IFS Data Synchronization provides the framework runtime, configuration and monitoring support to synchronize business data and transactional data between a central installation (hub) and one or more satellite installations. Typically, IFS Data Synchronization is to be introduced when different sites will be physically separated in different installations where each site should be able to process transactions on its own without connecting to the hub. Data is rather synchronized with the hub when the communication link becomes available.
Each satellite installation is mapped to a single site or group of sites and hold data specific to the mapped site. Hub database hold data for all the sites. Synchronization of data between satellite and hub is done using IFS Connect messaging.
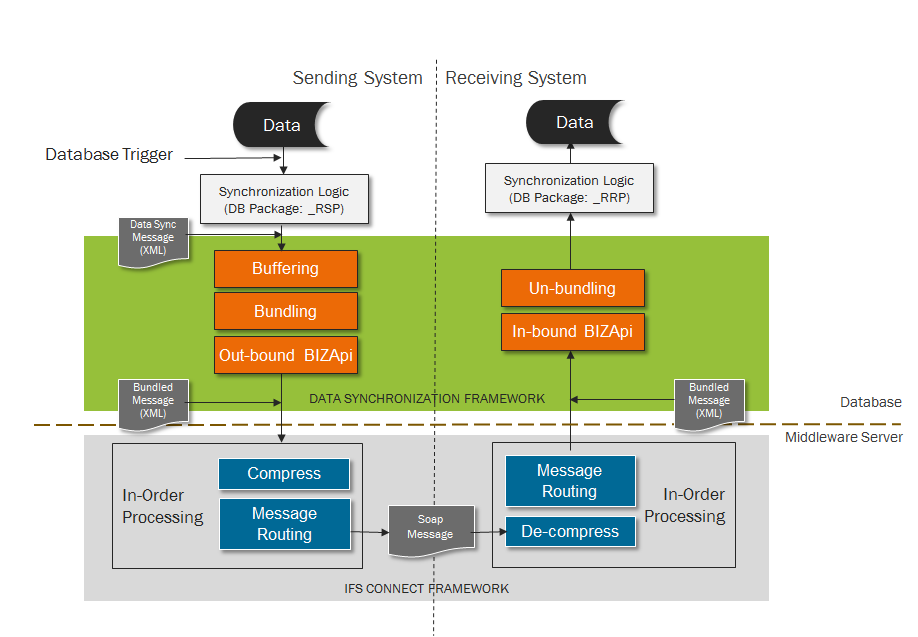
Data Synchronization process flow : When a particular entity needs to be synchronized among hub and satellite installations, code is generated using IFS Developer Studio that will generate the necessary code which will automate this process. A trigger is generated and deployed in the database for the entity. This will be fired when new, modify or delete actions are performed on the entity. This in turn will call the PL/SQL package Lu_Name_RSP. This Lu_Name_RSP is generated when Data Synchronization code is generated. The PL/SQL procedure will create a data synchronization message which will have the new attribute string and the old attribute string for that record. This message will be inserted into a buffer table. For each site a background job is launched which will read the buffer table and gather the messages that belong to a single site into one bundled message. The frequency with which the background job will execute, the length of time the job will run and the size of the bundled message is configurable.
After creating a message bundle an outbound bizapi is called. At this time an application message that encapsulates the bundled message will be inserted into fndcn_application_message_tab. The application message will have a batch processor queue assigned to it based on the site the data should be send to. This batch processor queue will be a Unit of Order queue which means messages are ordered within the queue and processed sequentially in the order that they are generated. The batch processor will process the routing rule that is assigned to the application message. The routing rule has a destination address which is the Application server access point of the destination that the message should be sent to. The HTTP Sender will be used to send the application message to the intended site. Once this is successful the application message will be marked as "Finished". This is the data synchronization message sending process.
The message will be received by the Soap Gateway of the receiving site. An application message is created for the message and a routing rule is picked based on the message attributes. This will assign a batch processor queue to the message. This queue will also be a Unit of Order queue because messages need to be processed in sequence that they are received. After the application message is created the batch processor will start processing the application message based on the routing rule. The destination of this routing rule is an inbound BizApi, The BizApi will call a PLSQL process that will start processing the bundled message. Each message in the message bundle is processed and based on the action (new, modify or delete) that should be performed a PL/SQL method in the Lu_Name_RRP package is called. The Lu_Name_RRP package is generated when data synchronization code is generated for the entity. When actions are performed on the receive side the standard validations are not performed. Only the referential integrity is checked. This is the flow at the receive side of Data Synchronization process.
Bundled XML Message: An example of the bundled XML message is shown
below.
Large Objects (LOB) Synchronization: If a particular entity contains a LOB column the synchronization of the value in the LOB column will take place separately. This measure is taken to ensure that system resources such as network bandwidth is not hogged by synchronization messages that have LOB data. If the synchronized entity contains a LOB column, that LOB value is inserted into a separate buffer table. A separate database task (Send LOB Data) can be scheduled to process the LOB buffer table. This task can be scheduled such that it does not interfere with standard data synchronization process. The task will gather the LOBs in the LOB buffer table and execute an outbound BizApi. There are two outbound BizApis, one to synchronize CLOB data and one to synchronize BLOB data. The BizApi will call a PLSQL procedure to generate the actual synchronization message. An application message will be inserted to fndcn_application_message_tab with a message queue which is determined by the routing rule. For each site there will be a separate queue for CLOB and BLOB synchronization. The bundled message will be sent to the destination given by the routing rule. A separate routing address is available for LOB replication. The destination Application server access point which is the IP Address of this routing address can be configured to use a separate port other than the one used by the standard synchronization data. Using this two port mechanism network resources can be optimally utilized between standard data synchronization and LOB data synchronization.
Note : This means that an entity that has LOB columns will post an additional message for it's LOB data (i.e. There will be two bundled messages). The entity will not be completely synchronized until the scheduled job Send_LOB_Data has been executed.
Base profiles and Quick reports are two functional areas where LOB columns are used.
Since they are Foundation1 concepts synchronization of these objects are enabled
in the Data Synchronization framework.
Synchronization of Data in Custom Fields and Custom Logical Units: Framework methods for synchronizing data in custom fields are generated in CFP packages. But, these methods are deployed to the databases where FNDRPL module is installed. These methods support to synchronize any type of data in persistent custom fields. If a particular entity is enabled for Data Synchronization, then data in custom fields of that particular LU can be synchronized.
Framework methods for synchronizing data in custom Logical Units are generated in CLP packages. But, these methods are also deployed to the databases where FNDRPL module is installed. These methods support to synchronize data in any type of custom attributes in particular Custom Logical Unit. Custom logical units are always synchronized to all satellites and both ways.
Transaction Based Message Bundling: For each site a background job is launched which will read the buffer table and gather the messages that belong to a particular transaction for that site, into one bundled message. Hence, Transaction ID is the main considerable factor, when bundling messages created per each operation. When bundling messages, it considers below factors.
Include all the messages belonging to one transaction into one bundled message, if number of message belongs to that transaction < bundled size
If number of message belonging to that transaction > bundled size, then create multiple bundled messages as suited
If a particular bundle have room to include all the messages of next transaction, then, it includes those messages also into the same bundled message
Broadcasting : There can be data that needs to be synchronized to all the sites. This is handled by the synchronization data broadcasting mechanism. A code generation property DbReplicationBroadcasting is set to true to enable broadcasting. Once this property is enabled, modifications done for the entity will be first send to the Hub from the originating Satellite. Then HUB will resend the synchronization message to the other Sattelites but will not send it back again to the originating site. Performing broadcasting this way is necessary because of the Star Topology of the Data Synchronization architecture.
IFSSYNC user FND_SYNC, FND_SYNCADMIN permission sets: A new user IFSSYNC
is introduced who is used to perform all Data Synchronization related work.
IFSSYNC user has the impersonate user capabilities because sometimes it will be
required to impersonate as another user at receive side. The permission set
assigned to IFSSYNC is FND_SYNC.
The permission set FND_SYNCADMIN has the grants necessary to perform all administration work related to Data Synchronization. Read more about this topic here.
Data Synchronization is not implemented for all Foundation1 concepts in core. Only the data related to following Foundation1 concepts are synchronized:
User passwords
Users & Permission Sets
Base profiles
Quick Reports
Application Configuration Packages with Custom Objects
Database Tasks
ToDo tasks
FND Notes
Object Connections