Applying Service Updates¶
Related Pages¶
- Developing with Dev-Studio
- Working with GIT
- Working with pull requests
- IFS Update Analyzer section of the Development Guide
Overview¶
This section describes the apply service update process in Release Update Studio. The applying service updates to release update studio process is almost similar to the Apply service update to Build Place process. There are minor differences specifically on the Impact Analysis process and working branch which are clearly described in this documentation.
Prerequisites¶
-
Release update is applied to customer-solution repository
-
A successful sanity build has been run after applying the release update to customer-solution repository and at least one successful sanity tag exists for the new release update
-
IFS Update Analyzer downloaded and installed on the users' workstation. The tool can be downloaded from the IFS Developer Portal.
Fetching a Service Update to the Release Update Studio - 22R2 & Beyond¶
There are three main steps when taking a service update to a Release Update Studio.
step 1: Apply service update to customer-baseline repository
step 2: Impact Analysis for new customer-baseline repository version
step 3: Apply service update to customer-solution repository
-
Apply Service Update to Customer Baseline Repository¶
Follow the below steps to fetch a service update to Customer Baseline repository.
- Go to IFS Lifecycle Experience portal and navigate to Release Update Studio view.
- Click on button "Service Update" in the Release Update Studio view. (Figure 10.1).

Figure 10.1 - Service Update button The popup dialog box appears when clicked on the service update button may vary, according to the versions of customer-baseline and customer-solution repositories in release update studio and the availability of service updates. There can have four different scenarios when applying a service update to a release update studio according to the two factors mentioned above. They are,
Scenario 1: When the versions of customer baseline and customer solution repositories in release update studio are same and IFS has released a new service update¶
The highlighted path of the following diagram shows the user flow of applying a service update to Customer Baseline repository (Figure 10.2).
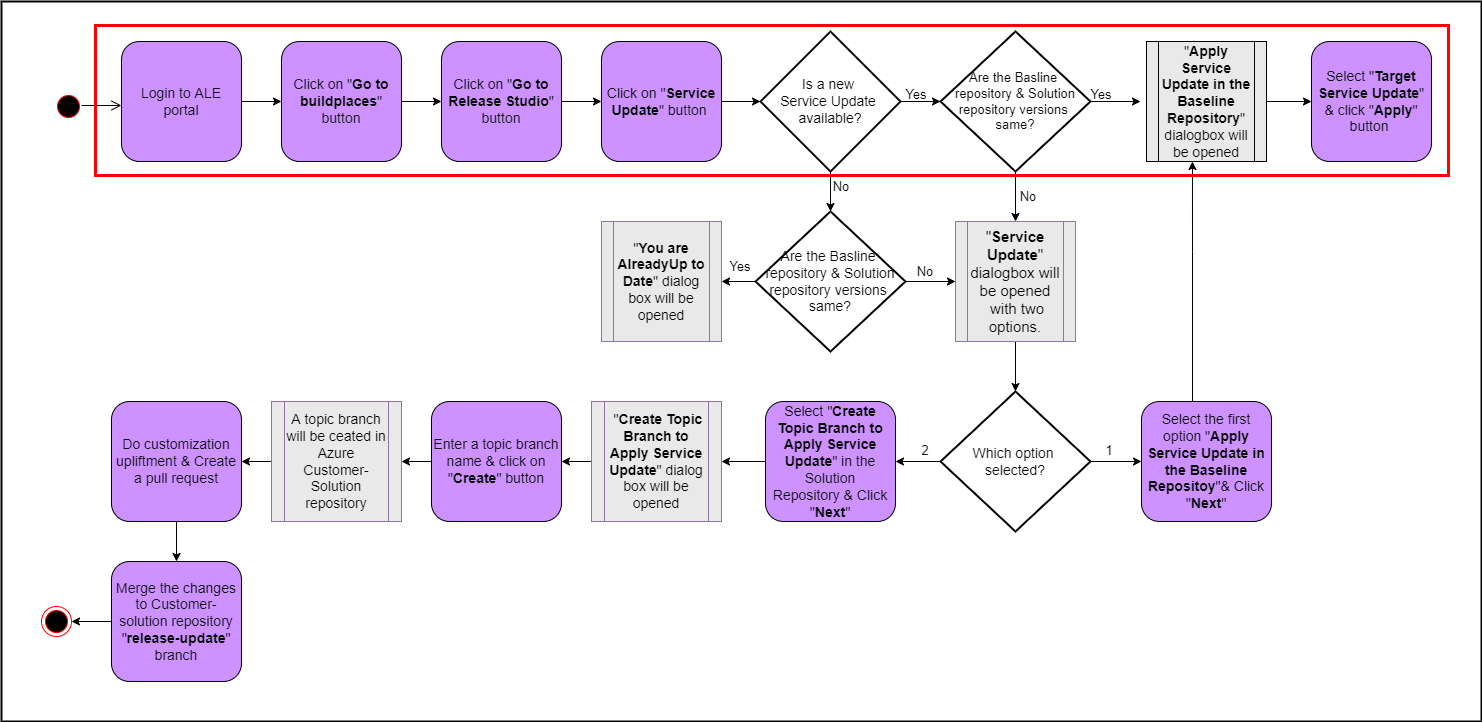
Figure 10.2 - Scenario 1 - User flow of applying a service update to Customer-Baseline repository A sample scenario with the versions of release update studio repositories that matches to this scenario is shown in the below image(Figure 10.3).
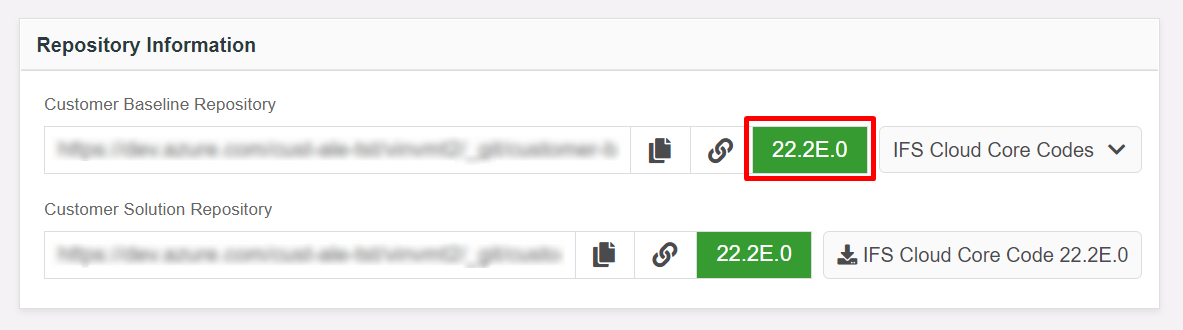
Figure 10.3 - Scenario 1 - Baseline repository version in release update studio before applying a service update - In this scenario, the below dialog-box appears when clicked on the "Service Update" button in the release update studio view (Figure 10.4).
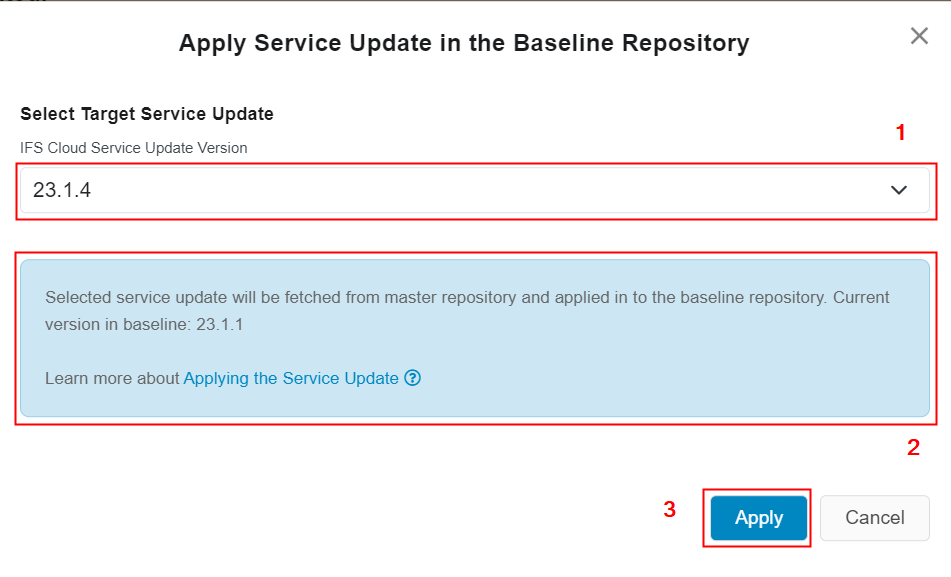
Figure 10.4 - Scenario 1 - Apply service update in the baseline repository popup-box - Select a later service update version from "IFS Cloud Service Update Version" drop-down list[1].
- Information text educates the user about the outcome of clicking the "Apply" button and the text contains the current version of the release update studio's customer-baseline repository as well[2].
- Upon clicking the "Apply" button [3], pipeline will trigger and job table record with the status "Pending" will be added by the pipeline itself. During this process pipeline will start fetching the selected service update to release update studio, customer-baseline repository and a text "Pending" will appear at the text-box allocated for the version (Figure 10.5).
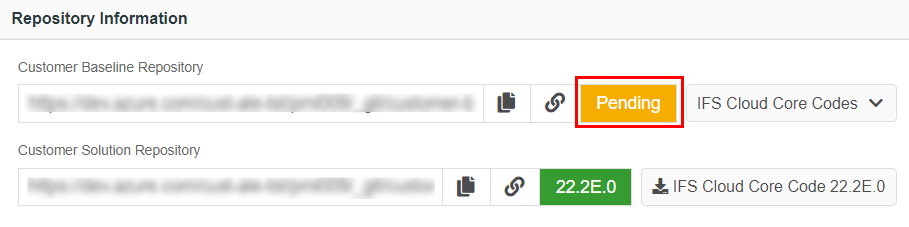
Figure 10.5 - Scenario 1 - Baseline repository in release update studio pending tag -
- Job table record can be viewed by clicking on the "Jobs" button in the top button list in the release update studio view (Figure 10.6).

Figure 10.6 - Jobs button - Once the pipeline run is successful, the customer-baseline repository version displayed in the repository information card will be updated with the new version as below (Figure 10.7).
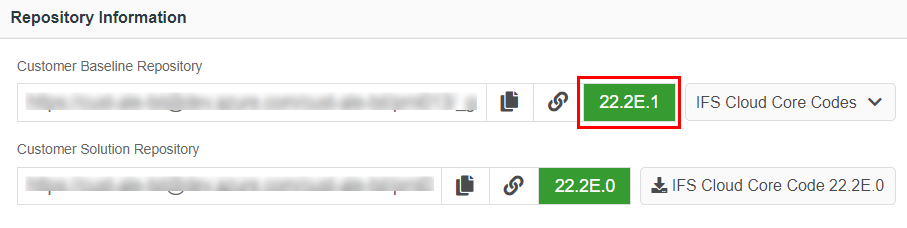
Figure 10.7 - Scenario 1 - Baseline repository version in release update studio after applying a service update Scenario 2: When the versions of customer baseline and customer solution repositories in release update studio are different and IFS has released a new service update¶
The highlighted path of the following diagram shows the user flow of applying a service update to Customer Baseline repository(Figure 10.8).
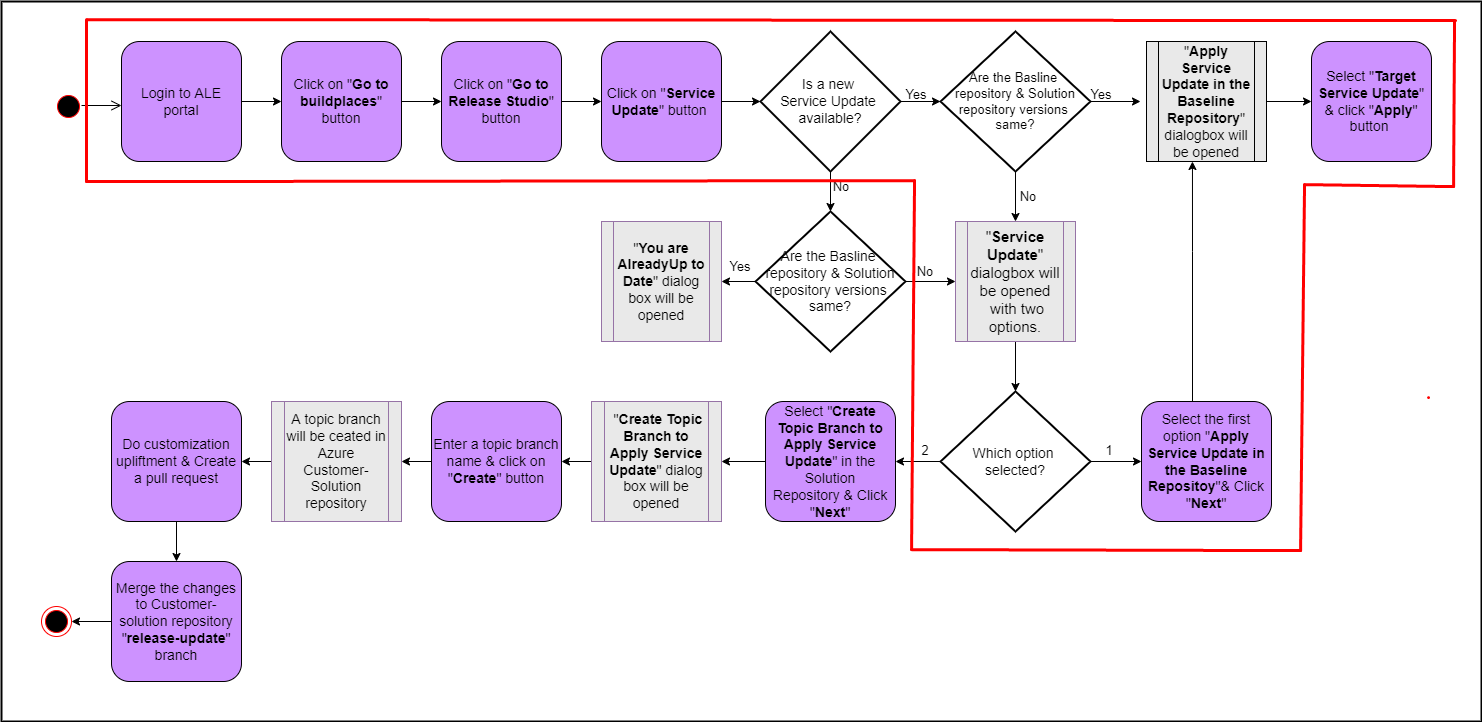
Figure 10.8 - Scenario 2 - User flow of applying a service update to Customer-Baseline repository A sample scenario with the versions of release update studio repositories that matches to this scenario is shown in the below image (Figure 10.9).
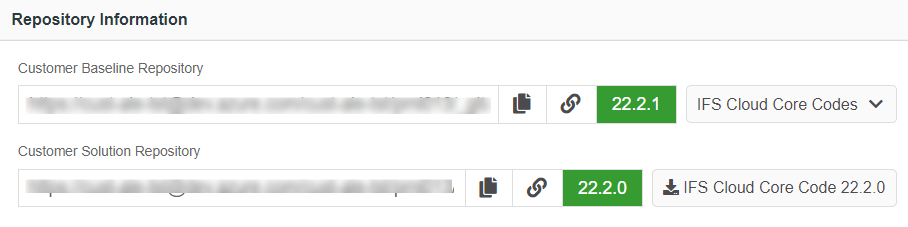
Figure 10.9 - Scenario 2 - Baseline repository version in release update studio after applying a service update - In this scenario, the below dialog-box appears when clicked on the "Service Update" button in the release update studio view (Figure 10.10).
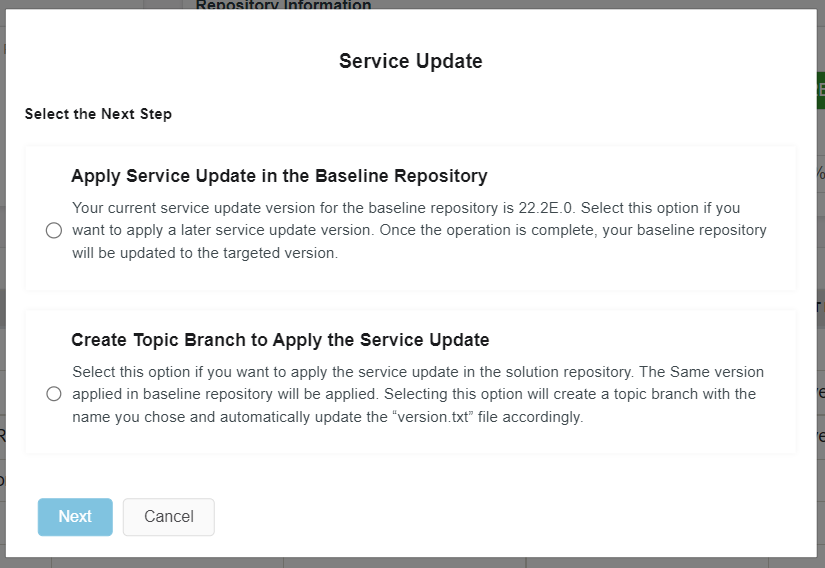
Figure 10.10 - Scenario 2 - Service Update popup-dialog box Initially the "Next" button will be disabled. Upon selecting an option it will be enabled.
-
Choose the first option in the popup-dialogbox to apply a later service update to the baseline repository.
-
Click on the "Next" button to proceed (Figure 10.11).
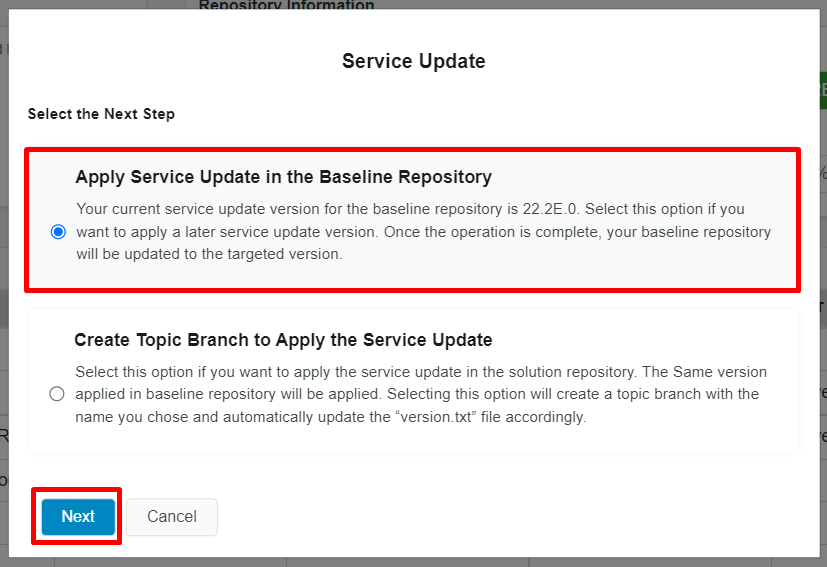
Figure 10.11 - Apply service update in the baseline repository in release update studio -
Once the "Next" button is clicked (Figure 10.11), "Service Update Apply to baseline" dialog box will popup (Figure 10.4).
-
Upon clicking the "Apply"[3] button (Figure 10.4), pipeline will trigger and job table record with the status "Pending" will be added by the pipeline itself. During this process pipeline will start fetching the selected service update to release update studio, customer-baseline repository.
-
Job table record can be viewed by clicking on the "Jobs" button in the top button list in the release update studio view (Figure 10.6).
-
Once the pipeline run is successful, the customer-baseline repository version displays in the repository information card will be updated with the new version as below (Figure 10.12).
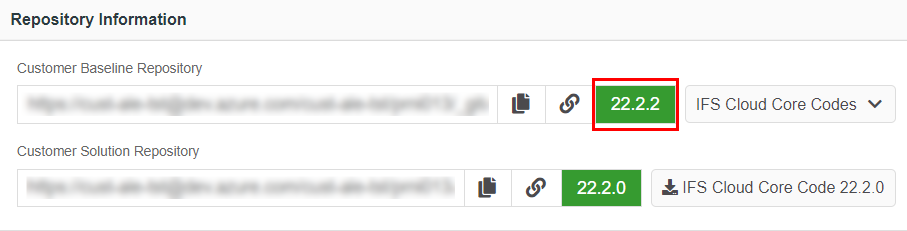
Figure 10.12 - Scenario 2 - Baseline repository version after applying a service update Scenario 3: When the versions of customer baseline and customer solution repositories in release update studio are different and there are no new service updates released by IFS¶
The highlighted path of the following diagram shows the user flow for this scenario (Figure 10.13).
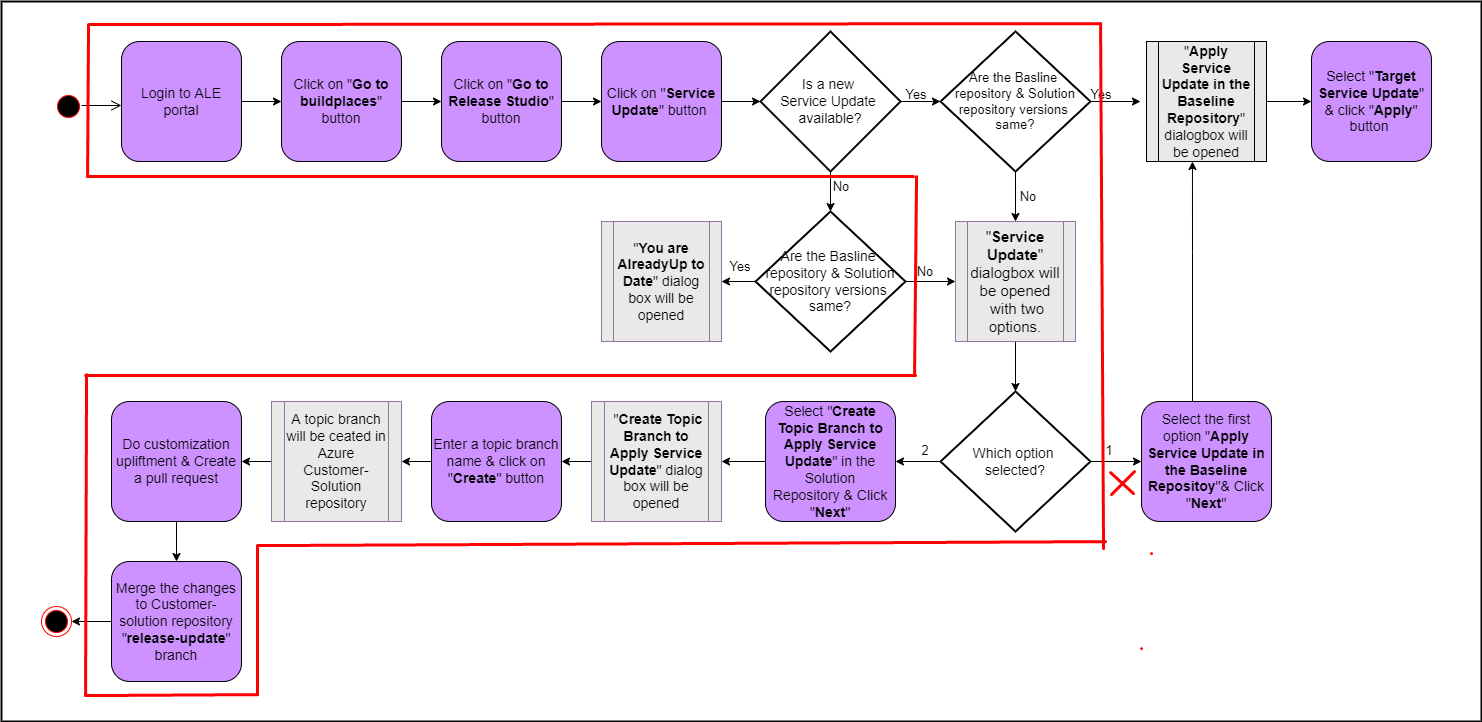
Figure 10.13 - Scenario 3 - User flow of applying a service update to Customer-Solution repository A sample scenario with the versions of release update studio repositories that matches to this scenario is shown in the below image(Figure 10.14).
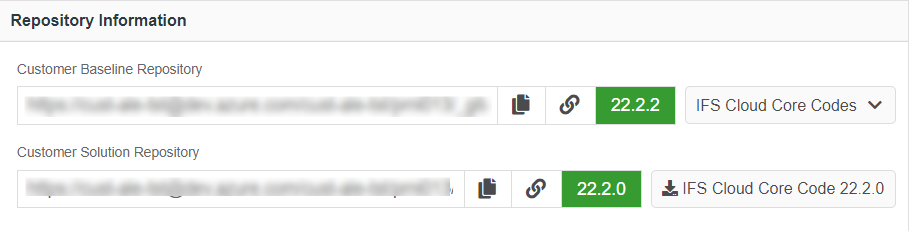
Figure 10.14 - Scenario 3 - Baseline repository version before applying a service update - In this scenario, the below dialogbox appears when clicked on the "Service Update" button in the release update studio view (Figure 10.15).
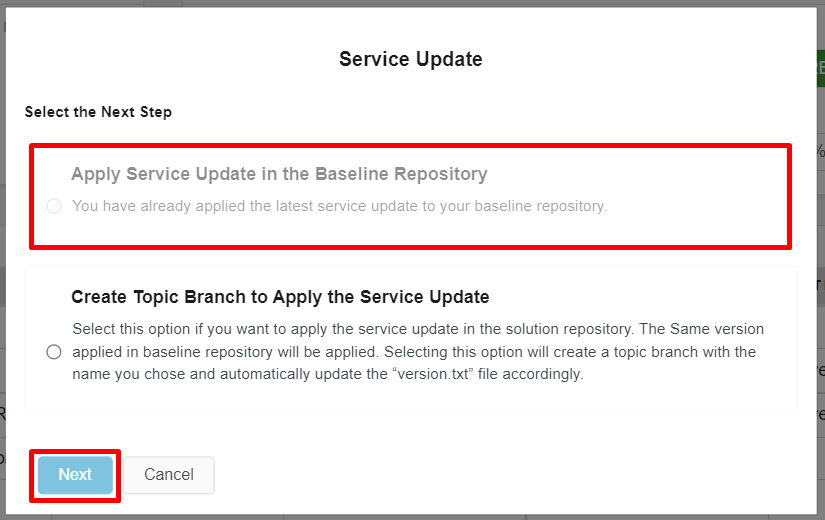
Figure 10.15 - Scenario 3 - Service Update popup-dialog box -
The 1st option ("Apply Service Update in the Baseline Repository") of this dialog-box will be disabled as there are no any later service update version to apply to the baseline repository.
-
Initially "Next" button also will be disabled and it will be enabled upon clicking on a radio button(Figure 10.15).
-
Choose "Create Topic Branch to Apply the Service Update" option, if you want to apply the version in baseline repository of release update studio to current version of the customer solution repository of release update studio(Figure 10.16). For more info: Apply service update to customer-solution repository
Note: Before choosing "Create Topic Branch to Apply the Service Update" option, Impact Analysis should be done. For more info: Impact Analysis for new customer-baseline repository version.
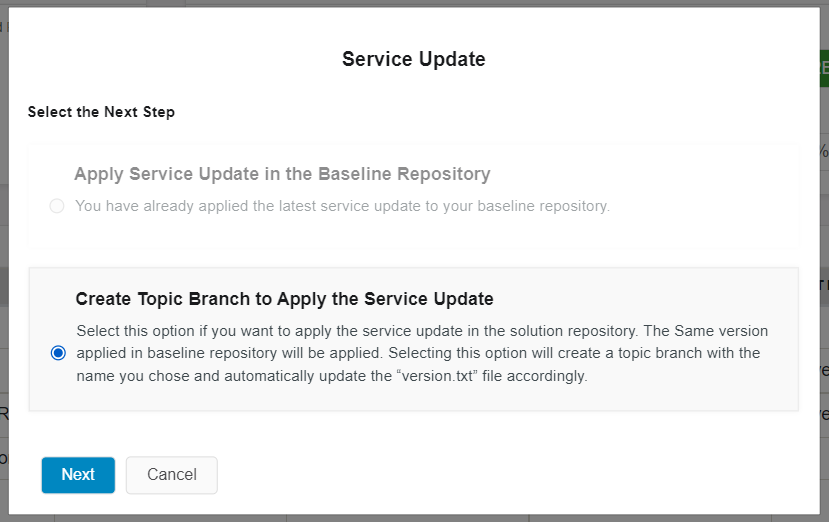
Figure 10.16 - Scenario 3 - Create topic branch to apply the service update Scenario 4: When the versions of customer baseline and customer solution repositories release update studio are same and there are no new service updates released by IFS¶
The highlighted path of the following diagram shows the user flow for this scenario (Figure 10.17).
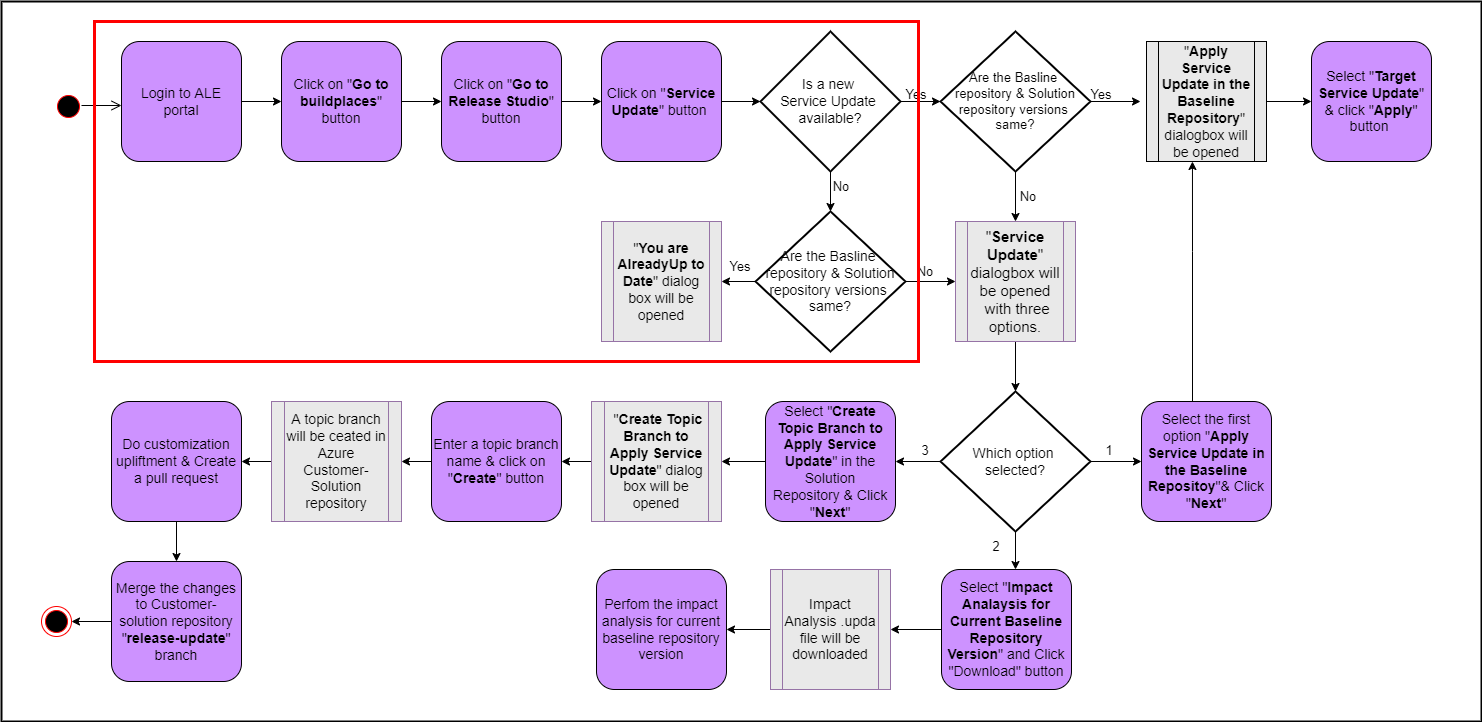
Figure 10.17 - Scenario 4 - User flow for already up-to-date user A sample scenario with the versions of release update studio repositories that matches to this scenario is shown in the below image (Figure 10.18).
Figure 10.18 - Scenario 4 - Create topic branch to apply the service update In this scenario, the below dialog-box appears when clicked on the "Service Update" button in the release update studio view (Figure 10.19).
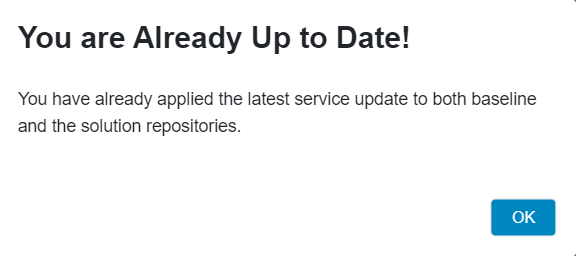
Figure 10.19 - Scenario 4 - Already up-to-date popup-dialogbox -
Impact Analysis for New Customer Baseline Repository Version¶
This is the second main step in the process of applying a service update to the release update studio. After the Customer Baseline repository has been updated with the service update, the Update Analyzer tool can be used to analyze the impacts of fetching this update to the Customer Solution which contain the customizations. To do this, follow the below steps;
- Click on the "Impact Analysis" button in the release update studio view (Figure 10.20).

Figure 10.20 - Impact analysis option in Service Update popup-dialogbox - Once clicked on the "Impact Analysis" button a file with ".upda" extension will be downloaded within two-three seconds to user's download folder.
Note: To do the impact analysis, Update Analyzer tool needs to be installed in the user's machine. Please refer Update Analyzer Installation Steps provided in the Development Guide to find the step-by-step guide on how to install the Update Analyzer tool.
-
On a machine which has pre-installed Update Analyzer, the file can be opened by double-clicking or by selecting the option “Open with Update Analyzer”.
-
The file will then open in Update Analyzer and will start cloning the repositories and will then run the impact analysis (Figure 10.21). The process will continue for approximately 5-15 minutes and complete.
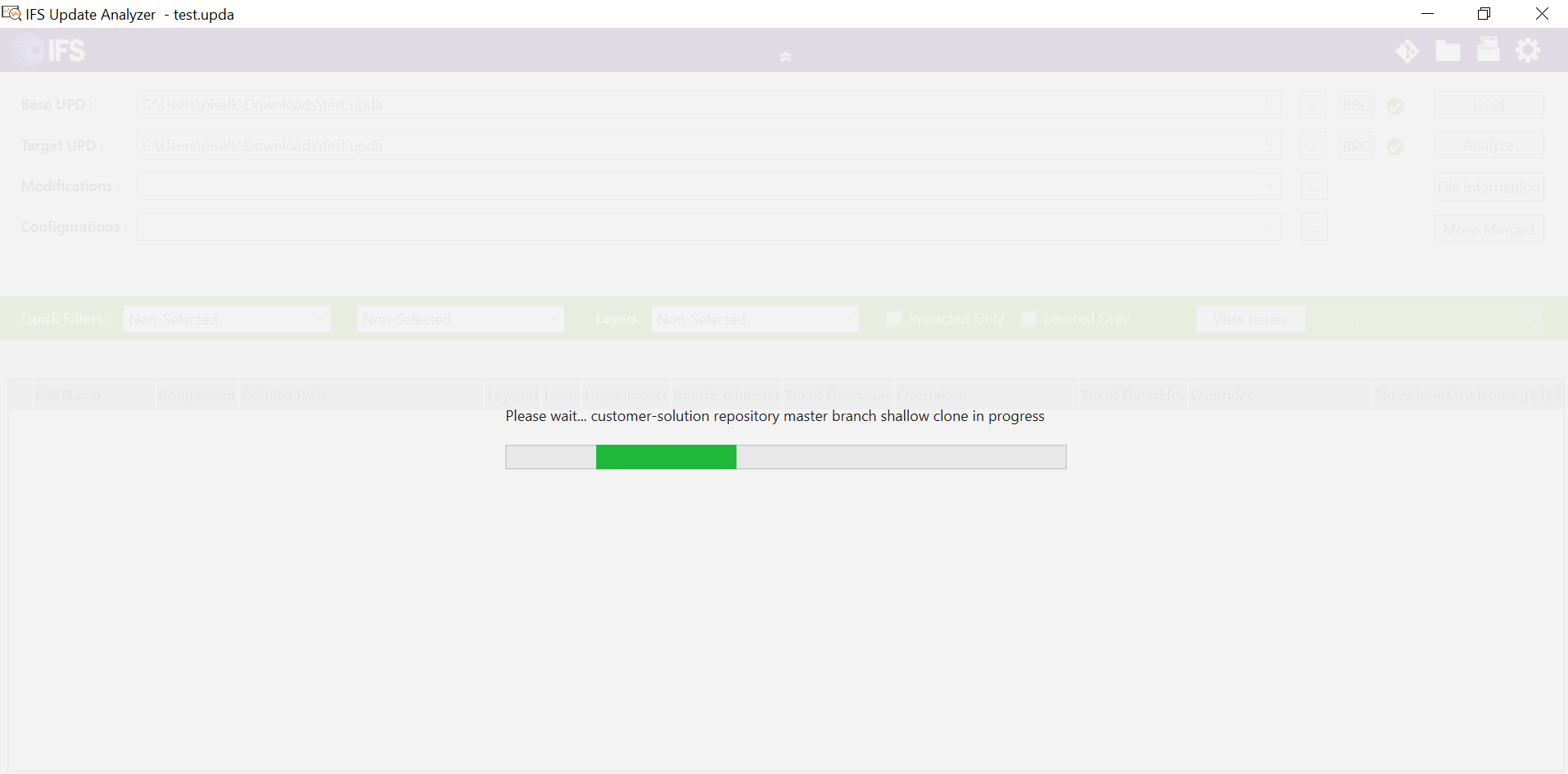
Figure 10.21 - Already up-to-date popup-dialogbox - At the completion of the analysis, a report will be generated with an overview of layer impacts, categorized by the severity of the impacted files as high, low, no, and unknown files (Figure 10.22).
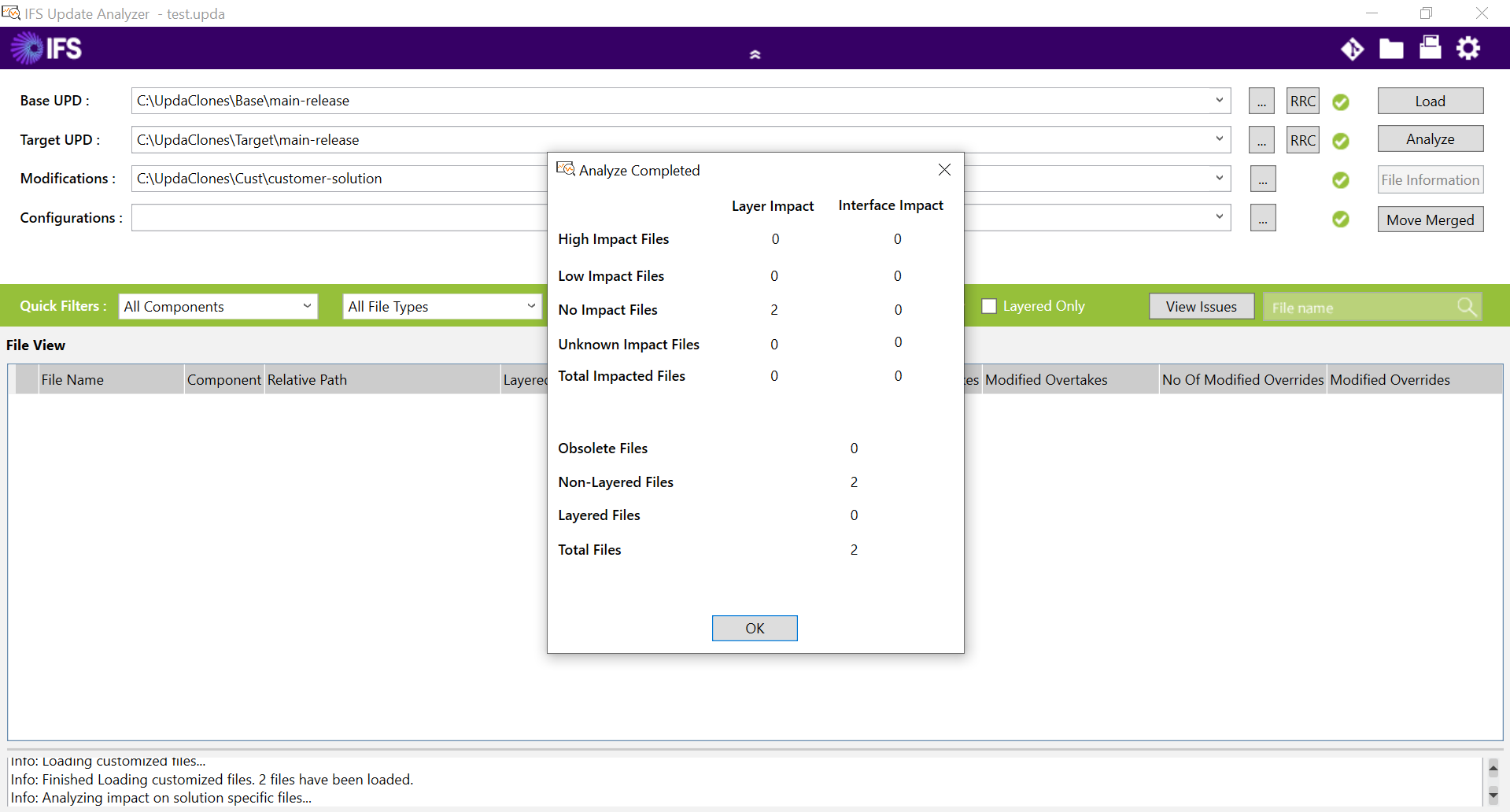
Figure 10.22 - Overview of the impacts shown in Update Analyzer Further, by clicking on one of the rows, a detailed diff analysis of those files can be viewed. For further details: For more info refer the Update Analyzer Analyzing Impacts section of the Development Guide in the Technical Documentation.
-
Continue from Apply service update to customer-solution repository
-
Apply Service Update to Customer Solution Repository¶
This is the third main step in the process of applying a service update to the release update studio. After the impact of the service update to the customizations has been identified by the impact analysis step, it is possible to apply the service update to customer solution repository "relese-update" branch. To do this, follow the below steps;
-
Click on the "Service Update" button in the release update studio view (Figure 10.1).
-
Then the select the second option in the popup-dialogbox as in the below image (Figure 10.23).
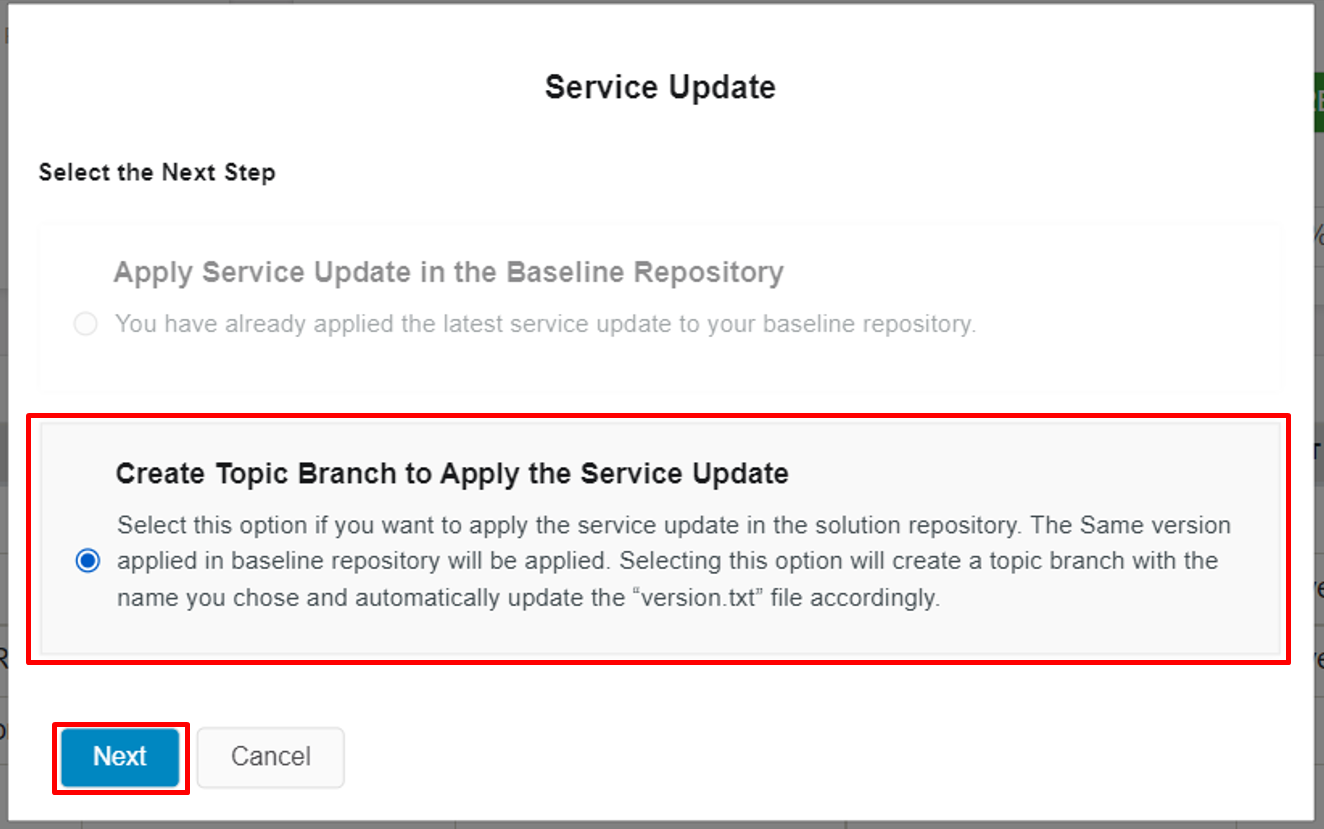
Figure 10.23 - Create topic branch to apply the service update option - Upon clicking the "Next" button a dialogbox will be poped-up (Figure 10.24).
The purpose of having this popup-dialogbox is to get the topic branch name for the automation pipeline as an input, to commit the new version.txt file as the automation pipeline has partially automated the merging of version.txt file to the customer-solution repository,"relese-update" branch during a service update. Thereafter, the above created topic branch should use for the customization upliftment process.
- If the topic branch name generated already exists in the Customer Solution Azure Repository, the following text that is marked in red[1] will be displayed and the Create[2] button will be disabled (Figure 10.24).
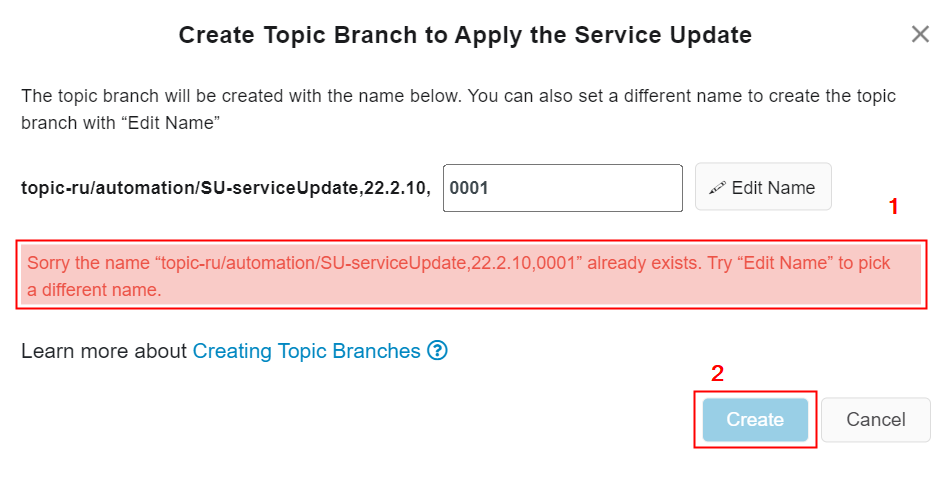
Figure 10.24 - When the default branch name already exists in the repository - There is a text to educate user that the topic branch will be created with the name shown in the popup dialog box (Figure 10.25).
- As in the above image, the topic branch name will be "topic/automation/SU-service-update.22.2.1,0001" [1,2].
- "Edit Name" button can be used to edit the placeholder[2] of the generated topic branch name which is a unique, generated number.
- Topic branch name placeholder field[2] keeps disabled until the "Edit Name" button is clicked[3].
- By clicking on the "Edit Name" button, it is possible to edit the generated number if it is required[3].
Note: However, editing the autogenerated branch name is optional. If the user want to create the branch name in a user specific way, then the "Edit Name" option can be used. However, autogenerated branch name is unique for each user.
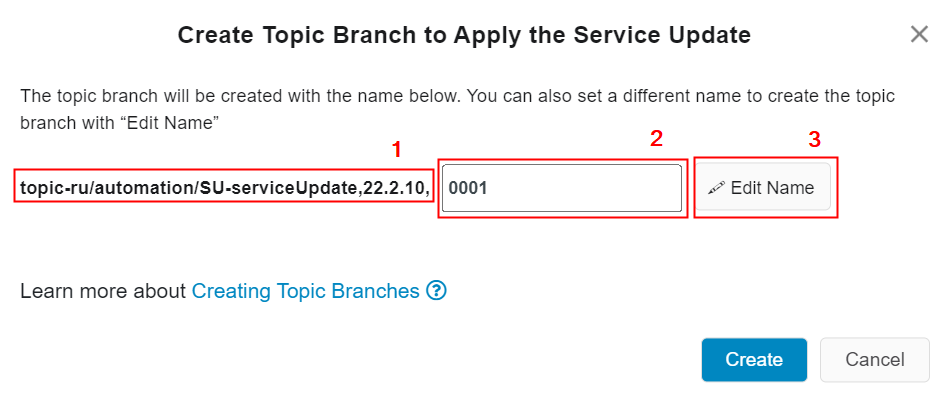
Figure 10.25 - Create topic branch to apply the service update option - When the suffix of the topic branch name is changed[1],
- the "Edit Name" button text turns to "Check"[2].
- the "Create" button gets disabled.
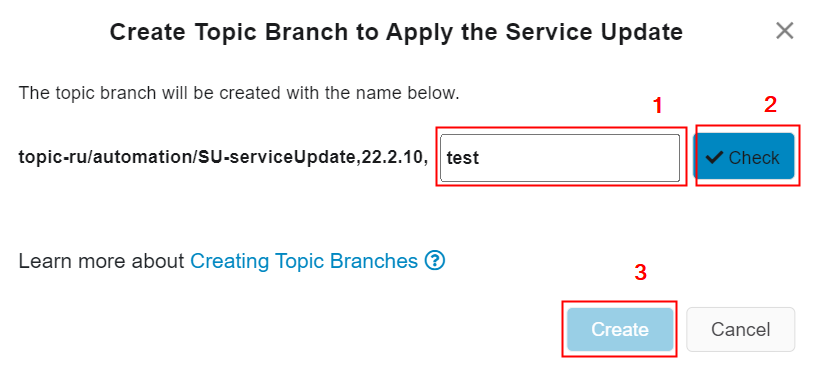
Figure 10.26 - Create topic branch to apply the service update option By clicking on the "Check" button, it is possible to check if the auto-generated branch name already exists in the customer solution azure project repository. If the branch is already exists in the user's customer solution azure repository it is not possible for the automation pipeline to create the topic branch. - Click the "Check" button. During the time of checking the existence of the edited topic branch name, - An information text highlighted in yellow colour will be visible above the buttons as in the below image (Figure 10.27) - The "Check" button turns to a spinner (Figure 10.27)
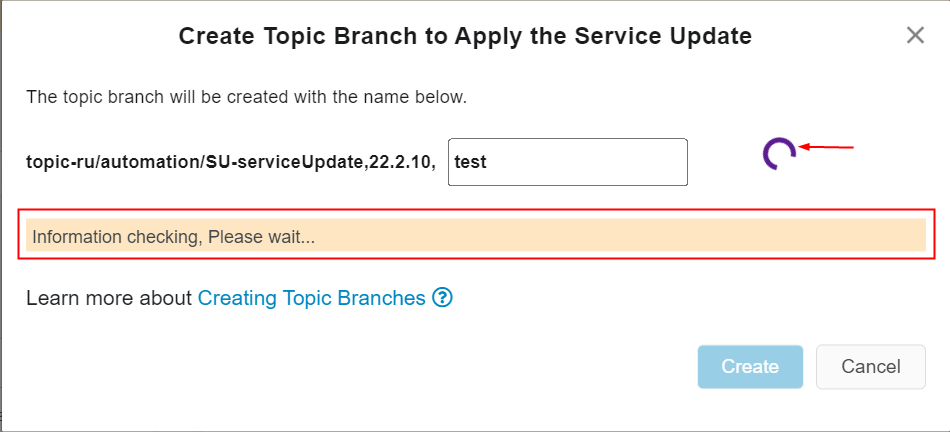
Figure 10.27 - Checking updated topic branch name - Upon the completion of checking the existence of the updated branch name, if the updated branch name not exists in the customer solution Azure repository (Figure 10.28),
- a text highlighted in green colour[2] will be appeared
- "Check" button also gets disables unless branch name is not changed[1]
- The "Create" button gets enabled[3]
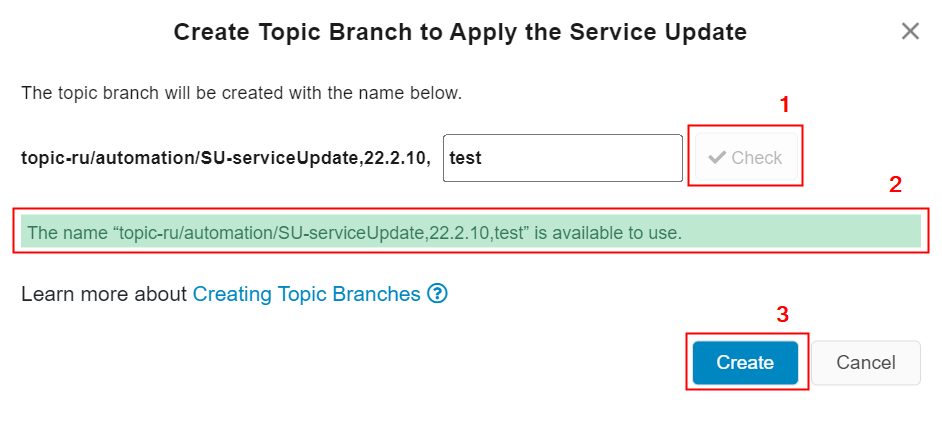
Figure 10.28- Valid topic branch name -
Upon the completion of checking the existence of the updated branch name, if the updated branch name already exists in the customer solution azure repository (Figure 10.29),
-
A text highlighted in red colour[2] will be appeared
- "Check" button also gets disables unless branch name is not changed[1]
- The "Create" button keeps disabled[3].
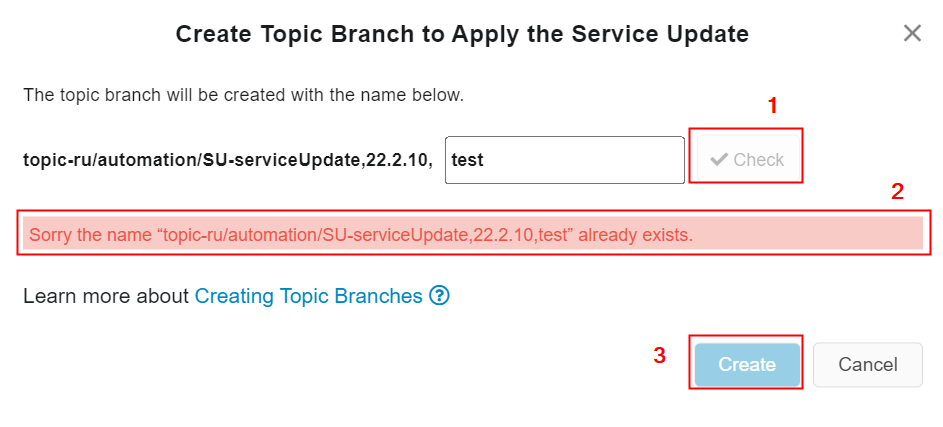
Figure 10.29 - Already existing topic branch name - If the user gets the above output, try using a different branch name by changing the suffix of the branch name.
-
If the user gets the output shown in the Figure 10.28, click on the "Create" button to proceed.
-
At this point a job table record will be created for the topic branch creation by the automation pipeline. Job records can be viewed by navigating to the jobs view by clicking on the "Jobs" button (Figure 10.6).
-
Once the topic branch creation pipeline is success, a success toast message will appear otherwise it will show a failure toast.
-
At this point the automation pipeline has created a topic branch in the customer solution repository with the name specified and has been pushed the new version.txt file to the branch.
-
Branch details can be seen by going to the customer solution Azure repository by clicking on the link icon (Figure 10.30)
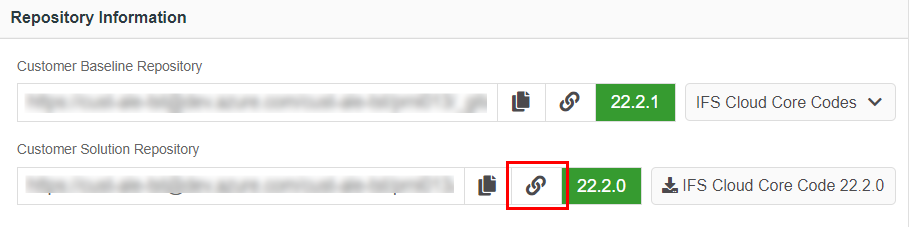
Figure 10.30- Valid topic branch name - To check if the topic branch specified in the previous steps, has been committed (Figure 10.31),
- go to the "Branches" [1]
- select "All" tab[2]
- Click on the branch name which has been created by the automation pipeline [3,4]
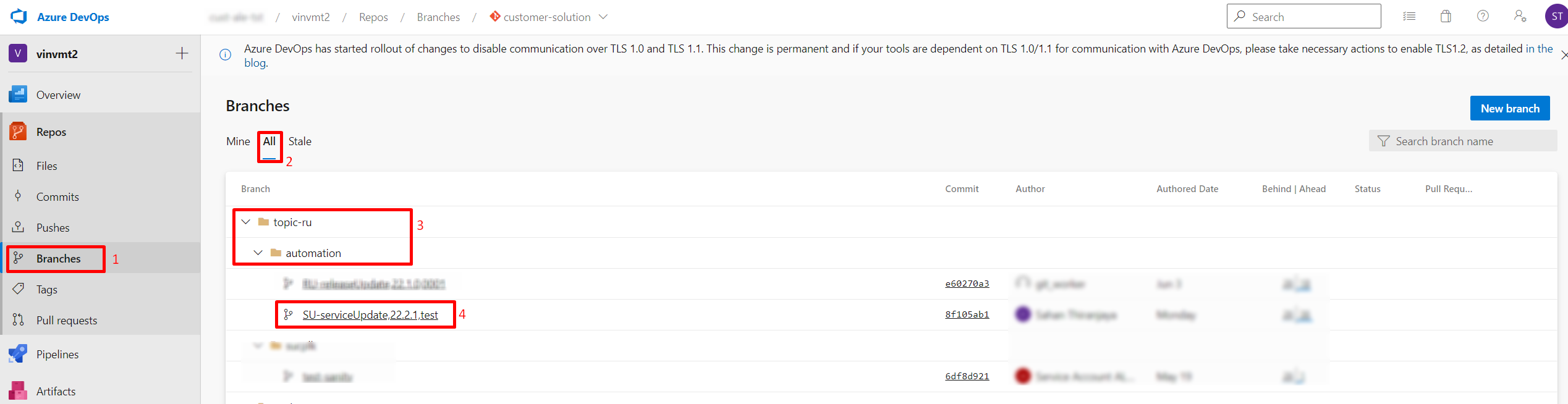
Figure 10.31 - Valid topic branch name - To check if the new version.txt file has been committed to the topic branch (Figure 10.32)
- go to "Files" in customer solution azure repository [1]
- select the topic branch name from the top top down list[2]
- navigate to the folder in "fndbas" => "source" [3]
- open the version.txt file and check the correct service update version contains there [4].
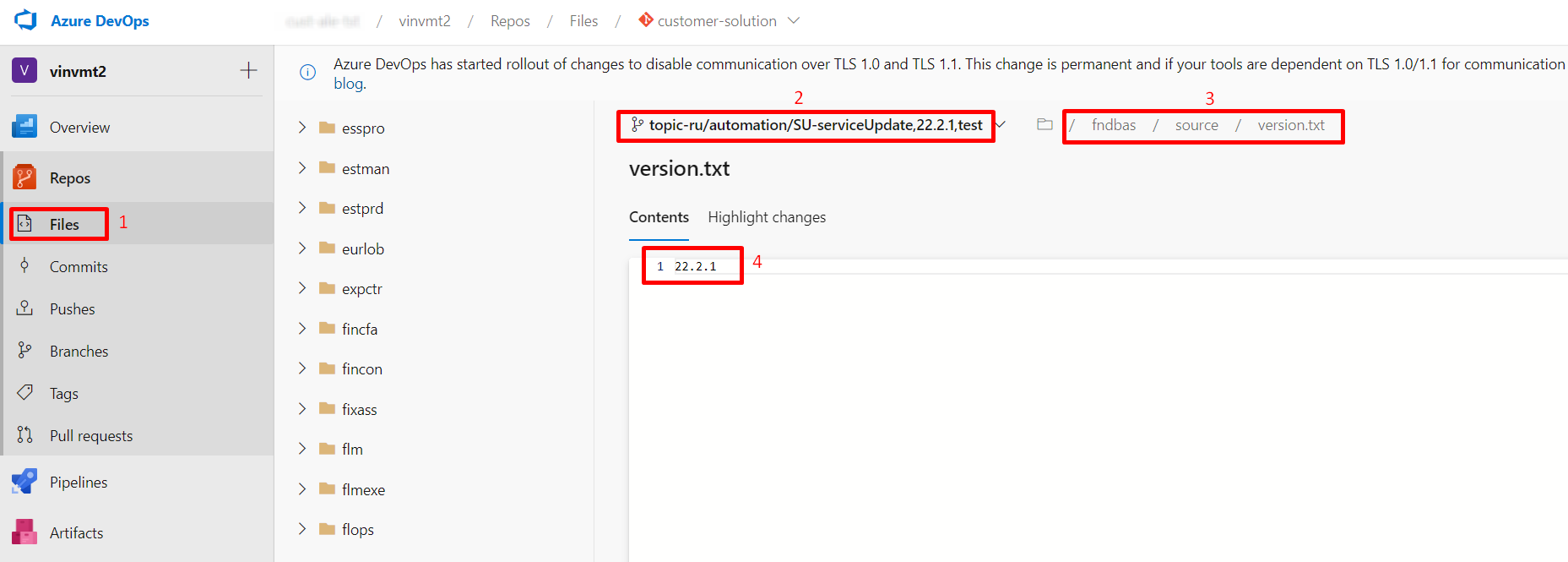
Figure 10.32 - Updated version.txt file - After verifying that the version.txt has been correctly committed to the topic branch, follow the below steps to manually uplift the customizations.
If there are customizations in the customer solution repository¶
-
Create and checkout the topic branch
If you already have the cloned customer-solution repository in your machine, it is recommended to use the existing clone for a better experience, instead of cloning the repository anew for each Buildplace activity.
If the cloned customer-solution repository exists locally on the machine run the following git commands¶
-
Checkout the master branch.
git checkout master -
Update the locally existing customer-solution repository with the latest changes in the master branch of the remote repository .
git pull origin master -
Checkout topic branch. Topic branch name can be copied by using the copy icon appear when hover the topic branch in the azure repository as in Figure 3.9 [4]. Eg: git checkout topic-ru/automation/SU-serviceUpdate,23.2.1,0001
git checkout <topic-branch-name>git pull origin <topic-branch-name>
If the cloned customer-solution repository does not exist locally on the machine proceed with the following guidelines¶
-
To clone the topic branch created by the automation, follow the below commands.
-
URL can be taken by clicking on the copy icon which is located next to the link icon as in Figure 3.8.
-
Topic branch name can be copied by using the copy icon appear when hover the topic branch in the azure repository as in Figure 3.9 [4]. eg: git clone --branch topic-ru/automation/SU-serviceUpdate,23.2.1,0001 --depth 1 https://org-name@dev.azure.com/org-name/bpname/_git/customer-solution
git clone --branch <topic-branch-name> --depth 1 <customer-solution-repo-url>
-
-
-
Carry out required changes identified by impact analysis. If needed it is possible to rerun the downloaded .upda file in the Impact Analysis for new customer-baseline repository version step.
Note
If there are non-layered files with customizations, and if you wish to keep the current customizations and disregard any changes from the service update for a specific non-layered file, please do a dummy change in that file (e.g.: Add new line at the end). This is to avoid, non-layered file getting overridden by the changes incoming from the Service Update.
-
There are some existing features in the Update Analyzer tool that can be used to make the process of handling the impacts of non-layered easily. Handling impacts of non-layered files
- Git add, commit and push local changes (Refer Naming Standards to use when working with GIT for the commit message naming standard)
git add .git commit -m "meaningful commit message"git push origin <branch-name>-
If there are corrections done in core files as a temporary fix for a bug in a core file(s) and the actual fix has been released in the applying service update, refer this documentation to remove the core files from customer-solution repository. When there are fixes done in core files as a temporary fix for a bug in a core file(s)
-
Test the changes using a topic environment. Refer Environments created from a topic branch for more details.
-
Create pull request to merge the topic branch to Customer Solution repository release-update branch. Refer Working With Pull Requests for more details.
Note: Make sure to add a meaningful Pull Request description and a title with space separated that is relevant to the commits contained in the PR. This will be included in reports generated by the portal.
-
Merge the Pull Request to Customer Solution repository release-update branch. Refer Working With Pull Requests for more details.
-
Delete local topic branch.
git branch -d <branch-name>- Delete remote topic branch (Figure 10.33).
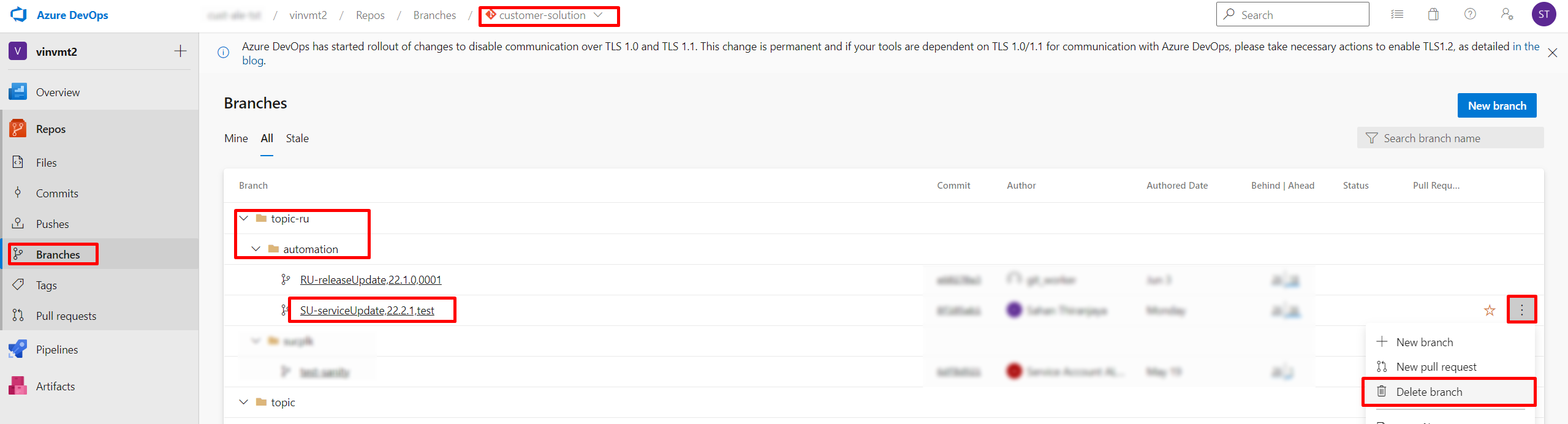
Figure 10.33 - Delete remote topic branch - Check if the customer solution repository version has been correctly updated in "Repository Information " card in the release update studio view.
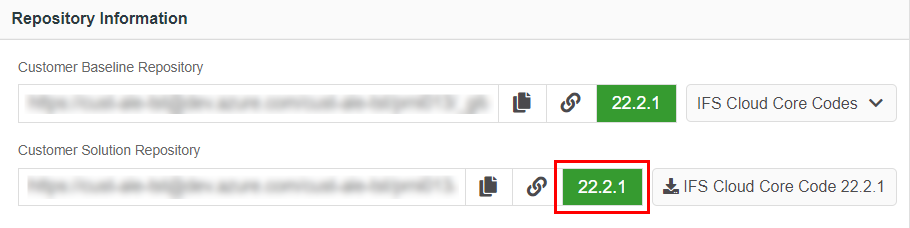
Figure 10.34 - Customer solution repository version after merging the topic branch - Run a sanity build and proceed with creating delivery
If there are no customizations in the customer solution repository¶
- Create pull request to merge the topic branch to Customer Solution repository release-update branch. Refer Working With Pull Requests for more details.
- Merge the Pull Request to Customer Solution repository release-update branch. Refer Working With Pull Requests for more details.
- Delete remote topic branch (Figure 10.33).
- Run a sanity build and proceed with creating delivery
Fetching a Service Update to the Release Update Studio - Prior to 22R2¶
Follow the below steps to fetch a service update to Customer Baseline repository.
- Go to IFS Lifecycle Experience portal and navigate to Release Update Studio view.
- Click on button "Service Update" in the Release Update Studio view.
- Select the target service update from the drop down.
- Click on 'Apply' (Figure 10.35).
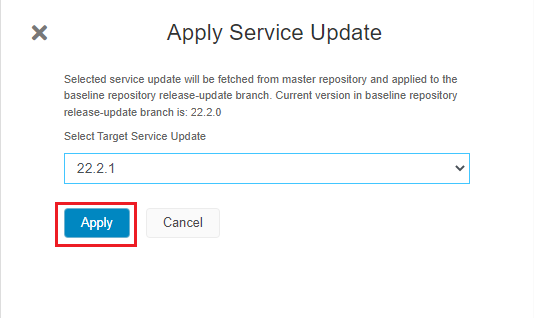 |
|---|
| Figure 10.35 - Service Update Dialogbox |
Once the service update has been applied to the customer baseline repository, a "Pending" status will be displayed for the Customer Baseline Repository. Once the service update is successful, the tag will indicate the new update.
Analyzing the impact of the Service Update¶
After the Customer Baseline repository has been updated with the service update, the Update Analyzer tool can be used to analyze the impacts of fetching this update to the Customer Solution which contain the customizations. To do this, follow the below steps;
- Open the Update Analyzer tool and select the Git integration button (Figure 10.36).
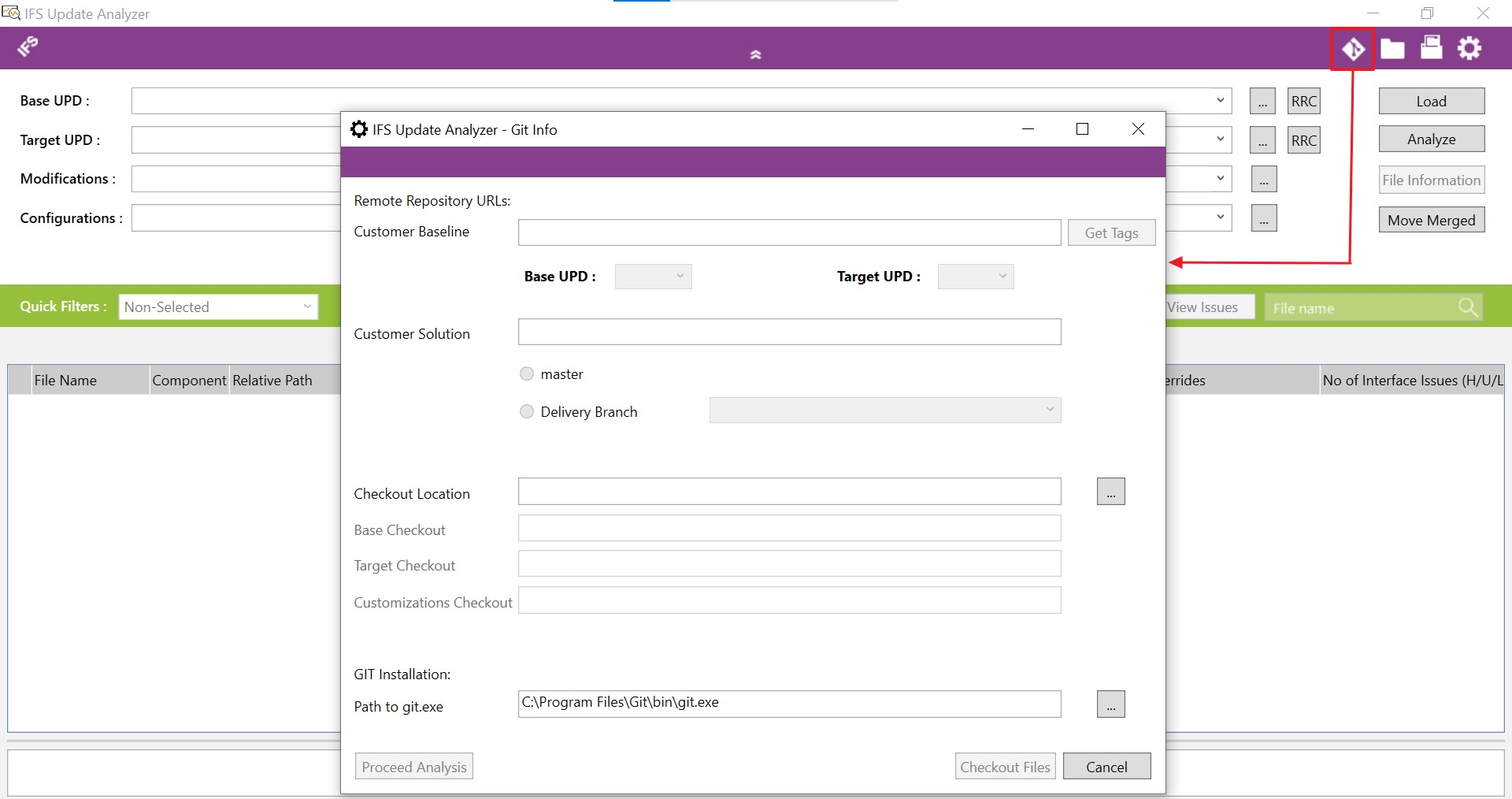 |
|---|
| Figure 10.36 - Update Analyzer git intergration dialogbox |
-
Provide below information to Update Analyzer GIT-Info dialog
- Customer Baseline repository URL
- Customer Solution repository URL
- An empty folder to checkout files
- Note: Provide a directory with a short path to avoid errors with cloning files having long directory paths. [This error occurs due to the windows limitation on file path length]
- Path to git.exe file
-
After entering Customer Baseline repository URL, click on button "Get Tags".
-
Base and Target UPD drop downs will be populated with tag names in Customer Baseline repository.
-
Select appropriate base and target tags from the drop downs. Base UPD refers to current update of the Customer s]Solution and the Target UPD refers to the update to be moved on to.
-
After entering Customer Solution repository URL, "master", "delivery branch" and "release-update" radio buttons get enabled.
-
Select the "release-update branch" option to analyze the impacts for customizations in Customer Solution repository release-update branch.
-
Upon checking the option, tool will run a validation to check if the release-update branch exists in Customer Solution repository.
-
If release-update branch does not exist, the selection will be automatically changed to the master branch option.
-
Once all input fields are filled in, click on button "Checkout Files".
-
Update Analyzer will create three folders inside the location given to checkout files
- Base folder: Will contain a shallow clone of Base UPD tag
- Target folder: Will contain a shallow clone of Target UPD tag
- Cust folder: Will contain a shallow clone of Customer Solution repository release-update branch
-
Once all three clones have been completed, click on button "Proceed Analysis".
-
Update Analyzer will then extract the customized files from Cust Folder and move them to a new folder called "ExtractedCust".
-
A list of file names extracted into this folder could be found in file "Customized Files.txt" inside the checkout location.
-
Paths to Base folder, Target folder and ExtractedCust folder will be populated into Update Analyzer main window at the end of extract operation.
-
Perform update analysis, a component structure analysis will be performed with the given input fields.
Merge the Service Update to the release-update branch¶
Service update can be merged to the release update branch in the customer solution repository by following the steps mentioned below.
-
Clone Customer Solution repository.
git clone <customer-solution-repo-url> -
Change directory to the cloned folder.
cd customer-solution -
Add Customer Baseline repository as an upstream to Customer Solution repository.
git remote add upstream <customer-baseline-repo-url> -
Create and checkout a topic branch based on the release-update branch.
git checkout -b <topic_branch_name> origin/release-updatee.g.:
git checkout -b topic-ru/piselk/RU-ALE-01-ServiceUpdate,21.2 origin/release-updateNote: Use proper naming standard as mentioned in Naming Standards to use when working with GIT. If not branch may not be listed in environment ordering dialog.
-
Pull from upstream. ( i.e. from Customer Baseline repository release-update branch)
git pull upstream release-update -X rename-threshold=95Sometimes VI editor (Figure 10.37) will be opened up during the auto merge process of the git pull command. In that case press "Esc"(Escape key) then ":q!" to quit the editor without saving.
Figure 10.37 - Git VI editor Follow the below steps if the customer solution repository contains customizations.¶
- Run git diff command. If there are merge conflicts, the output will contain '<<<<<<< HEAD' tag as mentioned in the below image (Figure 10.38).
git diff
Figure 10.38 - Git diff output when there are merge conflicts - Run Update Analyzer to identify the impacts
When you pull the upstream to apply the service update into topic branch, you may get merge conflicts from modified and unmodified files. In that case resolve only the real conflicts occurred to core files (non-layered) due to the customizations, by looking at the Update Analyzer result. However, Update Analyzer will list both impacted layered and non-layered files. Do not manually resolve the other conflicted files (unmodified files). Then run the below git commands.
- Stage the manually resolved files individually. eg: git add accrul/source/accrul/TaxBook.plsql
git add <path_to_conflicted_core_file>- Run the following command to accept all incoming changes from upstream release-update branch to resolve the rest of the conflicts on unmodified files.
git checkout --theirs *-
Carry out required changes identified by Impact Analysis run to uplift customizations. Refer Developing with IFS Developer Studio for more information on how to use Developer Studio tool for this.
-
After resolving conflicts and carrying out the required changes identified during the customization upliftment, run the git diff command. You will get an output as below, highlighting the removed and added contents (Figure 10.39). This output log should not contain any '<<<<<<< HEAD' tag.
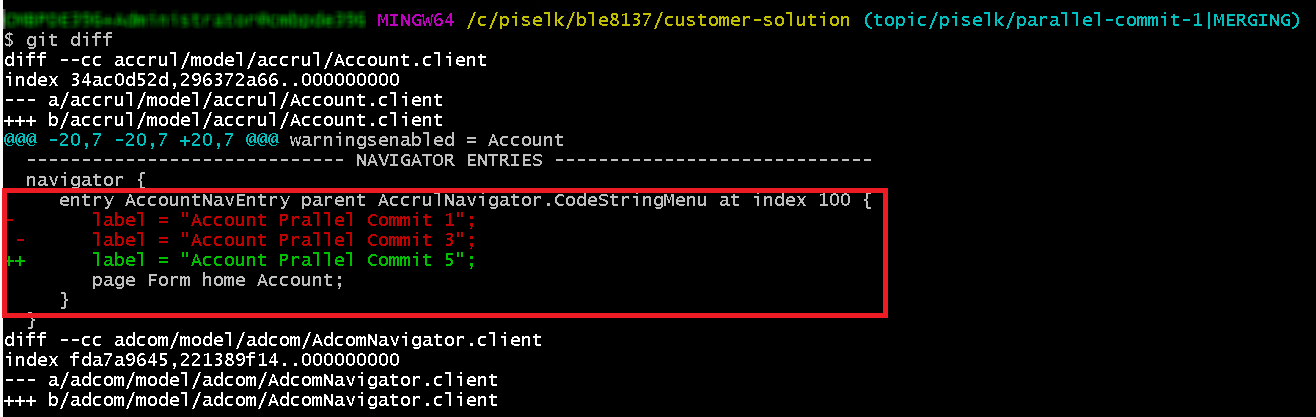
Figure 10.39 - Output when there are new changes and no merge conflicts - Continue from the step 6
Follow the below steps if the customer solution repository does not contain customizations.¶
Even though there are no customizations in the customer solution repository, merge conflicts may contain in the solution-set file. If the local repository contains conflicts after running pull upstream release-update command, git terminal log should contain a warning message as mentioned below (Figure 10.40).
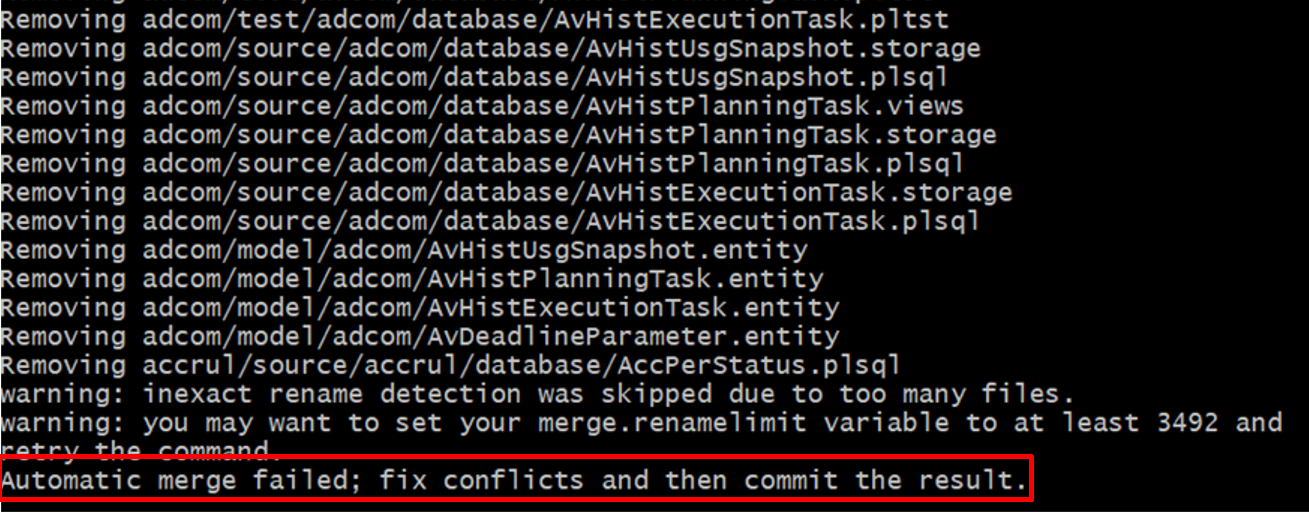
Figure 10.40 - Git terminal log message for merge conflicts Therefore, follow these precautions to avoid merging the topic branch to release-update branch with merge conflicts.
- Identify if there are merge conflicts (Figure 10.41)

Figure 10.41 - Branch name when there are merge conflicts - Run git diff command. If there are merge conflicts, the output will contain '<<<<<<< HEAD' tag as mentioned in the below image (Figure 10.42).
git diff
Figure 10.42 - Git diff output when there are merge conflicts - To accept all the incoming changes run the below command (Figure 10.43)
git checkout --theirs *
Figure 10.43 - Git accept all incoming changes - After accepting all the incoming changes, ensure that there are no merge conflicts. If you get an output as below (i.e with no <<<<<<< HEAD tag, Figure 10.44) by running git diff command, you are good to go.
git diff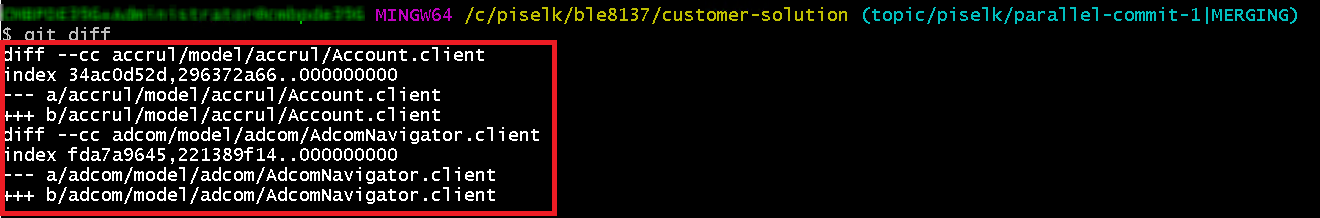
Figure 10.44 - Output when accept all incomming changes - If additional changes have been done during the time of resolving conflicts you will get an output as below, highlighting the removed and added contents (Figure 10.45).

Figure 10.45 - Output when there are new changes and no merge conflicts Move changes to the remote topic branch¶
-
Git add, commit and push local changes (Refer Naming Standards to use when working with GIT for the commit message naming standard)
git add .git commit -m "meaningful commit message"git push origin <topic branch name>- Once the merge conflicts have been resolved, the status of the branch will be changed to the normal state as shown in Figure 10.46.
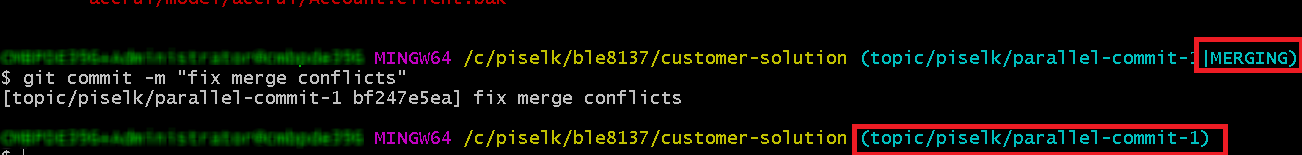
Figure 10.46 - Branch status when conflicts have been resolved -
Test the changes using a topic environment.
Follow the below steps to Create the Pull Request¶
-
Before creating the pull request, check if the version in the version.txt file has been updated to the version that the buildplace is being updated to. In azure project repository, go to the correct topic branch that you are working on. Then
- Go to "fndbas" component
- Go to "source" folder
- Check if the version of the version.txt has been correctly updated
-
Create a pull request from the Azure DevOps project. When performing this step, you may notice that Master branch of the Customer Solution repository will be automatically selected in the dropdown (Figure 10.47). switch the master branch into the release-update branch before creating the pull request as shown in Figure 10.48.
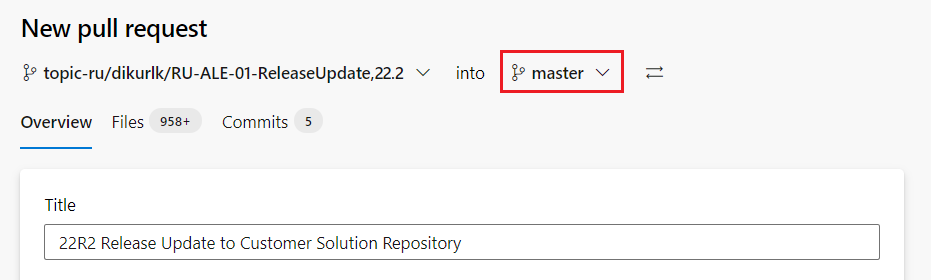
Figure 10.47 - Merging the topic branch to the master branch of the Customer Solution Repository 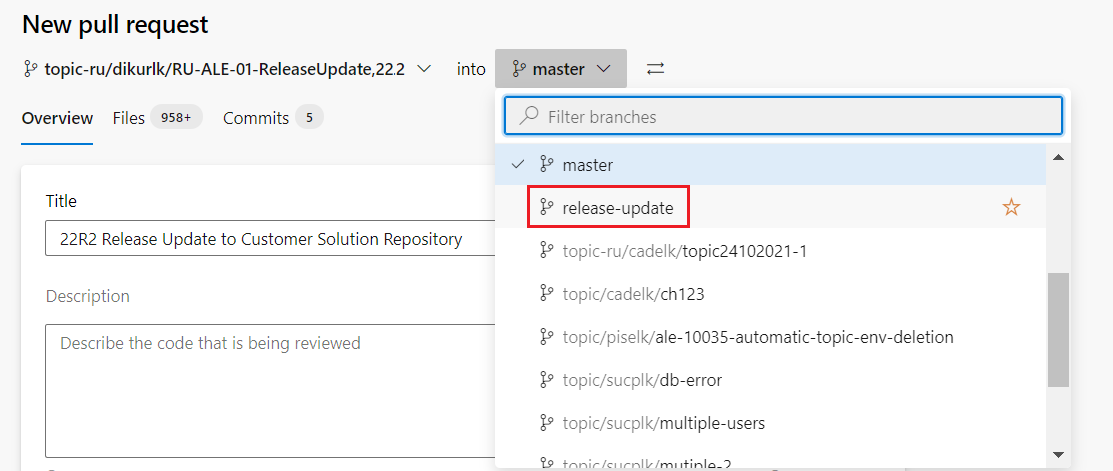
Figure 10.48 - Selecting the release-update branch to merge from the dropdown - Once the branch is switched, the PR should appear as shown in Figure 10.49.
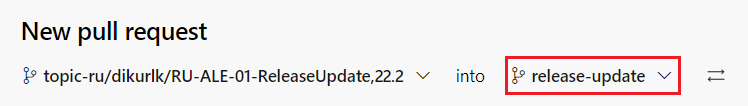
Figure 10.49 - Merging the topic branch to the release-update branch of the Customer Solution Repository Note: Please refer [What to do when there are merge conflicts in the PR?] if you get merge conflicts in your pull request
Note: Before reviewing the Pull Request reviewer should ensure if the developer has created the PR pointing to the correct branch.
Note: Make sure to add a meaningful Pull Request description that is relevant to the commits contained in the PR. This will be included in reports generated by the portal.
Follow the below steps to Merge the Pull Request¶
-
The next step is merging the topic branch to customer-solution repository release-update branch.
Note: Once the pull request is approved, before completing the Pull Request, check if the PR merge option chosen is "Merge (no fast forward)" (Figure 10.50) . Do not select other merge types, as the repository will end-up with a lot of merge conflicts when getting future service updates or release updates and repository will end-up in an unmanageable state.
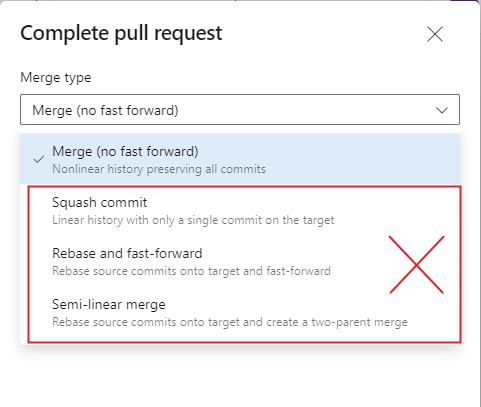
Figure 10.50 - Pull Request merge options Check if the versions in the buildplace are correctly updated¶
-
Go to the RU studio and check whether the version tags are correctly updated after merging. Sample images are shown below (Figure 10.51, 10.52).
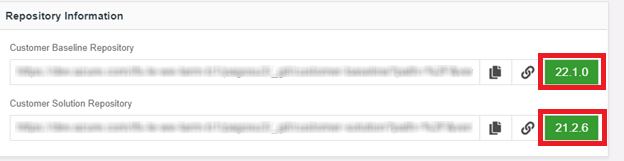
Figure 10.51 - Buildplace repository versions before merging the release to customer solution repository 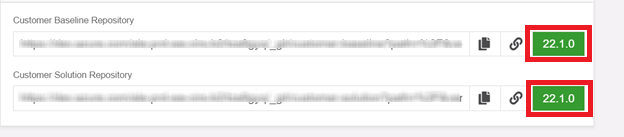
Figure 10.52 - Buildplace repository versions after merging the release to customer solution repository Delete remote and local topic branches.¶
-
Delete the remote topic branch from the azure repository (Figure 10.52).
Note: Don't delete the branch if a topic environment has been ordered pointing to the topic branch used to apply the service update, is in progress
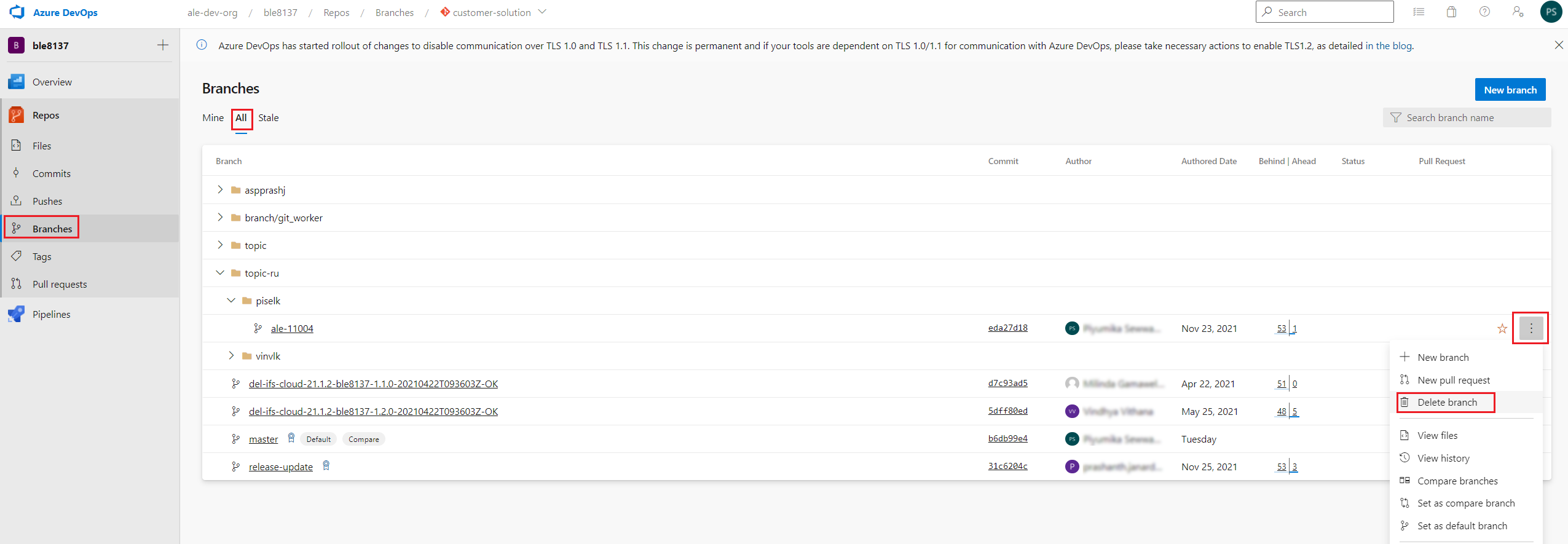
Figure 10.52 - Delete the remote topic branch -
Run a sanity build and proceed with creating delivery
What to do when there are merge conflicts in the pull request?¶
When you created the pull request to merge the Service Update changes with the customer solution repository release-update branch, there can have situations were merge conflicts occur between the changes of release update topic branch and the new changes in the release-update branch added by parallel branches (i.e when your topic branch is not up-to-date with remote release-update branch) (Figure 10.53). In that case before merging the pull request, we advice you to follow the below steps.
Note: Do not rebase the topic branch with release-update branch, as the repository will end-up with a lot of merge conflicts when getting future service updates and repository will end-up in an unmanageable state.
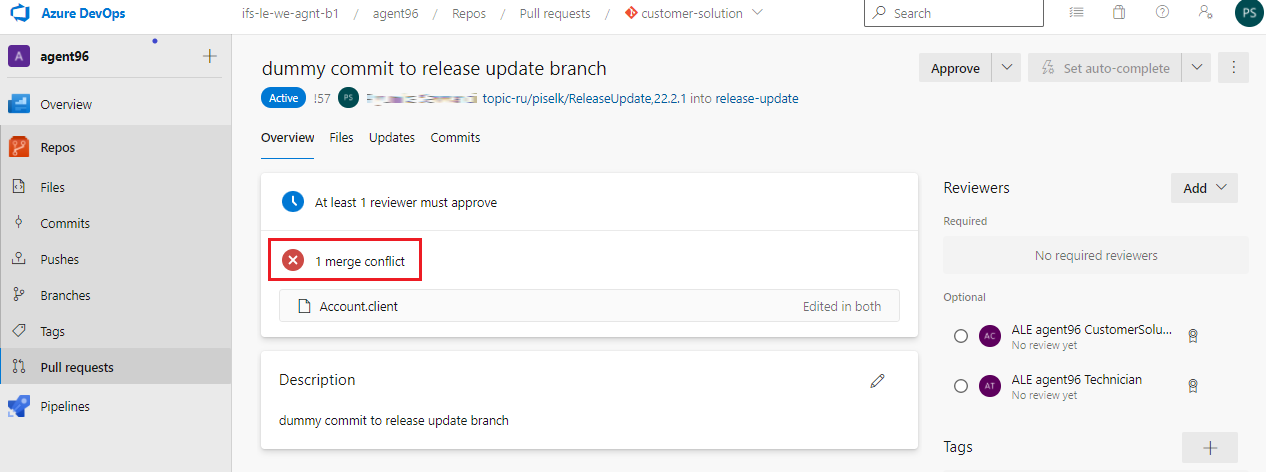 |
|---|
| Figure 10.53 - Merge Conflicts in Pull Request |
If you're not in the branch checkout to the topic branch else skip this.
git checkout <branch-name>
Then pull the changes from the remote customer solution repository release-update branch for the local release-update branch to be up-to-date with remote release-update (Figure 10.54).
git pull origin release-update
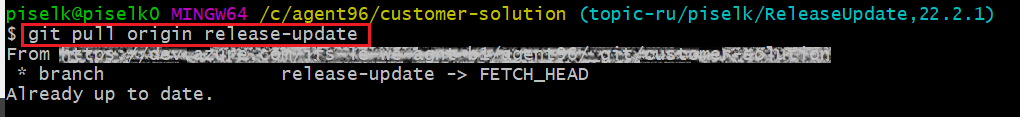 |
|---|
| Figure 10.54 - Git pull origin release-update |
Resolve merge conflicts if have.
git add .
git commit -m "commit-message"
git push origin <branch-name>
Now the pull request will be updated with the release-update branch changes.
What to do if the code has been merged with conflicts?¶
Sometimes there can be situations where the code has been merged to release-update or master branch with conflicts during the apply release update to customer solution repository stage or apply service update process. This will cause both the sanity build and topic environment creation fail during code generation. Usually this happens when there are no customizations and user assumes that there will not be any merge conflicts due to not having customizations. But there can be situations where contain merge conflicts in the solution-set file. You can find the log folder of the failed sanity build or topic environment creation by going to the log view. There you can find the log folder and download it.
For an example, if the sanity build has failed due to the merge conflicts, download the log folder named as "sanity-build-error-full-logs.zip" and go to "\ifs\cbs\code_generation" location and open _ifs_ant_generateddb.log file. There you will see error messages (Figure 10.55) and head tag as below (Figure 10.56).
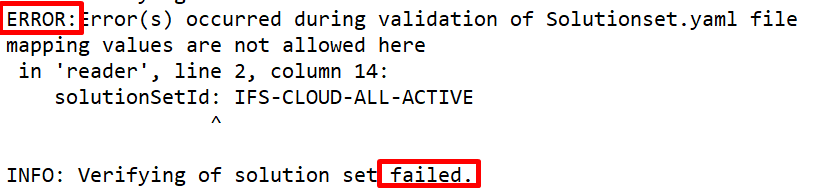 |
|---|
| Figure 10.55 - Code generation error message |
 |
|---|
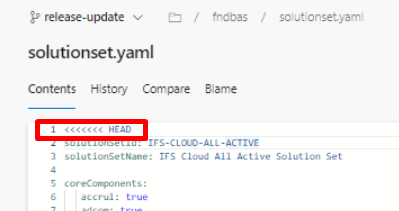
| Figure 10.56 - Conflict with head tag |
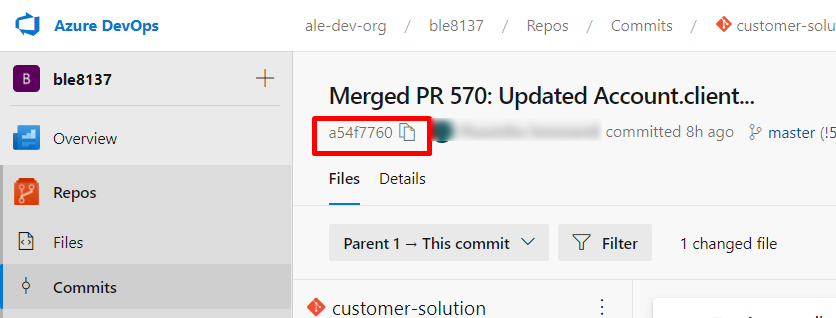
According to the error message you can find the file you have committed with conflicts. Then raise a support ticket with all the failed log files , information with the screenshots and the commit SHA of the commit point where you want the repository reset back to, immediately.
How to get the commit SHA:
- Go to the azure customer solution repository
- Switch to the correct branch (master/release-update)
- Go to the commit point where you want the repository reset back to (probably the point before the commit with merge conflicts)
- Copy the value as mentioned below and paste it in the description of the support ticket (Figure 10.57).
 |
|---|
| Figure 10.57 - How to get the commit SHA |