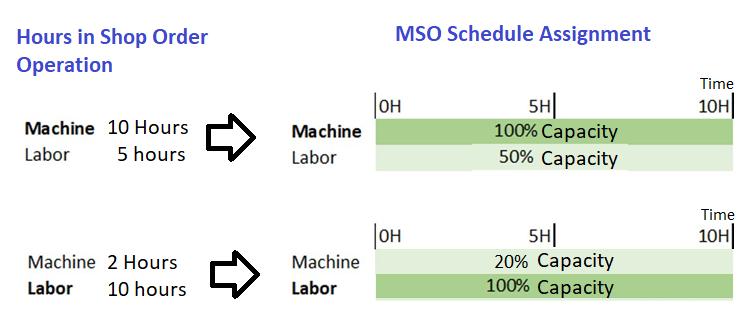
Figure 4 - Machine Or Labor; Largest time consuming constraint centric scheduling
When there are alternative resources, e.g., two or more resources in a work center, multiple persons and multiple tools, a preference must be made regarding the resources if it is required to load a single resource. Otherwise MSO would provide the most suitable schedule position in the Time line and will make a schedule result using a combination of resources based on their availabilty in respective work time calendars and also based on the Scheduling direction of Shop Order.
MSO will not use number of resources to perform a single labor or machine or tool operation. Example: If the labor Operation is 8 hours and Both Alain and Alex are in same respective labor class and Alain is working on morning shift (8.00AM to 12.00PM) and Aex is working (1.00PM to 5.00PM). In this situation MSO will not use both Alain and Alex to perform this operation. If Alain starts it Alain has to finish it consuming two days.MSO will always forcus on single resource assignment for a single operation.
If there is any partial operation report is done then the Same reported resource will be planned to do the remaining part of the operation.
If there any tools connected to Shop Order Operation then required quantity of tool instances also will be booked for full shop order operation duration. Tools availability also will be planned based on their respective calendars.
Infinite Workcenter resources will be considered as a single resource with unlimited capacity unless if there is any resource prefference. In case more than one infinite resource is available to choose from (e.g Infinite work center has 10 work center resources available), then MSO will give priority to primary resource when scheduling the operations. Functional thinking made on this approach is if a particular resource has an infinite capacity then there is no use of distributing loads on multiple infinite capacity machines. Using a single machine may help to reduce the carbon footprint, energy, etc.. This limited load distribution mechanism is natively supporting in MSO when scheduling the Operations.
If there is any partial operation report is done then the Same reported resource will be planned to do the remaining part of the operation.
For Infinite Capacity tools will also be considered in similar design thinking using this limited load distribution mechanism.
For Infinite Capacity labor persons number of simultaneous operations per person is limited to 10 numbers of maximum with a different thinking to reduce the number of simulatenuos load that can handle by a single person even he/she is defined as infinite. If it is neccesary this number can be changed by customization.
Resource Share given in Resource Share column in Shop Order Operation is considered by MSO when scheduling. This resource capacity share will be applied to resource capacity balance resulted from labor & machine capacity allocation as described under Machine & Labor Operations Scheduling section above.
Limitation - Part charactersitics based Setup Matrices will not be considered when scheduling together with resource share. In such situation resource share will be applied without sequencing based on different characteristics.
Decimal values given in labor Setup & labor Run crew size columns also will be considered to set partial capacity booking when scheduling in MSO. This resource capacity share also will be applied to resource capacity balance resulted from labor & machine capacity allocation as described under Machine & Labor Operations Scheduling section above.
Efficiency given in Shop Order Operations is considered when scheduling with MSO
The operation efficiency affects only the run time, not the setup time. When operation efficiency is set to less than 100% (default value) the remaining run time for machine and labor will be increased. This will result in an increased value for remaining manufacturing hours which could affect the scheduled start and/or stop date of the operation. When changing the operation efficiency, the change will also affect the standard cost of the operation. Changing the operation efficiency can be done on specific operations, if there is running-in periods for a while, which temporarily will affect the performance of the operation.
Efficiency given in Work center resource is considered.
The resource efficiency affects both run time and set up time. If the resource efficiency is less than 100% (default value), the operation will be scheduled during a longer time period, because the set up and run time will increase. Only scheduling is affected (start and finish date on the operation), not remaining manufacturing hours. Changing resource efficiency can be done if there are different machines (resources) operating in the same work center with different capabilities.
Limitation - When scheduling operations simultaneously MSO scheduling service will not follow the effeciency of the Dependent operations. This may affect simultanious labor & machine scheduling. i.e. Allocations of persons will not adapt the efficiency of machine resource so if machine efficiency is 50% and machine hour duration in 5 hours then machine will be booked for 10 hours. But even they are started together the Labor assingment will be ended in 5 hours.
Preffered Resource information will be considered as a preference when scheduling. If it is required to consider the preference as a hard constraint for MSO that also can be set by customization.
Transport time will be considered when scheduling with MSO scheduling service.
If two operations are parallel, it means that they can be done totally independent of each other. The MSO scheduling logic tries to schedule them so their output reaches the succeeding operation simultaneously.
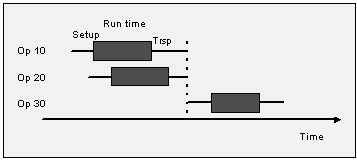
Figure 5 - Operations 10 and 20 are scheduled parallel
Operation Overlap will be considered when scheduling with MSO scheduling service.
Refer About Decription for Operation Overlap
A part's availability can be defined as Infinite, Finite (within a specific lead time), or Always Finite.
The parts with infinite availability do not constrain the schedule. For parts with finite availability, MSO checks for the required amount as it schedules.
The required amount can be comprised of an existing supply or from a new supply within the part's lead time. After the part's lead time, MSO assumes the part has infinite availability. For parts that always have finite availability, the required amount needs to be available to schedule an operation. As MSO schedules, it records the quantity and the date and time at which the material is consumed and produced.
Within the Scheduling horizon MSO is capable of planning the Finite material supplies coming from other shop orders for child semi-assembled parts and account it when scheduling the Shop Orders of final assemblies. This mechanism may provide vast advantages to users who are not using complex order structures like DOP and still they may able to plan finite material supplies coming from their own sub assemblies.
Obstructive maintainance tasks of manufacturing resource objects will be considered when scheduling with MSO scheduling service. MSO will consider the actual Work Task as a hard constraint that is booked for a defined time period from Planned Start to Planned Finish in the Work task. Remaining available time will be used for the Scheduling of shop order operations.
Note:- Maintainance Import is not a must to consider work tasks for MSO Finite scheduling since this is directly refereing the Work tasks from Maintainance management. Manually created maintainance tasks as Resource Breaks will not be considered for the MSO finite schedule.
Smart Manufacturing Planning Board is the Interactive scheduling tool designed to plan and schedule with MSO.
This will automatically enabled for all MSO dataset enabled sites. In this client planner can move, drag and drop or manually fix any operation that required to adjust based on any business requirement. The scheduling status of MSO scheduling service, accepted schedule quality and scheduled time is shown here.
User needs to enable the Insert Mode in the client to do adjustments of shop order operations. All manually made changes will be registered and applied to finite schedule of the Site upon the execution of finite schedule option given in the Board. This page can be accessed by different users in the same time and the schedule changes made by each user will be applied and updated into the finite schedule in the Site based on-demand latest change latest apply basis.
The Resource Gant chart can be used to view and adjust the allocations and also can be used to change the Workcenter or labor class assignements as a standalone tool that is designed to simplify the Work of a Manufacturing planner. Scheduling Status 'Fixed' can be set for operations using this client. 'Fixed' state operations are committed operations with time and resource assignment which are not moving with finite schduling adjustments performing by MSO. All Fixed and moved operations in the Gant will be applied upon the Finite Schedule action given in the Gant. That may clear the Unsaved Fixed Orders list as well.
By performing an Infinite schedule action User always can reset a shop order to initial state. In the Gant view user also can do shop order related changes like shop order operation split, change preffered resource, selective optimization, finite operation block creation, etc..
Note: - Change of preffered resource, shop order operation split will trigger infinite scheduler as standard. In a Automatic scheduling MSO site then this may create a finite schedule automatically. In a Manual scheduling site finite scheduling should be manually done in order to apply the modification into finite schedule.