IFS Signature Service¶
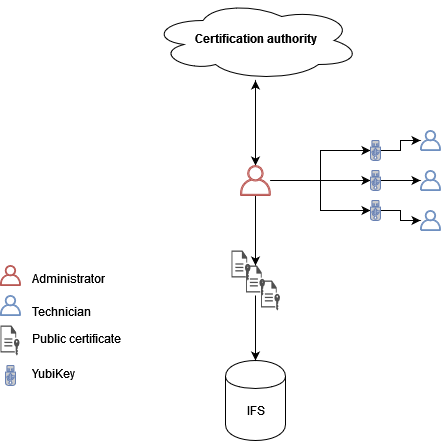
The IFS Signature Service enables a technician to sign a document after work is complete. The signature is stored and associated with the document.
With the IFS Signature Service, the organization is allowed to hand out flashed YubiKeys to their end users which contain the private and public key pair needed to sign documents.
The process of creating/ordering certificates and preparing the YubiKeys is outside of the scope for this document. Therefore, make sure to read the requirements first.
Overview¶
Preparation¶
Before an end user can start signing documents, an administrator needs to create or order certificates tailored specifically for the end user. Once the certificate signing requests have been approved, they can be flashed into a YubiKey and handed out to the end user. The certificates also must be registered before they can be used. The root and intermediate certificates might need to be registered and the user's public certificate must be mapped to the designated end user.
Signing¶
When the end user is ready to sign, the document is uploaded along with a meta document (json) and the user is prompted to sign using the YubiKey. The meta document is uploaded for verification purposes. The signature is then uploaded and verified together with the documents on the server. If the validation is successful, the signature is stored in association with the uploaded documents.

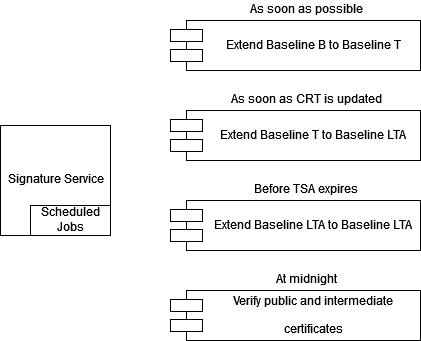
Extending¶
Once a document has been signed it needs to be extended in order to preserve its integrity. All documents are initially stored as Baseline-B and the server will attempt to extend it to Baseline-T as soon as possible. This means that a timestamp is added to the signature. When the documents have been extended to Baseline-T, the server attempts to extend to Baseline-LTA as soon as the certificate's revocation data has been updated and it can be certain that the document has not been signed with a revoked certificate. Documents using Baseline-LTA are considered valid for a long time, but need to be re-sealed before the Timestamp Server expires (which can be ten years into the future).